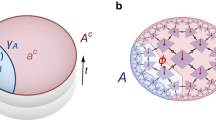
Abstract
The AdS/CFT correspondence realises the holographic principle where information in the bulk of a space is encoded at its border. We are yet a long way from a full mathematical construction of AdS/CFT, but toy models in the form of holographic quantum error correcting codes (HQECC) have replicated some interesting features of the correspondence. In this work we construct new HQECCs built from random stabilizer tensors that describe a duality between models encompassing local Hamiltonians whilst exactly obeying the Ryu-Takayanagi entropy formula for all boundary regions. We also obtain complementary recovery of local bulk operators for any boundary bipartition. Existing HQECCs have been shown to exhibit these properties individually, whereas our mathematically rigorous toy models capture these features of AdS/CFT simultaneously, advancing further towards a complete construction of holographic duality.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
G. ’t Hooft, Dimensional reduction in quantum gravity, Conf. Proc. C 930308 (1993) 284 [gr-qc/9310026] [INSPIRE].
L. Susskind, The world as a hologram, J. Math. Phys. 36 (1995) 6377 [hep-th/9409089] [INSPIRE].
A. Almheiri, X. Dong and D. Harlow, Bulk locality and quantum error correction in AdS/CFT, JHEP 04 (2015) 163 [arXiv:1411.7041] [INSPIRE].
F. Pastawski, B. Yoshida, D. Harlow and J. Preskill, Holographic quantum error-correcting codes: toy models for the bulk/boundary correspondence, JHEP 06 (2015) 149 [arXiv:1503.06237] [INSPIRE].
T. Kohler and T. Cubitt, Toy models of holographic duality between local Hamiltonians, JHEP 08 (2019) 017 [arXiv:1810.08992] [INSPIRE].
P. Hayden, S. Nezami, X.-L. Qi, N. Thomas, M. Walter and Z. Yang, Holographic duality from random tensor networks, JHEP 11 (2016) 009 [arXiv:1601.01694] [INSPIRE].
A. Bhattacharyya, Z.-S. Gao, L.-Y. Hung and S.-N. Liu, Exploring the tensor networks/AdS correspondence, JHEP 08 (2016) 086 [arXiv:1606.00621] [INSPIRE].
T.J. Osborne and D.E. Stiegemann, Dynamics for holographic codes, JHEP 04 (2020) 154 [arXiv:1706.08823] [INSPIRE].
B. Swingle, Constructing holographic spacetimes using entanglement renormalization, arXiv:1209.3304 [INSPIRE].
Z. Yang, P. Hayden and X.-L. Qi, Bidirectional holographic codes and sub-AdS locality, JHEP 01 (2016) 175 [arXiv:1510.03784] [INSPIRE].
B. Swingle, Entanglement renormalization and holography, Phys. Rev. D 86 (2012) 065007 [arXiv:0905.1317] [INSPIRE].
T. Kohler, S. Piddock, J. Bausch and T. Cubitt, Translationally invariant universal quantum hamiltonians in 1D, Annales Henri Poincaré 23 (2022) 223 [arXiv:2003.13753] [INSPIRE].
T. Faulkner, A. Lewkowycz and J. Maldacena, Quantum corrections to holographic entanglement entropy, JHEP 11 (2013) 074 [arXiv:1307.2892] [INSPIRE].
A.C. Wall, Maximin surfaces, and the strong subadditivity of the covariant holographic entanglement entropy, Class. Quant. Grav. 31 (2014) 225007 [arXiv:1211.3494] [INSPIRE].
T.S. Cubitt, A. Montanaro and S. Piddock, Universal quantum hamiltonians, Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 115 (2018) 9497.
R. Oliveira and B. Terhal, The complexity of quantum spin systems on a two-dimensional square lattice, Quant. Informat. Comput. 8 (2008) 900 [quant-ph/0504050].
W. Helwig and W. Cui, Absolutely maximally entangled states: existence and applications, arXiv:1306.2536.
S. Rubinstein, On the existence and uniqueness of invariant measures on locally compact groups, (2004).
C. Dankert, R. Cleve, J. Emerson and E. Livine, Exact and approximate unitary 2-designs and their application to fidelity estimation, Phys. Rev. A 80 (2009) 012304.
W. Dür, M. Hein, J.I. Cirac and H.-J. Briegel, Standard forms of noisy quantum operations via depolarization, Phys. Rev. A 72 (2005) 052326.
H. Chau, Unconditionally secure key distribution in higher dimensions by depolarization, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 51 (2005) 1451 [quant-ph/0405016].
J. Tits, Groupes et géométries de Coxeter (in French), unpublished manuscript, (1961).
M.W. Davis, The geometry and topology of Coxeter groups, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, U.S.A. (2012).
E.B. Vinberg, Discrete groups generated by reflections in Lobačevskĭ space, Math. USSR-Sbornik 1 (1967) 429.
P. Hayden, D.W. Leung and A. Winter, Aspects of generic entanglement, Commun. Math. Phys. 265 (2006) 95.
M. Ledoux, The concentration of measure phenomenon, volume 89 of Mathematical surveys and monographs, American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, U.S.A. (2001).
R.A. Low, Large deviation bounds for k-designs, Proc. Roy. Soc. A 465 (2009) 3289.
A.W. Harrow, The church of the symmetric subspace, arXiv:1308.6595.
D. Fattal, T. Cubitt, Y. Yamamoto, S. Bravyi and I. Chuang, Entanglement in the stabilizer formalism, quant-ph/0406168.
M. Fréchet, Généralisation du théorème des probabilités totales (in French), Fund. Math. 25 (1935) 379.
M. Fréchet, Sur les tableaux de corrélation dont les marges sont données (in French), Ann. Univ. Lyon A 9 (1951) 53.
S. Nezami and M. Walter, Multipartite entanglement in stabilizer tensor networks, Phys. Rev. Lett. 125 (2020) 241602 [arXiv:1608.02595] [INSPIRE].
S.W. Hawking and D.N. Page, Thermodynamics of black holes in anti-de Sitter space, Commun. Math. Phys. 87 (1983) 577 [INSPIRE].
I. Heemskerk, J. Penedones, J. Polchinski and J. Sully, Holography from conformal field theory, JHEP 10 (2009) 079 [arXiv:0907.0151] [INSPIRE].
S. El-Showk and K. Papadodimas, Emergent spacetime and holographic CFTs, JHEP 10 (2012) 106 [arXiv:1101.4163] [INSPIRE].
S. Piddock and A. Montanaro, Universal qudit Hamiltonians, arXiv:1802.07130.
X. Dong, The gravity dual of Rényi entropy, Nature Commun. 7 (2016) 12472 [arXiv:1601.06788] [INSPIRE].
X. Dong, D. Harlow and D. Marolf, Flat entanglement spectra in fixed-area states of quantum gravity, JHEP 10 (2019) 240 [arXiv:1811.05382] [INSPIRE].
M. Han and S. Huang, Discrete gravity on random tensor network and holographic Rényi entropy, JHEP 11 (2017) 148 [arXiv:1705.01964] [INSPIRE].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
ArXiv ePrint: 2105.12067
Rights and permissions
Open Access . This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0), which permits any use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Apel, H., Kohler, T. & Cubitt, T. Holographic duality between local Hamiltonians from random tensor networks. J. High Energ. Phys. 2022, 52 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP03(2022)052
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP03(2022)052