Abstract
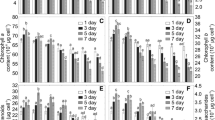
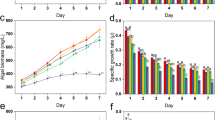
The toxicity of mercury ion, on Chlorella vulgaris, is largely influenced by amino acids. Five amino acids, namely alanine, asparagine, glutamic acid, cysteine and histidine, were added separately to the medium containing static dose of mercury. Survival (%) of the alga was reduced with the increasing concentrations of mercury. Of these five amino acids, cysteine was found to be the most effective while alanine and glutamic acid were the least effective on reducing the toxic effect of mercury on the alga measured in terms of growth, chlorophyll and protein content.
The order of detoxification was Alanine < Glutamate < Asparargine < Histidine < Cysteine. Amino acids form ligands with Hg2+ making it less toxic to the alga and produce an additional source of energy for growth and development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnon, D. I. (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplast: Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. Lancaster 24, 1–15.
Babich, M., Stotzky, G. (1983) Influence of chemical speciation on the toxicity of heavy metals to the microbiota. In: Nriagu, J. (ed.) Advances in Environmental Science and Technology, Vol. 13. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 1–16.
Baccini, P. (1983) Vom Stoffhaushalt aquatischer Ökosysteme. Zur Frage nach der chemischer Binding. Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 316, 575–581.
Borgmann, V., Ralph, K. M. (1983) Complexation and toxicity of copper and the free metal bioassay technique. Water Res. 17, 1697–1703.
Cowan, C. E., Jenne, E. A., Kinnison, R. R. (1984) A methodology for determining the toxic chemical species of copper in toxicity experiments and natural waters. In: Hemphill, D. D. (ed.) Trace Substances in Environmental Health, XVIII. University of Missori, Columbia, pp. 78–79.
De Filippis, L. F., Pallaghy, C. K. (1976) Effect of sublethal concentration of Hg2+ on Chlorella. I. Growth characteristics and uptake of metals. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 78, 197–207.
Farrell, R. E., James, J. G., Huang, P. M. (1990) Biotoxicity of mercury as influenced by Mercury (II) speciation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56, 3006–3016.
Fogg, G. E., Westlake, D. F. (1955) The importance of extracellular products of algae in fresh water. Verh. Int. Ler. Limnol. 12, 219–232.
Gerloff, G. C., Fitzgerald, G. P., Skoog, F. (1950) The isolation, purification and culture of blue-green algae. Amer. J. Bot. 37, 216–218.
Hongve, D., Skogheim, O. K., Hindar, A., Abrahamsen, H. (1980) Effect of heavy metal in combination with NTA, humic acid and suspended sediment on natural phytoplankton photosynthesis. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 25, 594–600.
Jones, G. E. (1970) Metal organic complexes formed by marine bacteria. In: Hood, D. W. (ed.) Organic Matter in Natural Waters. Inst. Mar. Sci. Alaska Occas. Pub. 1, 301–310.
Kosakowska, A., Leonard, F., Lewandowska, J. (1988) Effect of amino acids on the toxicity of heavy metals to phytoplankton. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 40, 532–538.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J. (1951) Protein measurement with Folin-Phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Mohanty, R. C., Mohanty, L., Mohapatra, P. K. (1993) Effect of glucose, glutamate and 2-oxoglutarate on mercury toxicity to Chlorella vulgaris. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 51, 130–137.
Mohapatra, P. K., Mohanty, R. C. (1992) Differential effect of dimethoate toxicity to Anabaena doliolum with change in nutrient status. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 48, 223–229.
Nioeber, E., Richardson, D. H. S. (1980) The replacement of the nondescript term “heavy metals” by a biologically and chemically significant classification of metal ions. Environ. Pollut. Ser. B 1, 3–26.
Rai, L. C., Singh, A. K., Mallick, N. (1991) Studies on photosynthesis, the Associated Electron Transport System and some physiological variables of Chlorella vulgaris under heavy metal stress. J. Plant Physiol. 138, 419–424.
Safferman, R. S., Morris, M. E. (1964) Growth characteristic of blue-green algal virus LPP1. J. Bact. 88, 771–775.
Snedecor, G. W., Cochran, W. G. (1967) Statistical methods. 6th ed. Oxford and IBH, London, p. 593.
WHO (1976) Mercury. Environmental Health Criteria 1, 8–115.
Wu, J. T., Lorenzen, H. (1984) Effect of copper on photosynthesis in synchronous Chlorella cells. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sci. 25, 125–132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohapatra, D.K., Mohanty, L., Mohanty, R.C. et al. Biotoxicity of mercury to Chlorella vulgaris as influenced by amino acids. BIOLOGIA FUTURA 48, 497–504 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03542959
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03542959