Abstract
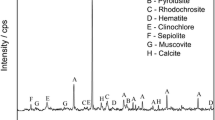
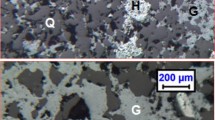
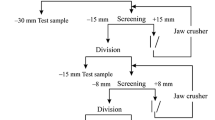
Jigging of the −2.8 +0.7-mm size fraction of a friable, low-grade manganese ore sample from Andhra Pradesh increased the Mn content of a concentrate by 7% to 8%, with an average recovery of 57%. The jig concentrate was mixed with the unjigged −0.7-mm size fraction and ground to −150 μm. The sample was then subjected to wet high-intensity magnetic separation (WHIMS). The magnetic fraction thus obtained showed an increase in Mn content of 6%, but with an overall recovery of only 50%. The results of hydrocyclone classification of −150-μm ground ore indicated that the method is not capable of upgrading the manganese content, as both ferromanganese oxides and aluminosilicate gangue minerals constitute the fine size fraction. However, when the nonmagnetic fraction obtained from the WHIMS of −150-μm ore is subjected to hydrocyclone classification and the underflow obtained is subjected to WHIMS again, an overall recovery of about 50% to 52% is obtained with at least a 7% to 8% increase in the Mn content of the product. The phosphorus content in the product is not reduced by either of the two combinations of methods. The complex association of phosphorus with all the major phases in the ore has been clearly demonstrated from the linear correlation between the distribution ratios of major constituent phases and phosphorus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanungo, S.B., Mishra, S.K. and Biswal, D., 2000, “Beneficiation of low-grade, high-phosphorus manganese ores of Andhra Pradesh, India, by wet high-intensity magnetic separation,” Minerals & Metallurgical Proc, Vol. 17, No. 3, August, pp.181–185
Narasingarao, A., 1965, “Studies on the beneficiation of low grade manganese ores from Srikakulam and Vizianagaram Districts with special references to the reduction of phosphorus,” J. Mines, Metals & Fuels, Feb. pp. 55–59.
Narasimharao, R.S., and Kameswararao, K., 1993, “Processing of manganese ore dumps of Garbham, Vizianagaram.” In Proc. 9th National Convention of Chemical Engineers, Vishakhapatnam, India, January 5–7, pp. 352–354.
Raju, K.K.V.S., 1996, “Distribution and behavior of phosphorus in the manganese ores of Vizianagaram, A.P., India,” Proc. National Workshop on Removal of Phosphorus from Manganese Ores, held at R.R.L., Bhubaneswar, May 24, pp. 1–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanungo, S.B., Mishra, S.K. & Biswal, D. Beneficiation of low-grade, high-phosphorus manganese ores of Andhra Pradesh, India, by wet high-intensity magnetic separation plus jigging or hydrocyclone classification. Mining, Metallurgy & Exploration 17, 269–275 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03403245
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03403245