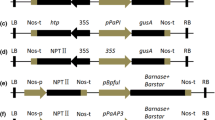
Regulatory elements in the promoter of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene 1 of pea (PSPAL1) in response to nonpathogenic attack were identified by in vivo footprinting analysis. The footprints determined AC-rich sequences, Box-I and Box-II, that were conserved at similar positions in the phenylpropanoid gene promoters from several plants. To reveal the functions of the AC-rich sequence in nonpathogen-responsiveness, we constructed Box-I-deletion PSPAL1 promoter (dB-1) with GUS reporter gene and transformed it into tobacco plant. The dB-1 had reduced basal expression and a complete loss of nonpathogen-responsiveness. These results indicate the essentiality of Box-I for PSPAL1 activation induced by nonpathogenic attack.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 27 October 1999/ Accepted in revised form 25 November 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
IMURA, Y., IGUCHI, S., TOYODA, K. et al. Importance of AC-rich Element on Pea Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase Gene 1 Promoter for Expression Induced by Nonpathogenic Attack. J Gen Plant Pathol 66, 123–127 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00012932
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00012932