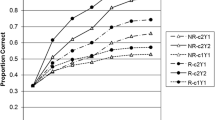
Abstract
We demonstrate that a wide variety of recently reported “rule-described” and “prototype-described” phenomena in perceptual classification, which have led to the development of a number of multiplesystem models, can be given an alternative interpretation in terms of a single-system exemplar-similarity model. The phenomena include various rule- and prototype-described patterns of generalization, dissociations between categorization and similarity judgments, and dissociations between categorization and old-new recognition. The alternative exemplar-based interpretation relies on the idea that similarity is not an invariant relation but a context-dependent one. Similarity relations among exemplars change systematically because of selective attention to dimensions and because of changes in the level of sensitivity relating judged similarity to distance in psychological space. Adaptive learning principles may help explain the systematic influence of the selective attention process and of modulation in sensitivity settings on judged similarity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J. R. (1991). The adaptive nature of human categorization. Psychological Review, 98, 409–429.
Anderson, J. R., & Lebiere, C. (1998). The atomic components of thought. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Ashby, F. G., Alfonso-Reese, L.A., Turken, A. U., & Waldron, E. M. (1998). A neuropsychological theory of multiple systems in category learning. Psychological Review, 105, 442–481.
Ashby, F. G., & Maddox, W. T. (1993). Relations between prototype, exemplar, and decision bound models of categorization. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 37, 372–400.
Ashby, F. G., & Townsend, J. T. (1986). Varieties of perceptual independence. Psychological Review, 93, 154–179.
Barsalou, L. W. (1985). Ideals, central tendency, and frequency of instantiation as determinants of graded structure in categories. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 11, 629–654.
Brooks, L. R. (1978). Nonanalytic concept formation and memory for instances. In E. Rosch & B. B. Lloyd (Eds.), Cognition and categorization (pp. 169–211). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Busemeyer, J. R., Dewey, G. I., & Medin, D. L. (1984). Evaluation of exemplar-based generalization and the abstraction of categorical information. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 10, 638–648.
Carey, S. (1985). Conceptual change in childhood. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Carroll, J.D., & Wish, M. (1974). Models and methods for three-way multidimensional scaling. In D. H. Krantz, R. C. Atkinson, R. D. Luce, & P. Suppes (Eds.), Contemporary developments in mathematical psychology (Vol. 2, pp. 57–105). San Francisco: W. H. Freeman.
Erickson, M.A., & Kruschke, J. K. (1998). Rules and exemplars in category learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 127, 107–140.
Estes, W. K. (1986). Array models for category learning. Cognitive Psychology, 18, 500–549.
Estes, W. K. (1994). Classification and cognition. New York: Oxford University Press.
Garner, W. R. (1974). The processing of information and structure. New York: Wiley.
Gelman, S. A., & Markman, E. M. (1986). Categories and induction in young children. Cognition, 23, 183–209.
Gentner, D. (1983). Structure-mapping: A theoretical framework for analogy. Cognitive Science, 7, 155–170.
Getty, D. J., Swets, I. A., Swets, J. B., & Green, D. M. (1979). On the prediction of confusion matrices from similarity judgments. Perception & Psychophysics, 26, 1–19.
Gibson, J. J., & Gibson, E. J. (1955). Perceptual learning: Differentiation or enrichment? Psychological Review, 62, 32–41.
Goldstone, R. L. (1994a). The role of similarity in categorization: Providing a groundwork. Cognition, 52, 125–157.
Goldstone, R. L. (1994b ). Similarity, interactive interaction, and mapping. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 20, 3–28.
Grunwald, P. (2000). Model selection based on minimum description length. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 44, 133–152.
Heit, E. (1994). Models of the effects of prior knowledge on category learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 20, 1264–1282.
Heit, E. (1997). Knowledge and concept learning. In K. Lamberts & D. Shanks (Eds.), Knowledge, concepts, and categories (pp. 7–41). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Hintzman, D. L. (1986). “Schema abstraction” in a multiple-trace memory model. Psychological Review, 93, 411–428.
Hintzman, D. L. (1988). Judgments of frequency and recognition memory in a multiple-trace memory model. Psychological Review, 95, 528–551.
Homa, D. (1984). On the nature of categories. Psychology of Learning & Motivation, 18, 49–94.
Keil, F. C. (1989). Concepts, kinds, and cognitive development. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Knowlton, B. J., Mangels, J. A., & Squire, L. R. (1996). A neostriata! habit learning system in humans. Science, 273, 1399–1402.
Knowlton, B. I., & Squire, L. R. (1993). The learning of categories: Parallel brain systems for item memory and category knowledge. Science, 262, 1747–1749.
Kruschke, I. K. (1992). ALCOVE: An exemplar-based connectionist model of category learning. Psychological Review, 99, 22–44.
Lamberts, K. (1994). Flexible tuning of similarity in exemplar-based categorization. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 20, 1003–1021.
Levine, M. (1975). A cognitive theory of learning: Research on hypothesis testing. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Lewandowsky, S. (1995). Base-rate neglect in ALCOVE: A critical reevaluation. Psychological Review, 102, 185–191.
Logan, G. D. (1988). Toward an instance theory of automatization. Psychological Review, 95, 492–527.
Lovett, M. (1998). Choice. In I. R. Anderson & C. Lebiere (Eds.), The atomic components of thought (pp. 255–296). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Luce, R. D. (1963). Detection and recognition. In R. D. Luce, R. R. Bush, & E. Galanter (Eds.), Handbook of mathematical psychology (pp. 103–189). New York: Wiley.
Maddox, W. T., & Ashby, F. G. (1993). Comparing decision bound and exemplar models of classification. Perception & Psychophysics, 53, 49–70.
McKinley, S. C., & Nosofsky, R. M. (1995). Investigations of exemplar and decision-bound models in large-size, ill-defined category structures. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception & Performance, 21, 128–148.
McKinley, S. C., & Nosofsky, R. M. (1996). Selective attention.and the formation of linear decision boundaries. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception & Performance, 22, 294–317.
Medin, D. L., Goldstone, R. L., & Gentner, D. (1990). Similarity involving attributes and relations: Judgments of similarity and differences are not inverses. Psychological Science, I, 64–69.
Medin, D. L., Goldstone, R. L., & Gentner, D. (1993). Respects for similarity. Psychological Review, 100, 254–278.
Medin, D. L., & Schaffer, M. M. (1978). Context theory of classification learning. Psychological Review, 5, 207–238.
Medin, D. L., & Smith, E. E. (1981). Strategies and classification learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Learning & Memory, 7, 241–253.
Murphy, G. L., & Medin, D. L. (1985). The role of theories in conceptual coherence. Psychological Review, 92, 289–316.
Myung, I. J. (2000). The importance of complexity in model selection. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 44, 190–204.
Myung, I. J., & Pitt, M. A. (1997). Applying Occam's razor in modeling cognition: A Bayesian approach. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 4, 79–95.
Nosofsky, R. M. (1984). Choice, similarity, and the context theory of classification. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 10, 104–114.
Nosofsky, R. M. (1985). Overall similarity and the identification of separable-dimension stimuli: A choice model analysis. Perception & Psychophysics, 38, 415–432.
Nosofsky, R. M. (1986). Attention, similarity, and the identification — categorization relationship. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, ll5, 39–57.
Nosofsky, R. M. (1987). Attention and learning processes in the identification and categorization of integral stimuli. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 13, 87–109.
Nosofsky, R. M. (1988). Exemplar-based accounts of relations between classification, recognition, and typicality. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 14, 700–708.
Nosofsky, R. M. (1991a). Tests of an exemplar model for relating perceptual classification and recognition memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception & Performance, 17, 3–27.
Nosofsky, R. M. (1991b). Typicality in logically defined categories: Exemplar-similarity versus rule instantiation. Memory & Cognition, 19, 131–150.
Nosofsky, R. M. (1992). Similarity scaling and cognitive process models. Annual Review of Psychology, 43, 25–53.
Nosofsky, R. M. (1998a). Optimal performance and exemplar models of classification. In M. Oaksford & N. Chater (Eds.), Rational models of cognition (pp. 218–247). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Nosofsky, R. M. (1998b). Selective attention and the formation of linear decision boundaries: Reply to Maddox and Ashby (1998). Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception & Peiformance, 24, 322–339.
Nosofsky, R. M., Clark, S. E., & Shin, H. J. (1989). Rules and exemplars in categorization, identification, and recognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 15, 282–304.
Nosofsky, R. M., Gluck, M. A., Palmeri, T. J., McKinley, S. C., & Glauthier, P. (1994). Comparing models of rule-based classification learning: A replication and extension of Shepard, Hovland, and Jenkins (1961). Memory & Cognition, 22, 352–369.
Nosofsky, R. M., Kruschke, J. K., & McKinley, S.C. (1992). Combining exemplar-based category representations and connectionist learning rules. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 18, 211–233.
Nosofsky, R. M., & Palmeri, T. J. (1996). Learning to classify integraldimension stimuli. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 3, 222–226.
Nosofsky, R. M., & Palmeri, T. J. (1997). An exemplar-based randomwalk model of speeded classification. Psychological Review, 104, 266–300.
Nosofsky, R. M., Palmeri, T. J., & McKinley, S.C. (1994). Rule-plusexception model of classification learning. Psychological Review, 101, 53–79.
Nosofsky, R. M., & Zaki, S. R. (1998). Dissociations between categorization and recognition in amnesic and normal individuals: An exemplar-based interpretation. Psychological Science, 9, 247–255.
Palmeri, T. J. (1997). Exemplar similarity and the development of automaticity. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 23, 324–354.
Palmeri, T. J., & Nosofsky, R. M. (1995). Recognition memory for exceptions to the category rule. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 21, 548–568.
Pavel, M., Gluck, M. A., & Henkle, V. (1988). Generalization by humans and multi-layer networks. In Proceedings of the Tenth Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Posner, M.I., & Keele, S. W. (1968). On the genesis of abstract ideas. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 11, 353–363.
Reed, S. K. (1972). Pattern recognition and categorization. Cognitive Psychology, 3, 382–407.
Rips, L. J. (1989). Similarity, typicality, and categorization. In S. Vosniadou & A. Ortony (Eds.), Similarity and analogical reasoning (pp. 21–59). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Rips, L. J., & Collins, A. (1993). Categories and resemblance. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 122, 468–486.
Ross, B. H. (1987). This is like that: The use of earlier problems and the separation of similarity effects. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 13, 629–639.
Shepard, R.N. (1958). Stimulus and response generalization: Tests of a model relating generalization to distance in psychological space. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 55, 509–523.
Shepard, R.N. (1964). Attention and the metric structure of the stimulus space. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 1, 54–87.
Shepard, R. N. (1986). Discrimination and generalization in identification and classification: Comment on Nosofsky. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 115, 58–61.
Shepard, R.N. (1987). Toward a universal law of generalization for psychological science. Science, 237, 1317–1323.
Shepard, R.N., & Chang, J. J. (1963). Stimulus generalization in the learning of classifications. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 65, 94–102.
Shepard, R.N., Hovland, C. I., & Jenkins, H. M. (1961). Learning and memorization of classifications. Psychological Monographs, 15 (13, Whole No. 517).
Shin, H. J., & Nosofsky, R. M. (1992). Similarity scaling studies of dot pattern classification and recognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 121, 278–304.
Sloman, S. A. (1996). The empirical case for two systems of reasoning. Psychological Bulletin, 119, 3–22.
Smith, E. E., & Sloman, S. A. (1994). Similarity- versus rule-based categorization. Memory & Cognition, 22, 377–386.
Smith, J.D., & Minda, J.P. (1998). Prototypes in the mist: The early epochs of category learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 24, 1411–1436.
Smith, J.D., Murray, M. I., & Minda, J.P. (1997). Straight talk about linear separability. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, & Cognition, 23, 659–680.
Smith, L. B. (1989). A model of perceptual classification in children and adults. Psychological Review, 96, 125–144.
Squire, L. R., & Knowlton, B. J. (1995). Learning about categories in the absence of memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 92, 12470–12474.
Trabasso, T., & Bower, G. H. (1968). Attention in learning: Theory and research. New York: Wiley.
Vandierendonck, A. (1995). A parallel rule activation and rule synthesis model for generalization in category learning. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 2, 442–459.
Wickens, T. D. (1982). Models for behavior: Stochastic processes in psychology. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Grant ROI MH48494-09 from the National Institute of Mental Health. We thank F. Gregory Ashby, John Wixted, and two anonymous reviewers for their helpful criticisms of earlier versions of this article. We are also indebted to Michael Erickson for providing us with the original program code used to conduct Experiment I from Erickson and Kruschke ( 1998), and to J. David Smith for providing us with the individual subject data from J. D. Smith, Murray, and Minda (1997).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nosofsky, R.M., Johansen, M.K. Exemplar-based accounts of “multiple-system” phenomena in perceptual categorization. Psychon Bull Rev 7, 375–402 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03543066
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03543066