Abstract
Objective and design
To clarify the molecular mechanism of polyenylphosphatidylcholine (PPC), we examined the involvement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and NADPH oxidase 4 (Nox4) in human hepatic stellate cells (HSCs).
Material
Using human LX-2 HSC cells, we examined the effects of PPC on expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and collagen 1, generation of ROS, Nox4 expression, p38 activation and cell proliferation, induced by transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1).
Results
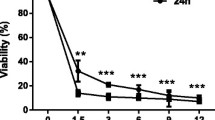
PPC suppressed ROS which are induced by TGFβ1, phosphorylation of p38MAPK, and expression levels of α-SMA and collagen 1 in a dose-dependent manner. Higher concentrations of PPC also suppressed Nox4 levels.
Conclusion
These results suggest that ROS and Nox4 induced by TGFβ1 are the therapeutic targets of PPC in the suppression of human hepatic stellate cell activation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PPC:
-
Polyenylphosphatidylcholine
- HSC:
-
Hepatic stellate cell
- Nox:
-
NADPH oxidase
- MFB:
-
Myofibroblast
- PDGF:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor
- TGFβ1:
-
Transforming growth factor β-1
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- LC:
-
Liver cirrhosis
References
Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroeterology. 2008;134:1655–69.
Proell MMV, Fischer ANM, Mikulits W. Activation of hepatic stellate cells induce tumor progression of neoplastic hepatocytes in a TGF-β dependent fashion. J Cell Physiol. 2006;209:560–7.
Cavin LG, Romieu-Mourez R, Panta GR, Sun J, Factor VM, Thorgeirsson SS, Sonenshein GE, Arsura M. Inhibition of CK2 activity by TGF-β1 promotes IκB-α protein stabilization and apoptosis of immortalized hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2003;38:1540–51.
Yanagitani A, Yamada S, Yasui S, Shimomura T, Murai R, Shiota G. Retinoic acid receptor α dominant negative form causes steatohepatitis and liver tumors in transgenic mice. Hepatology. 2004;40:366–75.
Aleynik SI, Leo MA, Ma X, Aleynik MK, Lieber CS. Polyenylphosphatidylcholine prevents carbon tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation while it attenuates liver fibrosis. J Hepatol. 1997;27:554–61.
Lieber CS, Robins SJ, DeCarli LM, Mak KM, Fasulo JM, Leo MA. Phosphatidylcholine protects against fibrosis and cirrhosis in the baboon. Gastroenterology. 1994;106:152–9.
Lieber CS, Leo MA, Aleynik LSI. Polyenylphosphatidylcholine decreases alcohol-induced oxidative stress in the baboon. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1997;21:375–9.
Brady LM, Fox ES, Fimmel CJ. Polyenylphosphadidylcholine inhibits PDGF-induced proliferation in rat hepatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;248:174–9.
Cao Q, Mak KM, Lieber CS. DLPC decreases TGF-β1-induced collagen mRNA by inhibiting p38 MAPK in hepatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol Gastroenterol Liver Physiol. 2002;283:G1051–61.
Garcia-Trevijano ER, Iraburu MJ, Fontana L, Dominguez-Rosales JA, Auster A, Covarrublas-Pinedo A, et al. Transforming growth factor β1 induces the expression of α1(I) procollagen mRNA by a hydrogen peroxide-C/EBPβ-dependent mechanism in rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology. 1999;13:1193–202.
Chang L, Karin M. Mammmalian MAP kinase signaling cascades. Nature. 2001;410:37–40.
Anania FA, Womack L, Jiang M, Saxena NK. Aldehydes potentiate α2(I)collagen gene activity by JNK in hepatic stellate cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2001;30:846–57.
Xu L, Hui AY, Albanis E, Arthur MJ, O’Byrne SM, Blaner WS, et al. Human hepatic stellate cell lines, LX-1 and LX-2: new tools for analysis of hepatic fibrosis. Gut. 2005;54:142–51.
Boudreau HE, Emerson SU, Korzeniowska A, Jendrysik MA, Leto TL. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) proteins induce NADPH oxidase 4 expression in a transforming growth factor β-dependent manner: a new contributor to HCV-induced oxidative stress. J Virol. 2009;83:12934–46.
de Mochel NSR, Seronello S, Wang SH, Ito C, Zheng JX, Liang TJ, Lambeth JD, Choi J. Hepatocyte NAD(P)H oxidase as an endogenous source of reactive oxygen species during hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology. 2010;52:47–59.
Liu SX, Athar M, Lippai I, Waldren TC, Hey TK. Induction of oxyradicals by arsenic: implication for mechanism of genotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:1643–8.
Rhyu DY, Yang Y, Ha H, Lee GT, Song JS, Uh S, et al. Role of reactive oxygen species in TGFβ-1-induced mitogen-activated protein activation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:667–75.
Reeves HL, Dack CL, Peak M, Burt AD, Day CP. Stress-activated protein kinases in the activation of rat hepatic stellate cells in culture. J Hepatol. 2000;32:465–72.
Okiyama W, Tanaka N, Nakajima T, Tanaka E, Kiyosawa K, Gonzalez FJ, Aoyama T. Polyenephosphatidylcholine prevents alcoholic liver disease in PPARα-null mice through attenuation of increases in oxidative stress. J Hepatol. 2009;50:1236–46.
Koike K, Miyoshi H. Oxidative stress and hepatitis C viral infection. Hepatol Res. 2005;34:65–73.
Tsuchiya H, Akechi Y, Ikeda R, Hoshikawa Y, Kurimasa A, Shiota G. Suppressive effects of retinoids on iron-induced oxidative stress in the liver. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:341–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Liwu Li.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, R., Ishii, K., Hoshikawa, Y. et al. Reactive oxygen species and NADPH oxidase 4 induced by transforming growth factor β1 are the therapeutic targets of polyenylphosphatidylcholine in the suppression of human hepatic stellate cell activation. Inflamm. Res. 60, 597–604 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-011-0309-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-011-0309-6