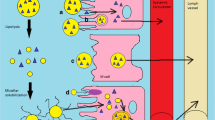
Abstract
Low-oral bioavailability as a consequence of low-water solubility of drugs is challenging for formulation scientists in the development of new pharmaceutical products. This review aims to highlight relevant considerations when implementing a rational strategy for the development of lipid-based oral drug delivery systems and to discuss shortcomings and challenges to the current classification of these delivery systems such as nanoemulsion, Solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN), Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC), Self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS). Lipid-based drug delivery systems consist of a diverse group of formulations, each consisting of varying functional and structural properties that are amenable to modifications achieved by varying the composition of lipid excipients and other additives thereby facilitating the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. In addition, lipid nanoparticles may also protect the loaded drugs from chemical and enzymatic degradation and gradually release drug molecules from the lipid matrix into the blood, resulting in improved therapeutic profiles compared to free drugs. Therefore, due to their physiological and biodegradable properties, lipid molecules may decrease adverse side effects and chronic toxicity of the drug-delivery systems when compared to others of polymeric nature. Accordingly, the present review is mainly centred on the various lipid-based drug delivery system and excipients used in lipid-based drug delivery systems (LBDDS).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Poonia, R. Kharb, V. Lather, D. Pandita, Nanostructured lipid carriers: Versatile oral delivery vehicle. Future Sci. OA 2(3), 135 (2016)
K. Pathak, S. Raghuvanshi, Oral Bioavailability: Issues and Solutions via Nanoformulations. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 54(4), 325–357 (2015)
P.P. Desai, A.A. Date, V.B. Patravale, Overcoming poor oral bioavailability using nanoparticle formulations—opportunities and limitations. Drug Discov. Today. 9(2), e87–e95 (2012)
A. Müllertz, A. Ogbonna, S. Ren, T. Rades, New perspectives on lipid and surfactant based drug delivery systems for oral delivery of poorly soluble drugs. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 62(11), 1622–1636 (2010)
L.X. Yu, G.L. Amidon, J.E. Polli, H. Zhao, M.U. Mehta, D.P. Conner et al., (2002) Biopharmaceutics classification system: the scientific basis for biowaiver extensions. Pharm. Res. 19(7), 921–925 (2002)
G.L. Amidon, H. Lennernäs, V.P. Shah, J.R. Crison, A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: the correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res. An Off. J. Am. Assoc. Pharm. Sci. 12(3), 413–420 (1995)
R.K. Shirodkar, L. Kumar, S. Mutalik, S. Lewis, Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: emerging lipid-based drug delivery systems. Pharm Chem J. 53(5), 440–453 (2019)
D.K. Patel, R. Kesharwani, V. Kumar, Lipid nanoparticle topical and transdermal delivery: a review on production, penetration mechanism to skin. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 9(4), 148–153 (2019)
D. Patel, V. Kumar, R. Kesharwani, B. Mazumdar, Lipid nanoparticle a novel carrier for cosmetics and topical preparation: a review. Inven Rapid Cosmeceuticals. 3, 1–6 (2015)
J.A. Arnott, S.L. Planey, The influence of lipophilicity in drug discovery and design. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 7(10), 863–875 (2012)
B. Testa, P. Crivori, M. Reist, P.A. Carrupt, The influence of lipophilicity on the pharmacokinetic behavior of drugs: Concepts and examples. Perspect. Drug Discov. Des. 19(1), 179–211 (2000)
P. Leeson, Drug discovery: chemical beauty contest. Nature 481(7382), 455–456 (2012)
C.W. Pouton, C.J.H. Porter, Formulation of lipid-based delivery systems for oral administration: Materials, methods and strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60(6), 625–637 (2008)
C.J.H. Porter, C.W. Pouton, J.F. Cuine, W.N. Charman, Enhancing intestinal drug solubilisation using lipid-based delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60(6), 673–691 (2008)
C.M. O’Driscoll, B.T. Griffin, Biopharmaceutical challenges associated with drugs with low aqueous solubility-The potential impact of lipid-based formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 60(6), 617–624 (2008)
H.D. Williams, P. Sassene, K. Kleberg, J.C. Bakala-N’Goma, M. Calderone, V. Jannin et al., Toward the establishment of standardized in vitro tests for lipid-based formulations, Part 1: method parameterization and comparison of in vitro digestion profiles across a range of representative formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 101(9), 3360–3380 (2012)
K.M. Wasan, Formulation and physiological and biopharmaceutical issues in the development of oral lipid-based drug delivery systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 27(4), 267–276 (2001)
M. Kuentz, Lipid-based formulations for oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Drug Discov. Today: Technol. 9(2), e97–e104 (2012)
F. Ibrahim, P. Gershkovich, O. Sivak, E.K. Wasan, K.M. Wasan, Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of amphotericin B following oral administration of three lipid-based formulations to rats. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 39(9), 1277–1283 (2013)
J.S.L. Tan, C. Roberts, N. Billa, Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of an orally administered mucoadhesive chitosan-coated amphotericin B-Loaded nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) in rats. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 31(20), 141–154 (2020)
J.B. Cannon, M.A. Long, Emulsions, microemulsions, and lipid-based drug delivery systems for drug solubilization and delivery, part II. Oral Appl. 16, 227–254 (2008)
C.W. Pouton, Lipid formulations for oral administration of drugs: non-emulsifying, self-emulsifying and self microemulsifying drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 11(2), S93–S98 (2000)
J.D. Hauss, Oral lipid-based formulations: enhancing the bioavailability of poorly Water-soluble drugs. Drugs Pharm. Sci. 170, 1–85 (2013)
C.T. Phan, Intestinal lipid absorption and transport. Front Biosci. 6(3), 299–319 (2001)
E. Ros, Intestinal absorption of triglyceride and cholesterol: Dietary and pharmacological inhibition to reduce cardiovascular risk. Atherosclerosis 151(2), 357–379 (2000)
S. Kalepu, M. Manthina, V. Padavala, Oral lipid-based drug delivery systems: an overview. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 3(6), 361–372 (2013)
R. Ghadi, N. Dand, BCS class IV drugs: highly notorious candidates for formulation development. J. Controlled Release. 248, 71–95 (2017)
D. Wagner, H. Spahn-Langguth, A. Hanafy, A. Koggel, P. Langguth, Intestinal drug efflux: formulation and food effects. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 50, S13–S31 (2001)
P. Gershkovich, A. Hoffman, Effect of a high-fat meal on absorption and disposition of lipophilic compounds: The importance of degree of association with triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 32(1), 24–32 (2007)
E.A. Fouad, M. El-Badry, G.M. Mahrous, I.A. Alsarra, Z. Alashbban, F.K. Alanazi, In vitro investigation for embedding dextromethorphan in lipids using spray drying. Dig. J. Nanomater Biostruct. 6, 1129 (2011)
R. Litschel, GAS: management of ZFB and A. FPS 31(4), 368–375 (2015)
E.C. Umeyor, F.C. Kenechukwu, J.D. Ogbonna, S.A. Chime, A. Attama, Preparation of novel solid lipid microparticles loaded with gentamicin and its evaluation in vitro and in vivo. J. Microencapsul. 29(3), 296–307 (2012)
S. Khan, S. Baboota, J. Ali, R.S. Narang, J.K. Narang, Chlorogenic acid stabilized nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) of atorvastatin: Formulation, design and in vivo evaluation. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 42(2), 209–220 (2016)
H.N. Joshi, N. Shah, Review of lipids in pharmaceutical drug delivery systems: part 2. Am. Pharm. Rev. 8(5), 120 (2005)
C.J.H. Porter, N.L. Trevaskis, W.N. Charman, Lipids and lipid-based formulations: optimizing the oral delivery of lipophilic drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 6(3), 231–248 (2007)
A. Chime, Lipid-based drug delivery systems (LDDS): Recent advances and applications of lipids in drug delivery. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 7(48), 3034–3059 (2013)
L. Montenegro, F. Lai, A. Offerta, M.G. Sarpietro, L. Micicchè, A.M. Maccioni et al., From nanoemulsions to nanostructured lipid carriers: A relevant development in dermal delivery of drugs and cosmetics. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 32, 100–112 (2016)
H. Shrestha, R. Bala, S. Arora, Lipid-based drug delivery systems. J Pharm. (2014)
T. Lian, R.J.Y. Ho, Trends and developments in liposome drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 90(6), 667–680 (2001)
A. Nida Suhail, W. Khuzaim Alzahrani, J. Basha, N. Kizilbash, A. Zaidi, J. Ambreen, H.M. Khachfe, Microemulsions: unique properties, pharmacological applications, and targeted drug delivery. Front. Nanotechnol. 3, 754889 (2021)
C. Lovelyn, A.A. Attama, Current state of nanoemulsions in drug delivery. J Biomater Nanobiotechnol. 2(5), 626 (2011)
Y. Singh, J.G. Meher, K. Raval, F.A. Khan, M. Chaurasia, N.K. Jain et al., Nanoemulsion: Concepts, development and applications in drug delivery. J. Controll. Release 252, 28–49 (2017)
S. Kotta, A.W. Khan, K. Pramod, S.H. Ansari, R.K. Sharma, Ali J Exploring oral nanoemulsions for bioavailability enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 9(5), 585–598 (2012)
S. Choudhury, S. Dasgupta, D.K. Patel, Y.R. Ramani, S.K. Ghosh, B. Mazumder, Nanoemulsion as a Carrier for Topical Delivery of Aceclofenac (Springer, New York, 2013)
D.J. McClements, Nanoemulsions versus microemulsions: Terminology, differences, and similarities. Soft Matter 8(6), 1719–1729 (2012)
Gupta A. Nanoemulsions. In: Nanoparticles for biomedical applications: fundamental concepts, biological interactions and clinical applications. (2019)
P. Shah, D. Bhalodia, P. Shelat, Nanoemulsion: a pharmaceutical review. Systematic Rev. Pharm. 1, 158 (2010)
V.K. Rai, N. Mishra, K.S. Yadav, N.P. Yadav, Nanoemulsion as pharmaceutical carrier for dermal and transdermal drug delivery: Formulation development, stability issues, basic considerations and applications. J. Controll. Release 270, 203–225 (2018)
A.A. Attama, M.A. Momoh, P.F. Builders, Lipid nanoparticulate drug delivery systems: a revolution in dosage form design and development. Recent Adv. Novel Drug Carrier Syst. 5, 107–140 (2012)
A.A. Attama, M.A. Momoh, P.F. Builders, Lipid nanoparticulate drug delivery systems: a revolution in dosage form design and development in recent advance in novel drug carrrier systems. INTECH 5, 107–140 (2012)
P. Patil, P. Joshi, Paradkar A (20004) Effect of formulation variables on preparation and evaluation of gelled self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) of ketoprofen. AAPS PharmSciTech 5(3), 43–50 (2004)
B.S.M. Zadeh, S. Dahanzadeh, F. Rahim, Preparation and evaluation of the self emulsifying drug delivery system containing loratadine. Int. J. Adv. Pharm. Sci. 1(3), 15 (2010)
Y. Zhang, R. Wang, J. Wu, Q. Shen, Characterization and evaluation of self-microemulsifying sustained-release pellet formulation of puerarin for oral delivery. Int J Pharm. 427(2), 337–344 (2012)
Singh S, Singh SK, Vuddanda PR, Srivastava AK. A comparison between use of spray and freeze drying techniques for preparation of solid self-microemulsifying formulation of valsartan and in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Biomed Res Int. (2013)
S. Martins, B. Sarmento, D.C. Ferreira, E.B. Souto, Lipid-based colloidal carriers for peptide and protein delivery - Liposomes versus lipid nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed. 2(4), 595 (2007)
H. Muller, R Shegokar, M. Keck, 20 years of lipid nanoparticles (SLN & NLC): present state of development & industrial applications. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 8(3), 207–227 (2011)
M. Rawat, D. Singh, S. Saraf, S. Saraf, Nanocarriers: promising vehicle for bioactive drugs. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 29(9), 1790–1798 (2006)
Feix JB. Liposomes: A Practical Approach. Second Edition. Practical Approach Series, Volume 264. Edited by Vladimir Torchilin and Volkmar Weissig. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2003. Q Rev Biol. (2004)
T. Karamanidou, V. Bourganis, O. Kammona, C. Kiparissides, Lipid-based nanocarriers for the oral administration of biopharmaceutics. Nanomedicine 11(22), 3009–3032 (2016)
Y. Gan, X. Li, D. Chen, C. Le, C. Zhu, L. Hovgaard et al., Novel mucus-penetrating liposomes as a potential oral drug delivery system: preparation, in vitro characterization, and enhanced cellular uptake. Int. J. Nanomed. 6, 3151 (2011)
A. Laouini, C. Jaafar-Maalej, I. Limayem-Blouza, S. Sfar, C. Charcosset, H. Fessi, Preparation, characterization and applications of liposomes: state of the art. J Colloid Sci Biotechnol. 1(2), 147–168 (2012)
P. Severino, T. Andreani, A.S. Macedo, J.F. Fangueiro, M.H.A. Santana, A.M. Silva et al. Current state-of-art and new trends on lipid nanoparticles (SLN and NLC) for oral drug delivery. J Drug Deliv. (2012)
R.H. Müller, C. Freitas, A. Zurmühlen, W. Mehnert, Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 45(2), 149–155 (1996)
V. Kakkar, S. Singh, D. Singla, I.P. Kaur, Exploring solid lipid nanoparticles to enhance the oral bioavailability of curcumin. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 55(3), 495–503 (2011)
R. Kesharwani, A. Sachan, S. Singh, D. Patel, Formulation and evaluation of solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN) based topical gel of etoricoxib. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 6(10), 124–131 (2016)
D. Patel, R. Kesharwani, P.S. Gupta, Development & screening approach for lipid nanoparticle: a review. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 15, 1–7 (2015)
D.K. Patel, S. Tripathy, S.K. Nair, R. Kesharwani, Nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) a modern approach for topical delivery: a review. World J. Pharm. Pharma. Sci. 2, 921–938 (2013)
D.K. Patel, R. Kesharwani, V. Kumar, Etodolac loaded solid lipid nanoparticle based topical gel for enhanced skin delivery. Biocatal Agric. Biotechnol. 29, 101810 (2020)
S.A. Wissing, O. Kayser, R.H. Müller, Solid lipid nanoparticles for parenteral drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 56(9), 257–1272 (2004)
T.B. Dudala, P.R. Yalavarthi, H.C. Vadlamudi, J. Thanniru, G. Yaga, N.L. Mudumala, V.K. Pasupati, A perspective overview on lipospheres as lipid carrier systems. Int. J. Pharm. Invest. 4(4), 149–154 (2014)
S. Scalia, P.M. Young, D. Traini, Solid lipid microparticles as an approach to drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 12(4), 583–599 (2014)
P. Jaiswal, B. Gidwani, A. Vyas, Nanostructured lipid carriers and their current application in targeted drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 44(1), 27–40 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3109/21691401.2014.909822
S. Moghassemi, A. Hadjizadeh, Nano-niosomes as nanoscale drug delivery systems: an illustrated review. J. Controll. Release 185, 22–36 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.04.015
U.N. Wiesmann, S. DiDonato, N.N. Herschkowitz, Effect of chloroquine on cultured fibroblasts: release of lysosomal hydrolases and inhibition of their uptake. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 66(4), 1338–1343 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291x(75)90506-9
Bruschi ML, ed. Strategies to modify the drug release from pharmaceutical systems. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/c2014-0-02342-82015
Shegokar R, ed. Delivery of drugs. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/c2018-0-02191-x (2020)
E. Bombardelli, M. Spelta, Phospholipid-polyphenol complexes: a new concept in skin care ingredients. Cosm Toil. 106(3), 69–76 (1991)
O. Vaizoglu, P.P. Speiser, Pharmacosomes: a novel drug delivery system. Acta Pharm. Suec. 23, 163–172 (1986)
S.S. Biju, S. Talegaonkar, P.R. Mishra et al., Vesicular systems: an overview. Indian J Pharm Sci. 68, 141–153 (2006)
A. Singh, V.A. Saharan, M. Singh, A. Bhandari, Phytosome: drug delivery system for polyphenolic phytoconstituents. Iran J. Pharm. Res. 7(4), 209–219 (2011)
J. Khan, A. Alexander, S. Saraf et al., Recent advances and future prospects of phyto-phospholipid complexation technique for improving pharmacokinetic profile of plant actives. J. Control Release. 168(1), 50–60 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.02.025
J. Patel, R. Patel, K. Khambholja, N. Patel, An overview of phytosomes as an advanced herbal drug delivery system. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 4(6), 363–371 (2009)
M.S. Sikarwar, S. Sharma, A.K. Jain et al., Preparation, characterization and evaluation of marsupsin–phospholipid complex. AAPS PharmSciTech 9(1), 129–137 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-007-9020-x
R. Sachan, T. Parashar, S. Vishal Singh, G. Singh, S. Tyagi, C. Patel, A. Gupta, Transfersomes: a novel tool for transdermal drug delivery system. Int. J. Res. Dev. Pharm. Life Sci. 2(2), 309–316 (2013)
R.V. Kombath, M.S. Kumar, S. Anbazhagan, S. Sandhya, P. Saikumar, T.R. Reddy, D. Banji, Critical issues related to transfersomes – novel vesicular system. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 11(1), 67–82 (2012)
R. Kumar, M. Singh, R. Bala, N. Seth, A.C. Rana, Transferosomes : a novel approach for trans dermal drug delivery. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 3(1), 20–24 (2012)
S.N. Patel, N. Patel, K.R. Patel, N.M. Patel, A vesicular transdermal delivery system for enhance drug permeation-ethosomes and transfeosomed. Int. Pharm. Sci. 2(2), 24–34 (2012)
P. Verma, K. Pathak, Therapeutic and cosmeceutical potential of ethosomes: an overview. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 1(3), 274–282 (2010). https://doi.org/10.4103/0110-5558.72415
S.R. Nakka, M.S. Hui, F.P. Chong, Y.C. Foo, R. Rajabalaya, Formulation and in vitro evaluation of ethosomes as vesicular carrier for enhanced topical delivery of isotretinoin. Int. J. Drug Deliv. 5, 28–34 (2013)
L.N. Shen, Y.T. Zhang, Q. Wang, L. Xu, N.P. Feng, Enhanced in vitro and in vivo skin deposition of apigenin delivered using ethosomes. Int. J. Pharm. 460(1–2), 280–288 (2014)
C. Fan, X. Li, Y. Zhou, Y. Zhao, S. Ma, W. Li, Y. Liu et al., Enhanced topical delivery of tetrandrine by ethosomes for treatment of artritis. BioMed Res. Int. 15, 1–13 (2013)
E.R. Bendas, M.I. Tadros, Enhanced transdermal delivery of salbutamol sulfate via ethosomes. Am. Assoc. Pharm. Sci. Pharm Sci. Tech. 8(4), E1–E8 (2007)
A.R. Rathore, H. Khambete, S. Jain, Preparation and characterization of repaglinide loaded ethosomal gel for the treatment of NIDDM. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Archiv. 4(2), 385–390 (2013)
R.G.S. Maheshwari, R.K. Tekade, P.A. Sharma, G. Darwhekar, A. Tyagi, R.P. Patel et al., Ethosomes and ultradeformable liposomes for transdermal delivery of clotrimazole: a comparative assessment. Saudi Pharm. J. 20, 161–170 (2012)
P.K. Mukherjee, A. While, Integrated approaches towards drug development from ayurveda and other indian system of medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 10325–35, 2006 (2006)
N.K. Jain, Controlled and Novel Drug Delivery. published by CBS publishers &Distributors, Firsrt edition reprint. 24: 101–105 (2009)
C.W. Yie, Novel Drug Delivery Systems. published by Informa Healthcare, Second Edition Revised and Expanded pp. 301–306
T. Surendra, P.K. Dilip, B. Lipika, N.K. Suresh, A review on phytosomes characterization, advancement & potential for transdermal application. J. Drug Deliv. Therapeut. 3(3), 147–152 (2013)
K. Čerpnjak, A. Zvonar, M. Gašperlin, F. Vrečer, Lipid-based systems as a promising approach for enhancing the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Acta Pharm. 63(4), 427–445 (2013)
K. Mohsin, A.A. Shahba, F.K. Alanazi, Lipid based self emulsifying formulations for poorly water soluble drugs-An excellent opportunity. Ind. J. Pharm. Edu. Res. 46(2), 88–96 (2012)
B.K. Nanjwade, D.J. Patel, R.A. Udhani, F.V. Manvi, Functions of lipids for enhancement of oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Sci. Pharm 79(4), 705–728 (2011)
D.M. Small, A classification of biologic lipids based upon their interaction in aqueous systems. J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc. 45(3), 108–119 (1968)
S. Kumar, S. Kumar Gupta, S.P. Kumar, Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) for oral delivery of lipid based formulations. Afr. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 4, 7–11 (2012)
P. Jaiswal, G. Aggarwal, BIOAVAILABILITY ENHANCDEMENT OF POORLY SOLUBLE DRUGS BY SMEDDS: A REVIEW. J Drug Deliv Ther. 3(1), 14 (2013)
M. Stuchlík, S. Zák, Lipid-based vehicle for oral drug delivery. Biomed. Pap Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc. Czech Repub. 145(2), 17–26 (2001)
H. Harde, M. Das, S. Jain, Solid lipid nanoparticles: An oral bioavailability enhancer vehicle. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 8(11), 1407–1424 (2011)
D.J. Hauss, Oral lipid-based formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59(7), 667–676 (2007)
T.M. Allen, P.R. Cullis, Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 65(1), 36–48 (2013)
S. Ganta, M. Talekar, A. Singh, T.P. Coleman, M.M. Amiji, Nanoemulsions in translational research: opportunities and challenges in targeted cancer therapy. AAPS PharmSciTech 15(3), 694–708 (2014)
A. Garud, D. Singh, N. Garud, Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN): method, characterization and applications. Int. Curr. Pharm. J. 1(11), 384–393 (2012)
P.P. Constantinides, K.M. Wasan, Lipid formulation strategies for enhancing intestinal transport and absorption of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrate drugs: In vitro/in vivo case studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 96(2), 235–248 (2007)
P. Baghel, A. Roy, S. Verma, T. Satapathy, S. Bahadur, Amelioration of lipophilic compounds in regards to bioavailability as self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS). Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 6(1), 1–11 (2020)
J. Ahmad, K. Kohli, S.R. Mir, S. Amin, Lipid based nanocarriers for oral delivery of cancer chemotherapeutics: an insight in the intestinal lymphatic transport. Drug Deliv Lett. 3(1), 38–46 (2013)
Materials, process, and manufacturing considerations for lipid-based hard-capsule formats. In: Oral Lipid-Based Formulations. (2020)
S. Xie, L. Zhu, Z. Dong, Y. Wang, X. Wang, W.Z. Zhou, Preparation and evaluation of ofloxacin-loaded palmitic acid solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 6, 547 (2011)
M. Shah, K. Chuttani, A.K. Mishra, K. Pathak, Oral solid compritol 888 ATO nanosuspension of simvastatin: optimization and biodistribution studies. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 37(5), 526–537 (2011)
D. Patel, S. Dasgupta, S. Dey, Y. Roja Ramani, S. Ray, B. Mazumder, Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC)-based gel for the topical delivery of aceclofenac: Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation. Sci Pharm. 80(3), 749–764 (2012)
S. Chakraborty, D. Shukla, P.R. Vuddanda, B. Mishra, S. Singh, Utilization of adsorption technique in the development of oral delivery system of lipid based nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B. 81(2), 563–569 (2010)
C.J.H. Porter, W.N. Charman, In vitro assessment of oral lipid based formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 50(1), S127–S147 (2001)
L. Wei, P. Sun, S. Nie, W. Pan, Preparation and evaluation of SEDDS and SMEDDS containing carvedilol. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 31(8), 785–794 (2005)
S. Prabhu, M. Ortega, C. Ma, Novel lipid-based formulations enhancing the in vitro dissolution and permeability characteristics of a poorly water-soluble model drug, piroxicam. Int. J. Pharm. 301(1–2), 209–216 (2005)
G.A. Edwards, C.J.H. Porter, S.M. Caliph, S. Khoo, W.N. Charman, Animal models for the study of intestinal lymphatic drug transport. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 50(1–2), 45–60 (2001)
M. Rawat, D. Singh, S. Saraf, S. Saraf, Lipid carriers: a versatile delivery vehicle for proteins and peptides. Yakugaku Zasshi 128(2), 269–280 (2008)
J. Almeida, E. Souto, Solid lipid nanoparticles as a drug delivery system for peptides and proteins. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59(6), 478–490 (2007)
W. Choi, J. Kim, S. Choi, J. Park, W.S. Ahn, C. Kim, Low toxicity of cationic lipid-based emulsion for gene transfer. Biomaterials 25(27), 5893–5903 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kesharwani, R., Jaiswal, P., Patel, D.K. et al. Lipid-Based Drug Delivery System (LBDDS): An Emerging Paradigm to Enhance Oral Bioavailability of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Biomedical Materials & Devices 1, 648–663 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44174-022-00041-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s44174-022-00041-0