Abstract
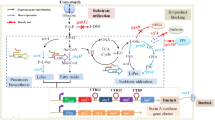
Production of Rifamycin with Amycolatopsis mediterranei (MTCC14) was studied using carbon and locally available cheaper nitrogen sources. A. Mediterranei gave initial yield of 650 mg/l with standard fermentation medium. This was improved to 1400 mg/l by using various Carbon, Nitrogen sources and optimizing various cultural conditions. Glucose, Ammonium sulphate and combination of soya bean and pea nut meals were found to induce more Rifamycin production in 7 days with a pH of 7.2, temperature 28 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received January 13, 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Venkateswarlu, G., Murali Krishna, P. & Venkateswar Rao, L. Production of Rifamycin using Amycolatopsis mediterranei (MTCC14). Bioprocess Engineering 20, 27–30 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009033
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009033