Abstract
Objective and design: To examine the effects of PTK787/ZK222584, a novel angiogenesis inhibitor, in a series of in vivo models of arthritis and inflammation.
Materials: The granulomatous air pouch and antigen-induced arthritis models were established in female OFA-1 mice. Female DBA/1LacJ mice were used for the collagen-induced arthritis model and male OFA rats were used for the carrageenan oedema and hyperalgesia tests.
Treatment: PTK787/ZK222584 was administered p.o., once daily, at various concentrations. Diclofenac (3 mg/kg) and DUP697 (0.5 mg/kg) were also given p.o, once daily.
Methods: The anti-angiogenic effects of PTK787/ZK222584 were directly assessed in the granulomatous air pouch model using the carmine red assay. The anti-arthritic effects of this compound were further examined in the mouse antigen-induced and collagen-induced models of arthritis, using macroscopic observations (calliper measurements of joints) and histological scores (as assessed by degree of cellularity, cell infiltration and erosions and proteoglycan loss). All compounds were administered orally. PTK787/ZK222584 at 10, 30, 50 and 100 mg/kg and positive control compounds, diclofenac and DUP697 at 3 mg/kg and 0.5 mg/kg, respectively. In addition, the effects of PTK787/ZK222584 in the rat carrageenan oedema model and Randall Selitto hyperalgesia test were observed.
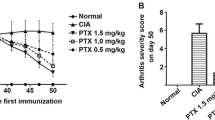
Results: PTK787/ZK222584 treatment caused dose dependent reduction in the vascularity of the granulomatous air pouch model. It inhibited knee swelling by 40% in antigen-induced arthritis, at the dose of 30 mg/kg p.o., once daily (s.i.d). and inhibited both severity scores (by 51%) and global histological scores in mice with collagen-induced arthritis following oral treatment (45 mg/kg p.o.), as compared to control animals. PTK787/ZK222584 demonstrated no effects on inflammatory mediators in the VEGF-independent rat carrageenan model and displayed interesting analgesic activity in the Randall Selitto test in the acute setting.
Conclusions: The anti-arthritic effects of this specific, receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor compound appear to be mediated by anti-angiogenic actions. This study represents a new indication for PTK787/ZK222584, namely, rheumatoid arthritis and further supports the belief that angiogenesis inhibition is likely to be beneficial in the therapy of this condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 23 May 2003; returned for revision 10 July 2003; accepted by M. Parnham 5 November 2003
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grosios, K., Wood, J., Esser, R. et al. Angiogenesis inhibition by the novel VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, PTK787/ZK222584, causes significant anti-arthritic effects in models of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm. res. 53, 133–142 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-003-1230-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-003-1230-4