Abstract
Background
Several immunotoxins in which antibodies are coupled to plant or bacterial toxins are now in clinical trials for the treatment of cancer. One of these is B3-LysPE38 in which MAb B3 which reacts with many human cancers, is coupled with a genetically modified form of Pseudomonas exotoxin (PE).
Materials and Methods
To investigate how cells can become resistant to PE-derived immunotoxins, we constructed an immunotoxin-sensitive MCF-7 breast cancer cell line that contains SV40 T antigen and allows episomal replication of SV40 origin containing Plasmids. We transfected a pCDM8/HeLa cDNA expression library into these cells, thereby causing over-expression of the plasmid-encoded genes. The transfected cells were treated with immunotoxin to select for resistance-mediating plasmids, which were reisolated from these cells and amplified in Escherichia coli. The resulting plasmid pool was transfected into cells for two further rounds of selection and plasmid reisolation.
Results
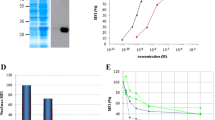
Several plasmids that caused immunotoxin resistance were enriched by this selection procedure. Four plasmids were stably transfected into MCF-7 cells and found to increase their resistance to PE-derived immunotoxins by 5- to 20-fold. These plasmids also confer resistance to native PE and to diphtheria toxin but not to ricin or cycloheximide. Thus, they appear to specifically interfere with the action of ADP-ribosylating toxins.
Conclusion
Cancer cells can become resistant to immunotoxins by deregulated expression of normal genes. The clinical significance of this type of resistance will be evaluated in clinical trials.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vitetta ES, Thorpe PE, Uhr JW. (1993) Immunotoxins: Magic bullets or misguided missiles? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 14: 148–154.
Pastan I, Chaudhary VK, FitzGerald DJ. (1992) Recombinant toxins as novel therapeutic agents. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 61: 331–354.
Vitetta ES. (1994) From the basic science of B cells to biological missiles at the bedside. J. Immunol. 153: 1407–1420.
Pastan I, Pai LH, Brinkmann U, FitzGerald DJ. (in press) Recombinant toxins: New therapeutic agents for cancer. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.
Brinkmann U, Pastan I. (1994) Immunotoxins against cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 1198: 27–45.
Kondo T, FitzGerald D, Chaudhary VK, Adhya S, Pastan I. (1988) Activity of immunotoxins constructed with modified Pseudomonas exotoxin A lacking the cell recognition domain. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 9470–9475.
Pastan I, Lovelace ET, Gallo MG, Rutherford AV, Magnani JL, Willingham MC. (1991) Characterization of monoclonal antibodies B1 and B3 that react with mucinous adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 51: 3781–3787.
Pai LH, FitzGerald DJ, Willingham MC, Pastan I. (1991) Anti-tumor activities of immunotoxins made of monoclonal antibody B3 and various forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88: 3358–3362.
Brinkmann U, Pai LH, FitzGerald DJ, Pastan I. (1991) B3(Fv)-PE38KDEL, a single chain immunotoxin that causes complete regression of a human carcinoma in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88: 8616–8620.
Moehring JM, Inocencio NM, Robertson BJ, Moehring TJ. (1993) Expression of mouse furin in a Chinese hamster cell resistant to Pseudomonas exotoxin A and viruses complements the genetic lesion. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 2590–2594.
Laurie SM, Robbins AR. (1991) A toxin-resistant mouse L-cell mutant defective in protein transport along the secretory pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 147: 215–223.
Kimata Y, Kohno K. (1994) Elongation factor 2 mutants deficient in diphthamide formation show temperature-sensitive cell growth. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 13497–13501.
Kido M, Miwatani H, Kohno K, Uchida T, Okada Y. (1991) Targeted introduction of a diphtheria toxin-resistant point mutation into the chromosomal EF-2 locus by in vivo homologous recombination. Cell Struct. Fund. 16: 447–453.
Fendrick JL, Iglewski WJ, Moehring JM, Moehring TJ. (1992) Characterization of the endogenous ADP-ribosylation of wild-type and mutant elongation factor 2 in eukaryotic cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 205: 25–31.
Chaudhary VK, Jinno Y, FitzGerald D, Pastan I. (1990) Pseudomonas exotoxin contains a specific sequence at the carboxyl terminus that is required for cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87: 308–312.
Zdanovsky AG, Chiron M, Pastan I, FitzGerald DJ. (1993) Mechanism of action of Pseudomonas exotoxin: Identification of a rate-limiting step. J. Biol. Chem. 29: 21791–2179.
Goldstein LJ, Galski H, Fojo A, et al. (1989) Expression of a multidrug resistance gene in human cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 81: 116–124.
Endicott JA, Ling V. (1989) The biochemistry of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 58: 137–171.
Gottesman MM, Pastan I. (1993) Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 62: 385–427.
Schimke RT. (1984) Gene amplification in cultured animal cells. Cell 37: 705–713.
Schimke RT. (1988) Gene amplification in cultured cells. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 5989–5992.
Buchner J, Pastan I, Brinkmann U. (1992) A method to increase the yield of properly folded recombinant fusion proteins: E.g., single-chain immunotoxins from renaturation of bacterial inclusion bodies. Anal. Biochem. 205: 263–270.
Ogryzko VV, Hirai TH, Shih CE, Howard BH. (1994) Dissociation of retinoblastoma gene protein hyperphosphorylation and commitment to enter S phase. J. Virol. 68: 3724–3732.
Maniatis T, Sambrook J, Frisch EF. (1989) Molecular cloning. A Laboratory Manual. 2nd Ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Hirt B. (1967) Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J. Mol. Biol. 26: 365–369.
Martin R, Hoover C, Grimme S, Grogan C, Holtke J, Kessler, C. (1990) A highly sensitive, nonradioactive DNA labeling and detection system. BioTechniques 9: 762–768.
Cory AH, Owen TC, Barltrop JA, Cory JG. (1991) Use of an aqueous soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth assays in culture. Cancer Commun. 3: 207–212.
Brinkmann U, Reiter Y, Jung S-H, Lee B, Pastan I. (1993) A recombinant immunotoxin containing a disulfide-stabilized Fv fragment (dsFv). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90: 7538–7542.
Okayama H, Berg P. (1982) High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2: 161–170.
Suter W, Negro L, Barrera I, Schneider B. (1992) Resistance to Pseudomonas exotoxin A: A sensitive marker to screen for mutagenic substances using V79 cells. Mutagenesis 7: 125–135.
Tiah M, Ronen A. (1991) Dominant lethal cell mutants detected by the autoradiographic assay for exotoxin A resistance. Mutat. Res. 249: 211–222.
Hwang J, Richert N, Pastan I, Gottesman MM. (1987) Mutant KB cells with decreased EGF receptor expression: Biochemical characterization. J. Cell. Physiol. 133: 127–134.
Lyall RM, Hwang J, Cardarelli C, et al. (1987) Isolation of human KB cell lines resistant to epidermal growth factor-Pseudomonas exotoxin conjugates. Cancer Res. 47: 2961–2966.
Gudkov AV, Kazarov AR, Thimmapaya R, Axenovich SA, Mazo LA, Roninson IB. (1994) Cloning mammalian genes by expression selection of genetic suppressor elements: Association of kinesin with drug resistance and cell immortalization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91: 3744–3748.
Gudkov AV, Zelnick CR, Kazarov AR, et al. (1993) Isolation of genetic suppressor elements, inducing resistance to topoisomerase II-interactive cytotoxic drugs, from human topoisomerase II cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90: 3231–3235.
Kruh GD, Chan A, Myers K, Gaughan K, Miki T, Aaronson SA. (1994) Expression complementary DNA library transfer establishes mrp as a multidrug resistance gene. Cancer Res. 54: 1649–1652.
Chan AM, Miki T, Meyers KA, Aaronson SA. (1994) A human oncogene of the RAS superfamily unmasked by expression cDNA cloning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91: 7558–7562.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brinkmann, U., Brinkmann, E. & Pastan, I. Expression Cloning of cDNAs That Render Cancer Cells Resistant to Pseudomonas and Diphtheria Toxin and Immunotoxins. Mol Med 1, 206–216 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03401568
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03401568