Abstract
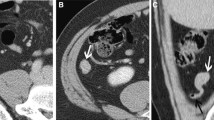
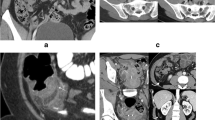
CT has become the primary imaging modality for evaluation of possible appendicitis. About 20 % of patients taken to surgery for appendicitis without CT have had a normal appendix removed. CT has demonstrated overall accuracy of between 93 % and 98 %. Alternative diagnoses are seen in 34–80 % of patients without appendicitis but who were suspected of having appendicitis. For evaluation of appendicitis different techniques have been successful, including the use of no contrast, use of oral and intravenous contrast, and use of rectally administered contrast. Scanning of the entire abdomen and pelvis and scanning of an area limited to the right lower quadrant are also options. Ultrasonography has been shown to have a role in pediatric patients. If ultrasonography is positive, CT is not necessary. If ultrasonography is negative, CT should follow.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rhea, J. CT evaluation of appendicitis and diverticulitis. Part I: Appendicitis. Emergency Radiology 7, 160–172 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00011821
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00011821