Abstract
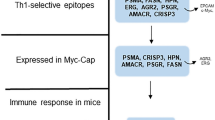
The TRAMP-C1 (C1) and TRAMP-C2 (C2) cell lines were derived from a prostate tumor that arose in a mouse from the transgenic adenocarcinoma mouse prostate (TRAMP) model. However, their similarity to primary prostate tumors and therefore their usefulness in immunotherapy studies has not been clearly defined. We showed using RT-PCR that these cell lines exhibited a variety of prostate-specific genes expressed by human prostate tumors that may be used as tumor-associated antigens for immunotherapy. Interestingly, several of these genes are also expressed in cell lines that are not prostatic in origin. The prostate cell lines were also shown to grow in an androgen-independent manner, to be capable of expressing MHC class I and to be susceptible to specific lysis by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Therefore, these cell lines will provide us with the ability to evaluate immune responses to and tolerance of prostate-specific protein peptides in an animal model.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grossmann, M., Wood, M. & Celis, E. Expression, specificity and immunotherapy potential of prostate-associated genes in murine cell lines. World J Urol 19, 365–370 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00007104
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00007104