Summary
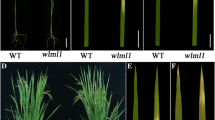
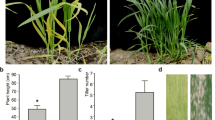
Richer genetic diversities in leaf color mutations were detected in temperature-sensitive male sterile (TSGMS) line 2177S after gamma-irradiation treatment. According to temperature response, it could be classified into two types. In temperature-insensitive type, some mutations expressed during the whole growth period, some only at specific developmental stage. Further observation indicated that some mutants could be recovered to normal green, some only partly greenish. However, temperature-sensitive mutants only expressed under specific higher or lower temperatures. Biological effect analysis revealed that expression of some mutations would induce rice plant lethal. It was also observed that some exotic substances could mediate leaf color phenotype effectively. Genetic research showed that a single recessive nuclear gene controlled the leaf color phenotype. Allele test demonstrated there were richer genetic diversities in loci controlling these mutations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carpenter CD, Kerps JA, Simon AE, 1988. Gene’s expression encoding glycine-rich Aradopsis thaliana with RNA-binding motifs are influenced by cold treatment and endogenous circadian rhythm. Plant Physiol, 104:1015–1025
Constatins. 1984. Analysis of chlorophyll-deficient mutant in wheat. Acta agri Nul Sinica, 1:5–6
Dale PJ et al., Field performance of transgenic potato plants compared with controls regenerated from tuber discos and shooting cuttings, Theor Appl Genet, 1992, 84: 585–591
Dunn MA, Brown K, Lightowlers R, Huges MA, 1996. A low-temperature-responsive gene from barley encodes protein with single-stranded nucletic acid-binding activity which is phosporylated in vitro. Plant Mol Bio, 30:947–959
Hairui Cui et al., Insect resistance and agronomic performance of R3 transgenic lines in japonica rice Xiushui 11 transformed with crylA (b) gene, Abstracts of 18th international genetics conference, Beijing, China, 1998, 8P104
Hughes MA, Dunn MA, Pearce RS, White AJ, Zhang L, 1992. An abscisic-acid-responsive, low temperature barley gene has homology with a maize phospolipid transfer protein. Plant Cell Env, 15: 861–865
Hughes MA, Pearce RS. 1988. Low temperature treatment of barley plants causes altered gene expression in shoot meresems. J Exp Bot, 39: 1461–1467
Jiang SY et al. 1993. Progress of sterile lines of two-line hybrid rice, J. Beijing Agri Uni, 6–10
Meyer P., Understanding and controlling transgene expression, TibTech, 1995, 13:332–337
Micke, A., Mutation breeding review: Induced mutations for crop breeding, 1990, (7):10–13
Shu QY, Xia YW, Liu GF. 1996. Marker-assisted elimination of contamination in two-line hybrid rice production and multiplication. J Zhejiang Uni, 22(1):56–60
Shu QY, Xia YW, Liu GF. 1995. Using colored-leaf mutants of thermo-sensitive genie male sterile line. IRRN, 20(3): 7
Shu QY, Liu GF, Xia YW. 1996. Temperature-sensitive leaf color mutation in rice. Acta agri Nul Sinica, 10(1): 6–10
Sing RB, Limani SS. 1990. Recent progress in the technology and development of hybrid rice in Asia. Int Rice Committee Newsl, 39:133
Schuh W et al., The phenotypic characterization of R2 generation transgenic rice plants under field conditions, Plant Sci, 1993, 89:69–79
Wu DX, Xia YW, Shu QY 1995. Study on plants chlorophyll-deficient mutant and its application. Chinese Agri Sci Bulletin, 11(4): 36–39
Wu DX, Xia YW, Shu QY, GF Liu. 1997. Induction and identification of temperature-sensitive albino genes in indica rice (Oryza sativa L). Cereal Research Communications, 25(4): 905–910
Wu DX, Shu QY Xia YW. 1997, Measurement of genome changes of greenale albino mutation line c.v. W25. Acta agri Nul Sinica, 11(2): 89–92
Wu DX, Shu QY Xia YW. 1997, Carbohydrate and protein metabolism in seedling leaves of a greenalbe albino mutant line c.v. W25 of rice (Oraza sativa L). Acta Phytophysio Sinica, 23(3): 209–212
Zheng XP et al. 1998. Source of hybrid seed for Long-te-fu A and its analysis. Hybrid rice, 13(1): 8–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, D., Shu, Q. & Xia, Y. Irradiation-Induced Genetic Diversity of Leaf Color Mutation in Rice (Oryza sativa L). CEREAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 28, 255–262 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03543602
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03543602