Summary.
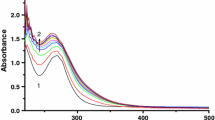
Complex formation of [Pt(H2O)4]2+ and [PtCl4]2− with thioglycolic acid has been studied as a function of temperature (288.2–308.2 K) using spectrophotometry in 1.00 M aqueous perchloric acid; the statistically corrected corresponding second-order rate constants are k 1 298=5.25×10−2 M −1ċs−1 and 0.624 M −1ċs−1, respectively. The temperature dependence of the rate constants gives the following activation parameters: ΔH 1 ‡=34±2 kJċmol−1, ΔS 1 ‡=−142±8 Jċ K−1ċmol−1 for [Pt(H2O)4]2+, ΔH 1 ‡=31±2 kJċmol−1, ΔS 1 ‡=−133± 6 JċK−1ċmol−1 for [PtCl4]2−. The negative values for the entropies of activation are consistent with an associative mode of activation. A LFER diagram observed for the complex formation of [Pt(H2O)4]2+ with sulfur containing ligands support an A mechanism. The reactivity of sulfur-bonding ligands towards [Pt(H2O]4]2+ follows the order H2O <Me2SO <SHCH2COOH <SCN− <S(CH2)4O<Et2S< S(CH2)4S<Me2S<SC(NH2)2 (1:3:7.4×103:4.8×104:5.2×104:6.8×104:8.8×104:1.3×105:5×105). A trigonal bipyramidal transition state stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the entering thioglycolic acid and the leaving aqua or chloro ligand is suggested..
Zusammenfassung.
Die Komplexbildungsreaktionen von [Pt(H2O)4]2+ und [PtCl4]2− mit Thioglycolsäure wurden in 1.00 M Perchlorsäure spektrophotometrisch als Funktion der Temperatur (288.2–308.2 K) untersucht; die entsprechenden statistisch korrigierten Geschwindigkeitskonstanten zweiter Ordnung wurden zu k 1 298=5.25×10−2 und 0.624 M −1ċs−1 ermittelt. Die Temperaturabhängigkeit der Geschwindigkeitskonstanten liefert die folgenden Aktivierungsparameter: ΔH 1 ‡ 34±2 kJċmol−1, ΔS 1 ‡=−142±8 Jċ mol−1ċK−1 für [Pt(H2O)4]2+, ΔH 1 ‡=31±2 kJċmol−1, ΔS 1‡=−133±6 Jċmol−1K−1 für [PtCl4]2−. Die negativen Werte für die Aktivierungsentropien stimmen mit einem assoziativen Aktivierungsverlauf überein. Ein LFER-Diagramm, das für die Komplexbildung zwischen [Pt(H2O)4]2+ und schwefelhaltigen Liganden erstellt wurde, legt das Auftreten eines Mechanismus des Typs A nahe. Die Reaktivität von über Schwefel bindenden Liganden gegenüber [Pt(H2O)4]2+ folgt der Reihe H2O<Me2SO<SHCH2COOH<SCN2− <S(CH2)4O<Et2S<S(CH2)4S<Me2S<SC(NH2)2 (1:3:7.4×103:4.8×104:5.2×104:6.8× 104:8.8×104:1.3×105:5×105). Es wird ein trigonal-bipyramidaler Übergangszustand vorgeschlagen, der durch Wasserstoffbrückenbindungen zwischen der eintretenden Thioglycolsäure und dem austretenden Aqua- oder Chloroliganden stabilisiert wird..
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bugaričić, Ž., Djordjević, B. Kinetics and Mechanism of the Reaction of Platinum(II) Complexes with Thioglycolic Acid. Monatshefte fuer Chemie 129, 1267–1274 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00010138
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00010138