Abstract
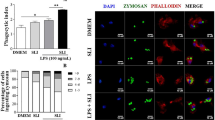
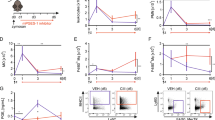
Zymosan-induced peritonitis represents a well-described model of acute inflammation. The binding of zymosan with its specific Toll-like receptors (TLR2 and TLR6) on leukocytes initiates activation and phosphorylation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB, which leads to accumulation of NF-κB p65 subunits in the nucleus and subsequently up-regulation of the proinflammatory cytokine genes expression. Intraperitoneal co-administration of zymosan and morphine significantly inhibits peritonitis in several strains of mice by decreasing the influx of exudatory cells; however, mechanisms of this action still remain unclear. We aimed to verify the effects of morphine on NF-κB and TLRs expression at messenger RNA and protein levels during the early stages of zymosan-induced peritonitis. Peritonitis was induced by a single injection of zymosan A or zymosan supplemented with morphine in Swiss mice. At selected time points, after stimulation, peritoneal leukocytes were harvested. The TLRs and NF-κB expression was assessed by real-time PCR and flow cytometry. In comparison with the mice injected with zymosan only, morphine co-injection significantly decreased the expression of phospho-NF-κB and TLR2 in all investigated immunocompetent cells as well as up-regulated the levels of nitric oxide (NO) in peritoneal fluid. Moreover, supplementation of zymosan with morphine altered the TLR, NF-κB and some proinflammatory cytokines (keratinocyte-derived chemokine, tumor necrosis factor-α) gene expression during ongoing inflammation. We may postulate that after morphine stimulation peritoneal leukocytes recognize less effectively zymosan antigens because of impaired TLRs expression. The lower TLR expression attenuates TLR-mediated signal transduction, which prevents NF-κB activation. Additionally, during zymosan-induced peritonitis, morphine may modulate the NF-κB expression, at least partially, by an up-regulated release of NO, as suggested by others.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajuebor MN, Virág L, Flower RJ et al (1998) Role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in the regulation of neutrophil migration in zymosan-induced inflammation. Immunology 95:625–630
Ajuebor MN, Das AM, Virag L et al (1999) Role of resident peritoneal macrophages and mast cells in chemokine production and neutrophil migration in acute inflammation: evidence for an inhibitory loop involving endogenous IL-10. J Immunol 162:1685–1691
Akira S (2006) TLR signaling. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 311:1–16
Akira S (2009) Innate immunity to pathogens: diversity in receptors for microbial recognition. Immunol Rev 227:5–8
Aktan F (2004) iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production and its regulation. Life Sci 75:639–653
Bischoff SC (2007) Role of mast cells in allergic and non-allergic immune responses: comparison of human and murine data. Nat Rev Immunol 7:93–104
Bonnet MP, Beloeil H, Benhamou D et al (2008) The mu opioid receptor mediates morphine-induced tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 inhibition in Toll-like receptor 2-stimulated monocytes. Anesth Analg 106:1142–1149
Cash JL, White GE, Greaves DR (2009) Chapter 17. Zymosan-induced peritonitis as a simple experimental system for the study of inflammation. Methods Enzymol 461:379–396
Chadzinska M, Kołaczkowska E, Seljelid R et al (1999) Morphine modulation of peritoneal inflammation in Atlantic salmon and CB6 mice. J Leukocyte Biol 65:590–596
Evans CH (1995) Nitric oxide: what role does it play in inflammation and tissue destruction? Agents Actions Suppl 47:107–116
Freyer D, Manz R, Ziegenhorn A et al (1999) Cerebral endothelial cells release TNF-alpha after stimulation with cell walls of Streptococcus pneumoniae and regulate inducible nitric oxide synthase and ICAM-1 expression via autocrine loops. J Immunol 163:4308–4314
Galli SJ, Kalesnikoff J, Grimbaldeston MA et al (2005) Mast cells as “tunable” effector and immunoregulatory cells: recent advances. Annu Rev Immunol 23:749–786
Giulietti A, Overbergh L, Valckx D et al (2001) An overview of real-time quantitative PCR: applications to quantify cytokine gene expression. Methods 25:386–401
Grimm MC, Ben-Baruch A, Taub DD et al (1998) Opiates transdeactivate chemokine receptors: d and μ opiate receptor mediated heterologous desensitization. J Exp Med 188:317–325
Hol J, Wilhelmsen L, Haraldsen G (2010) The murine IL-8 homologues KC, MIP-2, and LIX are found in endothelial cytoplasmic granules but not in Weibel–Palade bodies. J Leukoc Biol 87:501–508
Ikeda T, Funaba M (2003) Altered function of murine mast cells in response to lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan. Immunol Lett 88:21–26
Kawai T, Akira S (2007) Signaling to NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol Med 13:460–469
Kawai T, Akira S (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11:373–384
Kobayashi SD, Braughton KR, Whitney AR et al (2003) Bacterial pathogens modulate an apoptosis differentiation program in human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10948–10953
Kołaczkowska E, Seljelid R, Plytycz B (2001) Role of mast cells in zymosan-induced peritoneal inflammation in Balb/c and mast cell-deficient WBB6F1 mice. J Leukoc Biol 69:33–42
Kołaczkowska E, Arnold B, Opdenakker G (2008) Gelatinase B/MMP-9 as an inflammatory marker enzyme in mouse zymosan peritonitis: comparison of phase-specific and cell-specific production by mast cells, macrophages and neutrophils. Immunobiology 213:109–124
Kurt-Jones EA, Mandell L, Whitney C et al (2002) Role of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) in neutrophil activation: GM-CSF enhances TLR2 expression and TLR2-mediated interleukin 8 responses in neutrophils. Blood 100:1860–1868
Lafarge S, Hamzeh-Cognasse H, Chavarin P et al (2007) A flow cytometry technique to study intracellular signals NF-kappaB and STAT3 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. BMC Mol Biol 8:64
Magazine HI, Liu Y, Biffinger TV et al (1996) Morphine-induced conformational changes in human monocytes, granulocytes, and endothelial cells and in invertebrate immunocytes and microglia are mediated by nitric oxide. J Immunol 156:4845–4850
Makman MH, Bilfmger TV, Stefano GB (1995) Human granulocytes contain an opiate alkaloid-selective receptor mediating inhibition of cytokine-induced activation and chemotaxis. J Immunol 154:1323–1330
McCurdy JD, Olynych TJ, Maher LH et al (2003) Cutting edge: distinct Toll-like receptor 2 activators selectively induce different classes of mediator production from human mast cells. J Immunol 170:1625–1629
Menzebach A, Hirsch J, Hempelmann G et al (2003) Effects of endogenous and synthetic opioid peptides on neutrophil function in vitro. Br J Anaesth 91:546–550
Mrabet-Dahbi S, Metz M, Dudeck A et al (2009) Murine mast cells secrete a unique profile of cytokines and prostaglandins in response to distinct TLR2 ligands. Exp Dermatol 18:437–444
Mullaly SC, Kubes P (2007) Mast cell-expressed complement receptor, not TLR2, is the main detector of zymosan in peritonitis. Eur J Immunol 37:224–234
Natorska J, Płytycz B (2005) Strain-specific differences in modulatory effects of morphine on peritoneal inflammation in mice. Folia Biol 53:189–195
Ozinsky A, Underhill DM, Fontenot JD et al (2000) The repertoire for pattern recognition of pathogens by the innate immune system is defined by cooperation between toll-like receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:13766–13771
Płytycz B, Natorska J (2002) Morphine attenuates pain and prevents inflammation in experimental peritonitis. Trends Immunol 23:345–346
Ranta V, Orpana A, Carpen O et al (1999) Human vascular endothelial cells produce tumor necrosis factor-α in response to pro-inflammatory cytokine stimulation. Crit Care Med 27:2184–2187
Roy S, Ge BL, Loh LL et al (1992) Characterization of [3H]Morphine binding to interleukin-1 activated thymocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 263:451–456
Roy S, Cain KJ, Chapin RB et al (1998) Morphine modulates NF kappa B activation in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 245:392–396
Schmidt HW, Kelm M (1996) Determination of nitrite and nitrate by Griess reaction. In: Feelisch M, Stamler JS (eds) Methods in nitric oxide research. Wiley, New York, pp 491–497
Siebenlist U, Franzoso G, Brown K (1994) Structure, regulation and function of NF-kappa B. Annu Rev Cell Biol 10:405–455
Supajatura V, Ushio H, Nakao A et al (2002) Differential responses of mast cell Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in allergy and innate immunity. J Clin Invest 109:1351–1359
Szabo I, Wetzel M, McCarthy L et al (2001) Interactions of opioid receptors, chemokines, and chemokine receptors. Adv Exp Med Biol 493:69–74
Tergaonkar V (2006) NFkappaB pathway: a good signaling paradigm and therapeutic target. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38:1647–1653
Triantafilou M, Gamper FG, Haston RM et al (2006) Membrane sorting of toll-like receptor (TLR)-2/6 and TLR2/1 heterodimers at the cell surface determines heterotypic associations with CD36 and intracellular targeting. J Biol Chem 281:31002–31011
Wang J, Barke RA, Charboneau R et al (2005) Morphine impairs host innate immune response and increases susceptibility to Streptococcus pneumoniae lung infection. J Immunol 174:426–434
Wang J, Barke RA, Charboneau R et al (2008) Morphine induces defects in early response of alveolar macrophages to Streptococcus pneumoniae by modulating TLR9-NF-kappa B signaling. J Immunol 180:3594–3600
Wang J, Ma J, Charboneau R et al (2011) Morphine inhibits murine dendritic cell IL-23 production by modulating Toll-like receptor 2 and Nod2 signaling. J Biol Chem 286:10225–10232
Welters ID, Fimiani C, Bilfinger TV et al (2000a) NF-kappaB, nitric oxide and opiate signaling. Med Hypotheses 54:263–268
Welters ID, Menzebach A, Goumon Y et al (2000b) Morphine inhibits NF-kappaB nuclear binding in human neutrophils and monocytes by a nitric oxide-dependent mechanism. Anesthesiology 92:1677–1684
Welters ID, Menzebach A, Goumon Y et al (2007) Morphine inhibits AP-1 activity and CD14 expression in leukocytes by a nitric oxide and opioid receptor-dependent mechanism. Eur J Anaesthesiol 24:958–965
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grant No. N N303 35 69 33 from the Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wypasek, E., Natorska, J., Mazur, A.I. et al. Toll-Like Receptors Expression and NF-κB Activation in Peritoneal Leukocytes in Morphine-Mediated Impairment of Zymosan-Induced Peritonitis in Swiss Mice. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 60, 373–382 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-012-0186-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-012-0186-x