Abstract.
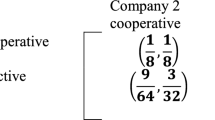
In economics, the n-person oligopoly game and the n-person IPD game are often considered close in spirit. Our analytical framework shows that this is not the case owing to the path dependence of the pay-off matrix of the oligopoly game. By simulating the evolution of a three-person oligopoly game with genetic algorithms, we explore the significance of the path dependence property to the rich ecology of oligopoly. The emergent behavior of oligopolists in the simulations indicates how the path dependence nature may shed light on the phenotypes and genotypes coming into existence. The features shown in this research can be further exploited in more practical contexts so that nontrivial policy issues in industrial economics can be seriously tackled.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 12 February 1999 / Revised 9 December 1999 / Accepted 3 April 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, SH., Ni, CC. Simulating the Ecology of Oligopolistic Competition with Genetic Algorithms. Knowledge and Information Systems 2, 285–309 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00011644
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00011644