Abstract
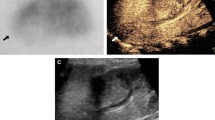
Objective: To compare noncontrast helical computed tomography (NCHCT) and intravenous urography (IVU) for diagnosis of urinary calculi in evaluation of renal colic. Materials and methods: A 4-month prospective paired study compared NCHCT and IVU in patients being evaluated for renal colic. Each patient was studied with NCHCT followed by an IVU. An IVU was regarded as positive if any of the following were identified: delayed filling, hydronephrosis, hydroureter, ureteral calculus, or extravasation of contrast. A NCHCT was regarded as positive if any of the following were identified: hydronephrosis, hydroureter, ureteral calculus, or perinephric or ureteral inflammatory change. The sensitivity (Se), specificity (Sp), positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were reported using the clinical outcome as the gold standard, by either observation of passage or retrieval of calculus. Bladder distention was noted on NCHCT relative to the level of the acetabulum. The charts were also reviewed retrospectively for the results of urinalysis. Results: One hundred sixty-eight patients had both examinations interpreted. Nineteen positive NCHCT and IVU studies were eliminated due to lack of observation or retrieval of calculus, leaving 149 studies for interpretation. NCHCT had Se 0.98, Sp 0.95, PPV 0.98, and NPV 0.95. IVU had Se 0.83, Sp 0.95, PPV 0.97, and NPV 0.67. In 13/168 (8 %) cases, and in 9/37 (24 %) negative cases, NCHCT offered an alternative diagnosis. Ureterovesical junction (UVJ) calculus was identified on 84 NCHCT scans, with near-even distribution between well, partially, and poorly distended bladder. No UVJ calculus was identified on IVU that was not present on NCHCT. Absence of hematuria was found in 26 % of patients with proven urolithiasis. Conclusion: NCHCT is superior to IVU for the evaluation of renal colic. NCHCT identifies significant pathology in 24 % of cases negative for ureteral obstruction/calculus. Bladder distention does not play an important role in detection of UVJ calculus. Hematuria is not universally present in patients with painful urolithiasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Longo, J., Akbar, S., Schaff, T. et al. A prospective comparative study of non-contrast helical computed tomography and intravenous urogram for the assessment of renal colic. Emergency Radiology 8, 285–292 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00011922
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00011922