Abstract.
Objective: The anesthetic ketamine has been reported to cause both an increase of the plasma histamine concentration, notably in cats, and a cardiovascular depression. The latter has been described in humans and in other species. However the relevance of the histamine fluctuation for the ketamine-induced hemodynamic changes has not been determined.
Subjects and treatment: We studied the contribution of histamine to the hemodynamic effects induced by IV ketamine (7 mg/kg) in 12 sevoflurane anesthetized cats, of which half had been pre-treated with combined H1- and H2 -receptor antagonists.
Methods: The mean arterial pressure (MAP) and the heart rate (HR) from both untreated (group C) and pre-treated (group AH) cats were recorded before and after the ketamine administration. The plasma histamine concentration was also measured.
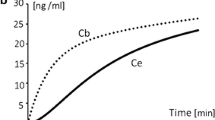
Results: Plasma histamine fluctuations in the control and the antihistamine-treated group followed a similar pattern (no statistical differences); an initial rise that peaked 2 min after ketamine injection (from 0.63 ± 0.11 ng/ml to 2.22 ± 0.69 ng/ml in the C group, and from 0.71 ± 0.10 ng/ml to 1.09 ± 0.28 ng/ml in the AH group) followed by an immediate decrease in plasma concentrations. As for the hemodynamic variables under analysis, in the control group ketamine administration was followed by an early 30.3 ± 8.1% reduction (p < 0.005) in the MAP with no associated changes in the HR. In the antihistamine pre-treated group, ketamine caused a further decrease of the MAP (41.7 ± 2.3%), and a significant (p < 0.01) 11.6 ± 2.9% reduction of the HR.
Conclusion: Ketamine in anesthetized cats triggers histamine release and induces cardiovascular depression. The depression is more pronounced under the blockade of histamine activity through histamine receptor antagonists.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 22 October 2004; returned for revision 5 January 2005; accepted by A. Falus 14 February 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa-Farré, C., García, F., Andaluz, A. et al. Effect of H1- and H2-receptor antagonists on the hemodynamic changes induced by the intravenous administration of ketamine in sevoflurane-anesthetized cats. Inflamm. res. 54, 256–260 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-005-1352-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-005-1352-y