Abstract
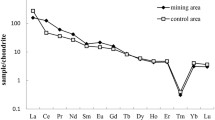
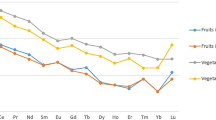
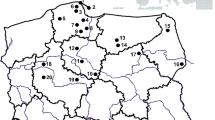
For detection and analysis of the potential accumulation of rare earth elements (REE) in food products originating from REE mining area the REE content of Camellia oleifera seeds from these area was determined by ICP-MS; the results for limits of detection of REE (mostly lower than 3.00 ng/L) and the relative standard deviation (1.97–11.7 %) for 10 REE demonstrate the significance of our analysis method. The content of REE in Camellia oleifera seeds from REE mining area is low (not significantly elevated) and should not be harmful to human health.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Z-Y (2005) Accumulation and toxicity of rare earth elements in brain and their potential effects on health. Rural Ecol Environ 21:72–73, 80
Chen Z-Y, Zhu X-D (2008) Accumulation of rare earth elements in bone and its toxicity and potential hazard to health. J Ecol Rural Environm 24:88–91
Jiao C-Z, Wei Z-L, Tian Z-H, Qu G-Q, Rui Y-K (2008) Application of ICP-MS to detect rare elements in wild Cistanc deserticola Y. C. Ma. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 28:1931–1932
Lee C-P, Shih P-H, Hsu C-L, Yen G-C (2007) Hepatoprotection of tea seed oil (Camellia oleifera Abel.) against CCl4-induced oxidative damage in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 45:888–895
Li M-L, Wang L-S, Peng X-L, Yang G-L, Huang X-W, Long Z-Q (2010) Determination of trace rare earth elements in phosphate or by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Metall Anal 30:47–50
Lu G, Wang X, Zhang J, Liu H, Gao Z, Wang N, Chen Q, Meng Y, Wang J (2007) Preliminary study on the contents and distribution characteristics of 15 rare earth elements in the adult human slap hair of a rare earth elements mining area in Shandong Province. Mod Instrum 1:33–37
Ma J, Hang Y, Rui Y, Chen G, Zhang N (2010) Fatty acid composition of Camellia oleifera oil. J Verbr Lebensm. doi:10.1007/s00003-010-0581-3
Miao L, Xu R, Ma Y, Zhu Z, Wang J, Cai R, Chen Y (2008) Characteristics of distribution, accumulation and transportation of rare earth elements in soil-plant systems of the Hetai goldfield. Ecol Environ 17:350–356
Peng R-L, Pan X-C, Xie Q (2003) Relationship of the hair content of rare earth elements in young children aged 0 to 3 years to that in their mothers living in a rare earth mining area of Jiangxi. J Prev Med 37:20–22
Zhang N-Y, Fan G-P (2009) Simultaneous determination of 10 kinds of rare earth elements in soil by ICP-MS. Stud Trace Elem Health 26:51–52
Zhang D-Q, Tan X-F, Peng W-X, Liu Q-M, Zeng Y-L, Chen H-P, Tian H, Ma Q-Z (2007) Improved application of Camellia oleifera on biomass energy by enlarging its production. Acta Sci Nat Univ Sunsyatseni 46(Suppl):109–110
Zhu J, Yuan Z, Hu M (2006) Analysis on content of rare earth in environment of rare earth mine area. Chin J Public Health 22:950–951
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Wang Xiaoyan (School of Public Health, Peiking University, China) for her assistance during experimental work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, D., Rui, Yk. Determination of rare earth elements in Camellia oleifera seeds from rare earth elements mining areas in Southern Jiangxi, China by ICP-MS. J. Verbr. Lebensm. 6, 349–351 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-010-0650-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-010-0650-7