Abstract
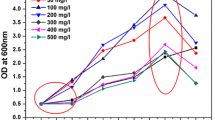
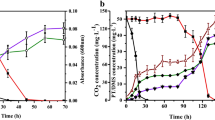
Pseudomonas putida (MTCC 1194) has been used to degrade phenol in water in the concentration range 100–1000 ppm. The inhibition effects of phenol as substrate have become predominant above the concentration of 500 ppm (5.31 mmoles/dm3). The optimum temperature and initial pH required for maximum phenol biodegradation were 30 °C and 7.00 respectively. From the degradation data the activation energy (E a ) was found to be equal to 13.8 kcal/g mole substrate reacted. The most suitable inoculum age and volume for highest phenol degradation were 12 hrs and 7% v/v respectively. Surfactants had negligible effect on phenol biodegradation process for this microorganism. Monod model has been used to interpret the free cell data on phenol biodegradation. The kinetic parameters have been estimated upto initial concentration of 5.31 mmoles/dm3. μ max and K S gradually increased with higher concentration of phenol. However, beyond the phenol concentration of 5.31 mmoles/dm3, the inhibition became prominant. The μ max has been to be a strong function of initial phenol concentration. The simulated and the experimental phenol degradation profiles have good correspondence with each other.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 24 June 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bandyopadhyay, K., Das, D. & Maiti, B. Kinetics of phenol degradation using Pseudomonas putida MTCC 1194. Bioprocess Engineering 18, 373–377 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00008996
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00008996