Abstract
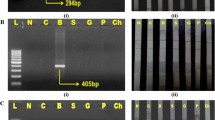
In 2015, the Bavarian Health and Food Safety Authority (Bayerisches Landesamt für Gesundheit und Lebensmittelsicherheit) initiated controls of Asian buffets to verify declaration of animal species. Especially Mongolian buffets, where raw meat of partly exotic animal species is offered with side dishes and sauces, enjoy high popularity in Germany. A total of 27 samples were collected in 5 Bavarian cities including nine mammalian meat, 1 frog, 3 crocodile, 10 fish, 1 squid, 2 shrimp, and 1 mussel sample. All samples were analyzed using molecular biological methods. The animal species was identified by DNA sequencing of the mitochondrial genes cytochrome c oxidase subunit I, cytochrome b or 16S ribosomal DNA with subsequent database mining. From the 27 samples, 5 were objectionable with either wrong or incomplete labelling. These included two fish samples, two samples falsely declared as zebra which were in fact beef, one guanaco sample which was depicted as camel and another guanaco sample which was marketed as llama. The results clearly show the need for continued surveillance of meat species in buffets covering a wide variety of meats and seafood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarado Bremer JR, Ditty JG, Turner JS, Saxton BL (2010) Molecular species identification of commercially important penaeid shrimp from the Gulf of Mexico using a multiplex haplotype-specific PCR assay. Biochem Syst Ecol 38(4):715–721
Ayaz Y, Ayaz ND, Erol I (2006) Detection of species in meat and meat products using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Muscle Foods 17(2):214–220
Bénard-Capelle J, Guillonneau V, Nouvian C, Fournier N, Le Loët K, Dettai A (2015) Fish mislabelling in France: substitution rates and retail types. PeerJ 2:e714
Bitanyi S, Bjornstad G, Ernest EM, Nesje M, Kusiluka LJ, Keyyu JD, Mdegela RH, Roed KH (2011) Species identification of Tanzanian antelopes using DNA barcoding. Mol Ecol Resour 11(3):442–449
Brodmann PD, Nicholas G, Schaltenbrand P, Ilg EC (2001) Identifying unknown game species: experience with nucleotide sequencing of the mitochondrial cytochrome b gene and a subsequent basic local alignment search tool search. Eur Food Res Technol 212(4):491–496
Brown WM, George M Jr, Wilson AC (1979) Rapid evolution of animal mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76(4):1967–1971
BVL (2014) Amtliche Sammlung von Untersuchungsverfahren nach § 64 LFGB, § 35 Vorl. Tabakgesetz, § 28 b Gentechnikgesetz. Beuth Verlag GmbH, Berlin
Cai Y, Zhang L, Shen F, Zhang W, Hou R, Yue B, Li J, Zhang Z (2011) DNA barcoding of 18 species of Bovidae. Chin Sci Bull 56(2):164–168
D’Amato ME, Alechine E, Cloete KW, Davison S, Corach D (2013) Where is the game? Wild meat products authentication in South Africa: a case study. Investig Genet 4:6
Fajardo V, Gonzalez I, Martin I, Rojas MA, Hernandez PE, Garci AT, Martin R (2008) Differentiation of European wild boar (Sus scrofa scrofa) and domestic swine (Sus scrofa domestica) meats by PCR analysis targeting the mitochondrial D-loop and the nuclear melanocortin receptor 1 (MC1R) genes. Meat Sci 78(3):314–322
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotechnol 3(5):294–299
Galimberti A, De Mattia F, Losa A, Bruni I, Federici S, Casiraghi M, Martellos S, Labra M (2013) DNA barcoding as a new tool for food traceability. Food Res Int 50(1):55–63
Günther B, Raupach MJ, Knebelsberger T (2017) Full-length and mini-length DNA barcoding for the identification of seafood commercially traded in Germany. Food Control 73(Part B):922–929
Haye PA, Segovia NI, Vera R, MdlÁ Gallardo, Gallardo-Escárate C (2012) Authentication of commercialized crab-meat in Chile using DNA Barcoding. Food Control 25(1):239–244
Hebert PD, Cywinska A, Ball SL, deWaard JR (2003) Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc Biol Sci 270(1512):313–321
Hebert PD, Stoeckle MY, Zemlak TS, Francis CM (2004) Identification of Birds through DNA Barcodes. PLoS Biol 2(10):312
Heintzman PD, Zazula GD, Cahill JA, Reyes AV, MacPhee RD, Shapiro B (2015) Genomic data from extinct North American Camelops revise camel evolutionary history. Mol Biol Evol 32(9):2433–2440
Hsieh YHP, Woodward BB, Ho SH (1995) Detection of species substitution in raw and cooked meats using immunoassays. J Food Prot 58(5):555–559
Hubert N, Hanner R, Holm E, Mandrak NE, Taylor E, Burridge M, Watkinson D, Dumont P, Curry A, Bentzen P, Zhang J, April J, Bernatchez L (2008) Identifying Canadian freshwater fishes through DNA barcodes. PLoS One 3(6):18
ISO (21571:2005). International Standard (ISO) 21571:2005 Foodstuffs — methods of analysis for the detection of genetically modified organisms and derived products — nucleic acid extraction
Ivanova NV, Zemlak TS, Hanner RH, Hebert PDN (2007) Universal primer cocktails for fish DNA barcoding. Mol Ecol Notes 7(4):544–548
Jacquet JL, Pauly D (2008) Trade secrets: Renaming and mislabeling of seafood. Mar Policy 32(3):309–318
Kappel K, Schröder U (2015) Species identification of fishery products in Germany. J Verbrauch Lebensm 10(1):31–34
Kappel K, Schröder U (2016) Substitution of high-priced fish with low-priced species: adulteration of common sole in German restaurants. Food Control 59:478–486
Karaiskou N, Apostolidis AP, Triantafyllidis A, Kouvatsi A, Triantaphyllidis C (2003) Genetic identification and phylogeny of three species of the genus Trachurus based on mitochondrial DNA analysis. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 5(5):493–504
Kocher TD, Thomas WK, Meyer A, Edwards SV, Paabo S, Villablanca FX, Wilson AC (1989) Dynamics of mitochondrial DNA evolution in animals: amplification and sequencing with conserved primers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86(16):6196–6200
Kyrova V, Surmanova P, Ostry V, Rehurkova I, Ruprich J, Jechova M (2016) Sea fish fraud? A confirmation of Gadoid species food labelling. Br Food J 119(1):122–130
Layton KKS, Martel AL, Hebert PDN (2014) Patterns of DNA barcode variation in canadian marine molluscs. PLoS One 9(4):e95003
Ling KH, Nichols PD, But PP (2009) Fish-induced keriorrhea. Adv Food Nutr Res 57:1–52
Lowenstein JH, Amato G, Kolokotronis SO (2009) The real maccoyii: identifying tuna sushi with DNA barcodes — contrasting characteristic attributes and genetic distances. PloS One 4(11):7866
Luo A, Zhang A, Ho SYW, Xu W, Zhang Y, Shi W, Cameron SL, Zhu C (2011) Potential efficacy of mitochondrial genes for animal DNA barcoding: a case study using eutherian mammals. BMC Genom 12:84
Mariani S, Griffiths AM, Velasco A, Kappel K, Jérôme M, Perez-Martin RI, Schröder U, Verrez-Bagnis V, Silva H, Vandamme SG, Boufana B, Mendes R, Shorten M, Smith C, Hankard E, Hook SA, Weymer AS, Gunning D, Sotelo CG (2015) Low mislabeling rates indicate marked improvements in European seafood market operations. Front Ecol Environ 13(10):536–540
Mikkelsen PM, Bieler R, Kappner I, Rawlings TA (2006) Phylogeny of Veneroidea (Mollusca: Bivalvia) based on morphology and molecules. Zool J Linn Soc 148(3):439–521
Muñoz-Colmenero M, Blanco O, Arias V, Martinez JL, Garcia-Vazquez E (2016) DNA authentication of fish products reveals mislabeling associated with seafood processing. Fisheries 41(3):128–138
Nicolè S, Negrisolo E, Eccher G, Mantovani R, Patarnello T, Erickson DL, Kress WJ, Barcaccia G (2012) DNA barcoding as a reliable method for the authentication of commercial seafood products. Food Technol Biotechnol 50:387–398
Palumbi SR, Martin A, Romano S, McMillan WO, Stice L, Grabowski G (1991) The simple fool’s guide to PCR, version 2.0, privately published document compiled by S. Palumbi. Dept. Zoology, Univ, Honolulu
Pappalardo AM, Ferrito V (2015) DNA barcoding species identification unveils mislabeling of processed flatfish products in southern Italy markets. Fish Res 164:153–158
Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for on the hygiene of foodstuffs. Off J Eur Union L139:55 (30.04.2004)
Rimbach G, Möhring J, Ebersdobler HF (2010) Lebensmittel-Warenkunde für Einsteiger. Springer, Berlin
Schäffer S, Zachos FE, Koblmüller S (2017) Opening the treasure chest: a DNA-barcoding primer set for most higher taxa of Central European birds and mammals from museum collections. PLoS One 12(3):e0174449
Shears P (2010) Food fraud — a current issue but an old problem. Br Food J 112(2):198–213
Sicherer SH, Sampson HA (2013) Food allergy: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol 133(2):291–307
Skidmore JA, Billah M, Binns M, Short RV, Allen WR (1999) Hybridizing old and new world camelids: Camelus dromedarius x Lama guanicoe. Proc Biol Sci 266(1420):649–656
Spink J, Moyer DC (2011) Defining the public health threat of food fraud. J Food Sci 76(9):R157–R163
Staats M, Arulandhu AJ, Gravendeel B, Holst-Jensen A, Scholtens I, Peelen T, Prins TW, Kok E (2016) Advances in DNA metabarcoding for food and wildlife forensic species identification. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:4615–4630
Staffen CF, Staffen MD, Becker ML, Löfgren SE, Muniz YCN, de Freitas RHA, Marrero AR (2017) DNA barcoding reveals the mislabeling of fish in a popular tourist destination in Brazil. PeerJ 5:e4006
Stern DB, Castro Nallar E, Rathod J, Crandall KA (2017) DNA Barcoding analysis of seafood accuracy in Washington, D.C. restaurants. PeerJ 5:3234
Teletchea F, Maudet C, Hanni C (2005) Food and forensic molecular identification: update and challenges. Trends Biotechnol 23(7):359–366
Tong JG, Chan TY, Chu KH (2000) A preliminary phylogenetic analysis of metapenaeopsis (Decapoda: Penaeidae) based on mitochondrial DNA sequences of selected species from the Indo-West Pacific. J Crustacean Biol 20(3):541–549
Trivedi S, Aloufi AA, Ansari AA, Ghosh SK (2016) Role of DNA barcoding in marine biodiversity assessment and conservation: an update. Saudi J Biol Sci 23(2):161–171
Vences M, Thomas M, van der Meijden A, Chiari Y, Vieites DR (2005) Comparative performance of the 16S rRNA gene in DNA barcoding of amphibians. Front Zool 2(1):5
Waiblinger HU, Bartsch D, Brockmeyer J, Bruenen-Nieweler C, Busch U, Haase I, Hahn A, Haarmann M, Hauser W, Huber I, Jany KD, Kirmse N, Lindeke S, Neumann K, Naumann H, Paschke A, Pietsch K, Pöpping B, Reiting R, Schroeder U, Schwägele F, Weller MG, Zagon J (2017) Methods of differentiating animal species in foods — status quo. Fleischwirtschaft Int 97(1):50–55
Ward R, Zemlak T, Innes B, Last P, Hebert P (2005) DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360:1847–1857
Wong EHK, Hanner RH (2008) DNA barcoding detects market substitution in North American seafood. Food Res Int 41(8):828–837
Acknowledgements
We thank Miriam Schrempp, Marzena Maggipinto, Ulrike Hohenberger and Angelika Wahl for their excellent laboratory work. We also thank Dr. Azuka Iwobi for critically reading our manuscript. Furthermore, we would like to acknowledge the financial support of the Bavarian State Ministry of the Environment and Consumer Protection.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spielmann, G., Gerdes, L., Miller, A. et al. Molecular biological species identification of animal samples from Asian buffets. J Consum Prot Food Saf 13, 271–278 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-018-1168-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-018-1168-7