Abstract
Serum activity of bone specific alkaline phosphatase, a product of differentiated osteoblasts, is thought to mirror fracture healing. The precise time course after various conditions involving bone healing is, however, poorly described. The aim of our study was to evaluate sequential changes of bone alkaline phosphatase over a period of 20 weeks in traumatized patients with and without bone injuries. The bone isoenzyme of alkaline phosphatase was determined in frozen serum samples using a new automated procedure based on the wheat germ lectin precipitation method. Patients were stratified into different groups: 1. ST – soft tissue injury without bone participation; 2. DF – diaphysial fracture of tibia or femur; 3. MT – patients suffering from multiple traumas; 4. PF – proximal femur fracture, treated with dynamic hip screw; and 5. EP – femur neck fracture, treated with cemented endoprosthesis.
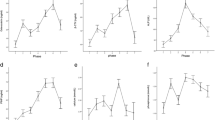
Similar values were obtained in all measured groups on the day of admission (ST 35.83±6.15 U/l; PF 27.37±4.43 U/l; EP 31.09±7.42 U/l). In the following measurements, enzyme activity decreased significantly in all groups to reach a nadir within the first week, ranging between 41 and 82% of the activity immediatly postoperative. Thereafter, a substantial increase occurred in all groups investigated. In the ST group, this increase led to an activity level that was comparable to the first posttraumatic value (39.06±7.81 U/l). In contrast, average values in all other groups revealed a further increase, which was significantly elevated compared to measurements taken the first day after trauma (DF 74.36±10.84 U/l; MT 177.87±30.0 U/l; PF 93.39±22.08 U/l; EP 51,52±7.33 U/l). Additionally, the time to reach the peak in enzyme activity differed between groups. In the MT group, it was observed as early as 3 weeks after injury, in the DF group the peak was reached as late as 6 weeks after trauma.
The results of the study indicate that bone alkaline phophatase activity undergoes a specific pattern of changes after trauma. It may be assumed that the initial decrease is part of a general stress response to trauma and operation. The subsequent increase seems to depend from the magnitude of bone repair and the type of fracture healing, e.g. diaphysial fracture healing takes longer time than cancellous bone healing. These results seem to be a useful basis in order to establish a laboratory monitoring of fracture healing in subsequent studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: August 10, 1999; accepted: November 29, 1999.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laurer, H., Hagenbourger, O., Quast, S. et al. Sequential Changes and Pattern of Bone-Specific Alkaline Phosphatase after Trauma. Eur J Trauma 26, 33–38 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00002436
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00002436