Abstract
Objective and design
This study is designed to investigate the role of p38 MAPK in modulating human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (HPAECs) survival and tissue repair functions.
Methods
HPAECs (passage 8–12) were used for all experiments. Cells were treated with IL-1β (0.5 or 2 ng/ml) or p38 inhibitor (SB203580 or SB220025, 5 μM each). Cells were also transfected with 50 nM siRNAs. Cell length was measured using ImageJ software. Collagen gel contraction and wound close assay were performed to evaluate tissue repair functions.
Results
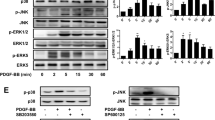
IL-1β activated p38 MAPK and induced morphologic change of HPAECs. The p38 inhibitors further augmented IL-1β-induced cell morphologic change, prevented cell death, and augmented collagen gel contraction. Suppression of p38α, γ, or δ, but not p38β resulted in cell morphologic alteration, and suppressing any one of p38 isoforms by siRNAs increased cell survival. Suppression of p38α or δ augmented gel contraction. While p38α suppression stimulated cell migration, suppressing the rest of three isoforms inhibit cell migration. Nuclear factor p65-siRNA blocked IL-1β-induced cell morphologic change, but did not affect p38 inhibitor-induced change.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that p38 MAPK may negatively modulate tissue repair functions of endothelial cells via p65 independent pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saklatvala J, Davis W, Guesdon F. Interleukin 1 (il1) and tumour necrosis factor (tnf) signal transduction. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996;351(1336):151–7.
Chaudhuri V, Zhou L, Karasek M. Inflammatory cytokines induce the transformation of human dermal microvascular endothelial cells into myofibroblasts: a potential role in skin fibrogenesis. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34(2):146–53.
Kanaji N, Sat T, Wang XQ, Kim M, Nakanishi M, Li YJ, Basma H, Patil A, Michalski J, Nelson AJ, Sun J, Liu X, Rennard SI Interleukin-1beta induces endothelial-mesenchymal transition via the nf-kappa b pathway. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179:A2343.
Raman M, Chen W, Cobb MH. Differential regulation and properties of mapks. Oncogene. 2007;26(22):3100–12.
Rossa C, Ehmann K, Liu M, Patil C, Kirkwood KL. Mkk3/6–p38 mapk signaling is required for il-1beta and tnf-alpha-induced rankl expression in bone marrow stromal cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2006;26(10):719–29.
Chopra P, Kanoje V, Semwal A, Ray A. Therapeutic potential of inhaled p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors for inflammatory pulmonary diseases. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008;17(10):1411–25.
Duan W, Chan JH, McKay K, Crosby JR, Choo HH, Leung BP, Karras JG, Wong WS. Inhaled p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase antisense oligonucleotide attenuates asthma in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171(6):571–8.
Raia V, Maiuri L, Ciacci C, Ricciardelli I, Vacca L, Auricchio S, Cimmino M, Cavaliere M, Nardone M, Cesaro A, et al. Inhibition of p38 mitogen activated protein kinase controls airway inflammation in cystic fibrosis. Thorax. 2005;60(9):773–80.
Renda T, Baraldo S, Pelaia G, Bazzan E, Turato G, Papi A, Maestrelli P, Maselli R, Vatrella A, Fabbri LM, et al. Increased activation of p38 mapk in copd. Eur Respir J. 2008;31(1):62–9.
Yoshida K, Kuwano K, Hagimoto N, Watanabe K, Matsuba T, Fujita M, Inoshima I, Hara N. Map kinase activation and apoptosis in lung tissues from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Pathol. 2002;198(3):388–96.
Schett G, Zwerina J, Firestein G. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (mapk) pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(7):909–16.
Sumioka T, Ikeda K, Okada Y, Yamanaka O, Kitano A, Saika S. Inhibitory effect of blocking tgf-beta/smad signal on injury-induced fibrosis of corneal endothelium. Mol Vis. 2008;14:2272–81.
Hui L, Bakiri L, Mairhorfer A, Schweifer N, Haslinger C, Kenner L, Komnenovic V, Scheuch H, Beug H, Wagner EF. P38alpha suppresses normal and cancer cell proliferation by antagonizing the jnk-c-jun pathway. Nat Genet. 2007;39(6):741–9.
Hale KK, Trollinger D, Rihanek M, Manthey CL. Differential expression and activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase alpha, beta, gamma, and delta in inflammatory cell lineages. J Immunol. 1999;162(7):4246–52.
Korb A, Tohidast-Akrad M, Cetin E, Axmann R, Smolen J, Schett G. Differential tissue expression and activation of p38 mapk alpha, beta, gamma, and delta isoforms in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Rheum. 2006;54(9):2745–56.
Peinado VI, Pizarro S, Barbera JA. Pulmonary vascular involvement in copd. Chest. 2008;134(4):808–14.
Carmi Y, Voronov E, Dotan S, Lahat N, Rahat MA, Fogel M, Huszar M, White MR, Dinarello CA, Apte RN. The role of macrophage-derived il-1 in induction and maintenance of angiogenesis. J Immunol. 2009;183(7):4705–14.
Madge LA, Pober JS. A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt pathway, activated by tumor necrosis factor or interleukin-1, inhibits apoptosis but does not activate nfkappab in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(20):15458–65.
Goedert M, Cuenda A, Craxton M, Jakes R, Cohen P. Activation of the novel stress-activated protein kinase sapk4 by cytokines and cellular stresses is mediated by skk3 (mkk6); comparison of its substrate specificity with that of other sap kinases. EMBO J. 1997;16(12):3563–71.
Bakin AV, Rinehart C, Tomlinson AK, Arteaga CL. P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for tgfbeta-mediated fibroblastic transdifferentiation and cell migration. J Cell Sci. 2002;115(Pt 15):3193–206.
Bates RC, Mercurio AM. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human colonic organoids. Mol Biol Cell. 2003;14(5):1790–800.
Rhyu DY, Yang Y, Ha H, Lee GT, Song JS, Uh ST, Lee HB. Role of reactive oxygen species in tgf-beta1-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16(3):667–75.
Jung YS, Jeong EM, Park EK, Kim YM, Sohn S, Lee SH, Baik EJ, Moon CH. Cadmium induces apoptotic cell death through p38 mapk in brain microvessel endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;578(1):11–8.
Moriue T, Igarashi J, Yoneda K, Nakai K, Kosaka H, Kubota Y. Sphingosine 1-phosphate attenuates h2o2-induced apoptosis in endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;368(4):852–7.
Nemoto S, Xiang J, Huang S, Lin A. Induction of apoptosis by sb202190 through inhibition of p38beta mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(26):16415–20.
Tourian L Jr, Zhao H, Srikant CB. P38alpha, but not p38beta, inhibits the phosphorylation and presence of c-flips in disc to potentiate fas-mediated caspase-8 activation and type i apoptotic signaling. J Cell Sci. 2004;117(Pt 26):6459–71.
Wang Y, Huang S, Sah VP, Ross J Jr, Brown JH, Han J, Chien KR. Cardiac muscle cell hypertrophy and apoptosis induced by distinct members of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase family. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(4):2161–8.
Silva G, Cunha A, Gregoire IP, Seldon MP, Soares MP. The antiapoptotic effect of heme oxygenase-1 in endothelial cells involves the degradation of p38 alpha mapk isoform. J Immunol. 2006;177(3):1894–903.
Meyer-Ter-Vehn T, Gebhardt S, Sebald W, Buttmann M, Grehn F, Schlunck G, Knaus P. P38 inhibitors prevent tgf-beta-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation in human tenon fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006;47(4):1500–9.
Jung JW, Hwang SY, Hwang JS, Oh ES, Park S, Han IO. Ionising radiation induces changes associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation and increased cell motility of a549 lung epithelial cells. Eur J Cancer. 2007;43(7):1214–24.
Yamanaka O, Saika S, Ohnishi Y, Kim-Mitsuyama S, Kamaraju AK, Ikeda K. Inhibition of p38map kinase suppresses fibrogenic reaction in conjunctiva in mice. Mol Vis. 2007;13:1730–9.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ms. Lillian Richards for the excellent secretarial support of this manuscript. Funding: Larson Endowment, University of Nebraska Medical Center and LB506.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Liwu Li.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanaji, N., Nelson, A., Allen-Gipson, D.S. et al. The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases modulate endothelial cell survival and tissue repair. Inflamm. Res. 61, 233–244 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-011-0405-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-011-0405-7