Abstract
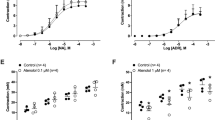
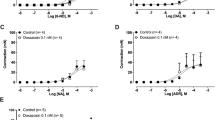
Changes in functional responsiveness to α1-adrenoceptor activation with noradrenaline and in [3H]prazosin binding in the epididymal portion of vas deferens from normotensive Wistar Kyoto (WKY) and spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) were investigated. The operational model fitting and the nested hyperbolic method were used to analyze the effects of irreversible receptor alkylation by phenoxybenzamine (0.1 μM) on the α1-adrenoceptor mediated contractile responses to noradrenaline of vasa deferentia from SHR and WKY rats. Saturation isotherms for [3H]prazosin revealed a significant increase (P < 0.05) in the Bmax in SHR vas deferens (145 ± 19 fmol/mg protein) compared with vas deferens from normotensive controls (75 ± 12 fmol/mg protein) without changes in the KD. No differences in the proportion of high and low affinity binding sites for WB-4101 and 5-methylurapidil were observed. The maximum contractile response, α, (P < 0.001) and the pEC50 (P < 0.05) values for noradrenaline were greater for SHR than for WKY rat tissues. The apparent affinity (pKA) determined by the nested hyperbolic method and by the operational model of agonism was found to be similar in the two strains. In agreement with relative pEC50, the efficacy (τ) value for SHR was greater than for WKY rats. However, the difference in the τ estimates did not reach statistical significance. In summary, in the epididymal portion of SHR vas deferens, the increased maximum contractile response to noradrenaline is due to an increase of Em. Taken together, the τ values and the results from binding experiments lead to the assumption that the transducer constant K E must be greater in SHR than in WKY rats, suggesting a deterioration in the transduction of the stimulus provided by the agonist in hypertensive animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 November 1996 / Accepted: 27 March 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vivas, N., Giraldo, J., Tabernero, A. et al. Use of the operational model of agonism and [3H]prazosin binding to assess altered responsiveness of α1-adrenoceptors in the vas deferens of spontaneously hypertensive rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 356, 383–391 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005066
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00005066