Abstract
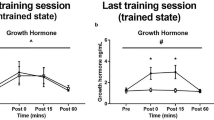
The response of plasma insulin-like growth factor I (IGF I) to exercise-induced increase of total human growth hormone concentration [hGHtot] and of its molecular species [hGH20kD] was investigated up to 48 h after an 1-h ergometer exercise at 60% of maximal capacity during normoxia (N) and hypoxia (H) (inspiratory partial pressure of oxygen = 92 mmHg (12.7 kPa);n = 8). Lactate and glucose concentrations were differently affected during both conditions showing higher levels under H. Despite similar maximal concentrations, the increase of human growth hormone (hGH) was faster during exercise during H than during N[hGHtot after 30 min: 8.6 (SD 11.4) ng · ml−1 (N); 16.2 (SD 11.6) ng · ml−1 (H);P < 0.05]. The variations in plasma [hGH20kD] were closely correlated to those of [hGHtot], but its absolute concentration did not exceed 3% of the [hGHtot]. Plasma IGF I concentration was significantly decreased 24 h after both experimental conditions [N from 319 (SD 71) ng · ml-1 to 228 (SD 72) ng · ml−1,P < 0.05; H from 253 (SD 47) to 200 (SD 47) ng · ml−1,P < 0.01], and was still lower than basal levels 48 h after exercise during H [204 (SD 44) ng · ml−1,P < 0.01]. Linear regression analysis yielded no significant correlation between increase in plasma [hGHtot] or [hGH20kD] during exercise and the plasma IGF I concentration after exercise. It was concluded that the exercise-associated elevated plasma [hGH] did not increase the hepatic IGF I production. From our study it would seem that the high energy demand during and after the long-lasting intensive exercise may have overridden an existing hGH stimulus on plasma IGH I, which was most obvious during hypoxia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirav I, Dowdeswell RJ, Plit M, Panz VR, Joffe BI, Seftel HC (1990) Growth hormone response to exercise in asthmatic and normal children. Eur J Pediatr 149:443–449
Bang P, Brandt J, Degerblad M, Enberg G, Kaijser L, Thoren M, Hall K (1990) Exercise-induced changes in insulin-like growth factors and their low molecular weight binding protein in healthy subjects and patients with growth hormone deficiency. Eur J Clin Invest 20:285–292
Baumann G, Stolar MW, Amburn K (1985a) Molecular forms of circulating growth hormone during spontaneous secretory episodes and in the basal state. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 60:1216–1220
Baumann G, Stolar MW, Buchanan TA (1985b) Slow metabolic clearance rate of 20,000-dalton variant of human growth hormone: implications for biological activity. Endocrinology 117:1309–1313
Baxter RC (1986) The somatomedins: insulin-like growth factors. Adv Clin Chem 25:49–115
Boyd RD, Bauman DE (1989) Mechanisms of action for somatotropin in growth. In: Campion DR, Hausman GJ et al (eds) Animal growth regulation. Plenum, New York, pp 257–293
Cappon J, Brasel JA, Mohan S, Copper DM (1994) Effect of brief exercise on circulating insulin-like growth factor I. J Appl Physiol 76:2490–2496
Celniker AC, Chen AB, Wert RM Jr, Sherman BM (1989) Variability in the quantitation of circulating growth hormone using commercial immunoassays. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 68: 469–476
Coggan AR, Kohrt WM, Spina RJ, Kirwan JP, Bier DM, Holloszy JO (1992) Plasma glucose kinetics during exercise in subjects with high and low lactate thresholds. J Appl Physiol 73: 1873–1880
Copeland KC, Underwood LE, Van Wyk JJ (1980) Induction of immunoreactive somatomedin C in human serum by growth hormone: dose-response relationships and effect on chromatographic profiles. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 50:690–697
Cuneo RC, Salomon F, Wiles CM, Hesp R, Sönsken PH (1991) Growth hormone treatment in growth hormone-deficient adults. II. Effects on exercise performance. J Appl Physiol 70:695–700
Daughaday WH, Mariz IK, Blethen SL (1980) Inhibition of access of bound somatomedin to membrane receptor and immunobinding sites: a comparison of radioreceptor and radioimmunoassay of somatomedin in native and acid-ethanol-extracted serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 51:781–788
Doré S, Brisson GR, Gournier A, Montpetit R, Perrault H, Boisvert D (1991) Contribution of hGH20k variant to blood hGH response in sauna and exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 62:130–134
Froesch ER, Schmidt C, Schwander J, Zapf J (1985) Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol 47:443–467
Jahreis G, Kauf E, Fröhner G, Schmidt HE (1991) Influence of intensive exercise on insulin-like growth factor I, thyroid and steroid hormones in female gymnasts. Growth Reg 1:95–99
Jörgensen JO, Möller N, Lauritzen T, Alberti KG, Orskov H, Christiansen JS (1990) Evening versus morning injections of growth hormone (GH) in GH-deficient patients: effects on 24-hour patterns of circulating hormones and metabolites. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 70:207–214
Kelly PJ, Eisman JA, Stuart MC, Pocock NA, Sambrook PN, Gwinn TH (1990) Somatomedin-C, physical fitness, and bone density. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 70:718–723
Kraemer RR, Kilgore JL, Kraemer GR, Castracane VD (1992) Growth hormone, IGF-I, and testosterone responses to resistive exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 24:1346–1352
Lassarre C, Girard F, Durand J, Raynaud J (1974) Kinetics of human growth hormone during submaximal exercise. J Appl Physiol 37:826–830
Luger A, Watschinger B, Deuster P, Svoboda T, Clodi M, Chrousos GP (1992) Plasma growth hormone and prolactin responses to graded levels of acute exercise and to a lactate infusion. Neuroendocrinology 56:112–117
Poehlman ET, Copeland KC (1990) Influence of physical activity of insulin-like growth factor-I in healthy younger and older men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 71:1468–1473
Raynaud J, Drouet L, Martineaud JP, Bordachar J, Coudert J, Durand J (1981) Time course of plasma growth hormone during exercise in humans at altitude. J Appl Physiol 50:229–233
Raynaud J, Capderou A, Martineaud JP, Bordachar J, Durand J (1983) Intersubject variability in growth hormone time course during different types of work. J Appl Physiol 55:1682–1687
Schmidt W, Maassen N, Heuer D, Heck J, Böning D (1990) Regulation of plasma volume and erythropoiesis during a ten day lasting cycling race. In: Hermans GPH, Mosterd WL (eds) Sports, medicine and health. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp 505–512
Smal J, Closset J, Hennen G, De Meyts P (1986) The receptor binding properties of the 20K variant of human growth hormone explain its discrepant insulin-like and growth promoting activities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 134:159–165
Smith AT, Clemmons DR, Underwood LE, Ben-Ezra V, McMurray P (1987) The effect of exercise on plasma somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I concentrations. Metabolism 36:533–537
Snyder DK, Clemmons DR, Underwood LE (1989) Dietary carbohydrate content determines responsiveness to growth hormone in energy restricted humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 69:745–752
Suikkari AM, Sane T, Seppälä M, Yki-Järvinen H, Karonen SL, Koivisto VA (1989) Prolonged exercise increases serum insulin-like growth factor-binding protein concentrations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 68:141–144
Sutton JR (1977) Effect of acute hypoxia on the hormonal response to exercise. J Appl Physiol 42:587–592
Sutton J, Lazarus L (1976) Growth hormone in exercise: comparison of physiological and pharmacological stimuli. J Appl Physiol 41:523–527
Underwood LE (1984) Report of the conference on uses and possible abuses of biosynthetic human growth hormone. N Engl J Med 311:606–608
Van Helder WP, Casey K, Radomski MW (1987) Regulation of growth hormone during exercise by oxygen demand and availability. Eur J Appl Physiol 56:628–632
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design. McGraw Hill, New York
Wolfel EE, Selland MA, Mazzeo RS, Reeves JT (1994) Systemic hypertension at 4100m is related to sympathoadrenal activity. J Appl Physiol 76:1643–1650
Yan Z, Biggs RB, Booth FW (1993) Insulin-like growth factor immunoreactivity increases in muscle after acute eccentric contractions. J Appl Physiol 74:410–414
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, W., Doré, S., Hilgendorf, A. et al. Effects of exercise during normoxia and hypoxia on the growth hormone—insulin-like growth factor I axis. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 71, 424–430 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00635876
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00635876