Abstract
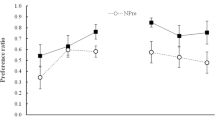
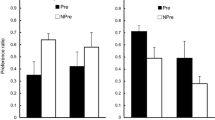
Two experiments investigated conditions that influence whether or not the presence of a flavor cue potentiates acquisition of an environmental aversion. Experiments 1 and 2 exposed rats to either a salient sucrose flavor or nonsalient water with black box-illness pairings. Half of the rats in the sucrose and water treatment groups became ill after exposure to the black chamber in their home cage. The other half of the rats in the two treatment conditions became ill in the black box. The results of each study indicated that a strong environmental aversion was established when illness was associated with exposure to the black box. The aversiveness of the black chamber was indicated by both less time spent in the black side and reduced intake in the black chamber. The presence of sucrose during conditioning did produce a stronger black box aversion than did water. Reliable potentiation of the environmental aversion, however, was seen only when the illness experience occurred in the black chamber but not when illness occurred in the home cage. A weaker aversion to the black chamber was also found in the water groups when illness occurred shortly after experience with the black box than when illness immediately followed exposure to the black chamber.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BEST, M. R., BATSON, J. D., MEACHUM, C. L., BROWN, E. R., & RINGER, M. (1985). Characteristics of taste-mediated environmental potentiation. Learning and Motivation, 16, 190–209.
BEST, P. J., BEST, M. R., & HENGGELER, S. (1977). The contribution of environmental non-ingestive cues in conditioning with aversive internal consequences. In L. M. Barker, M. R. Best, & M. Domjan (Eds.), Learning mechanisms in food selection. Waco, TX: Baylor University Press.
BEST, P. J., BEST, M. R., & MICKLEY, G. A. (1973). Conditioned aversion to distinct environmental stimuli resulting from gastrointestinal distress. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology, 85, 250–257.
BEST, M. R., BROWN, E. R., & SOWELL, M. K. (1984). Taste-mediated potentiation of non-ingestional stimuli in rats. Learning and Motivation, 15, 244–258.
BOUTON, M. E., & WHITING, M. R. (1982, March). A comparison or odor-taste compounds in toxophobic conditioning. Paper presented at the meeting of the Eastern Psychological Association, Baltimore, Maryland.
DURLACH, P. J., & RESCORLA, R. A. (1980). Potentiation rather than overshadowing in flavor-aversion learning: An analysis in terms of within-compound associations. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 6, 175–187.
KALAT, J., & ROZIN, P. (1970). “Salience” a factor which can override temporal contiguity in taste-aversion learning. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology, 71, 192–197.
KEITH-LUCAS, T., & GUTTMAN, N. (1975). Robust-single-trial delayed backward conditioning. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology, 88, 468–476.
KLEIN, S. B., FREDA, J. S., & MIKULKA, P. J. (1985). The influence of a taste cue on an environmental aversion: Potentiation or overshadowing. The Psychological Record, 35, 101–112.
KLEIN, S. B., & MIKULKA, P. J. (1979, November). The failure of a taste aversion to interfere with the establishment of an environmental aversion. Paper presented at Psychonomic Society Meeting, Phoenix, Arizona.
LETT, B. T. (1980). Taste potentiates color-sickness associations in pigeons and quail. Animal Learning and Behavior, 8, 193–198.
LINDSEY, G., & BEST, P. (1973). Overshadowing of the less salient of two novel fluids in a taste-aversion paradigm. Physiological Psychology, 1, 13–15.
LOGUE, A. W. (1979). Taste aversion and the generality of the laws of learning. Psychological Bulletin, 86, 276–296.
MARTIN, J. C., & ELLINWOOD, E. H., JR. (1974). Conditioned aversion in spatial paradigms following methamphetamine injections. Psychopharmacologia, 36, 323–335.
MELLGREN, R. L. (1972). Positive and negative contrast effects using delayed reinforcement. Learning and Motivation, 3, 185–193.
MIKULKA, P. J., PITTS, E., & PHILPUT, C. (1982). Overshadowing not potentiation in taste aversion learning. Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society, 20, 101–104.
MORRISON, G. R., & COLLYER, R. (1974). Taste-mediated conditioned aversion to an exteroceptive stimulus following LiCI poisoning. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology, 86, 51–55.
PALMERINO, C. C., RUSINIAK, K. W., & GARCIA, J. (1980). Flavor-illness aversions: The peculiar role of odor and taste in memory for poison. Science, 208, 753.
PAVLOV, I. P. (1927). Conditioned reflexes. (G. V. Annep, Trans.). London: Oxford University Press.
RESCORLA, R. A., & WAGNER, A. R. (1972). A theory of Pavlovian conditioning: Variations in the effects of reinforcement and nonreinforcement. In A. Black & W. F. Prakasy (Eds.), Classical conditioning Ii (pp. 64–99). New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
REVUSKY, S. (1971). The role of interference in association over a delay. In W. K. Honig & P. H. R. James (Eds.), Animal memory. New York: Academic Press.
REVUSKY, S., & PARKER, L. A. (1976). Aversions to drinking out of a cup and to unflavored water produced by delayed sickness. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 2, 342–353.
RUSINIAK, K. W., HANKINS, W. G., GARCIA, J., & BRETT, L. P. (1979). Flavor-illness aversions: Potentiation of odor by taste in rats. Behavioral and Neural Biology, 25, 1–17.
RUSINIAK, K. W., PALMERINO, C. C., RICE, A. G., FORTHMAN, D. L., & GARCIA, J. (1982). Flavor-illness aversions: Potentiation of odor by taste with toxin but not shock in rats. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology, 96, 527–539.
SHANAB, M. E., SANDERS, R., & PREMACK, D. (1969). Positive contrast in the runway obtained with delay of reward. Science, 164, 724–725.
SHERMAN, J. E. (1978). Us inflation with trace and simultaneous fear conditioning. Animal Learning and Behavior, 6, 463–468.
TAKULIS, H., & ST. GEORGE, S. (1982). Overshadowing of environmental cues by an odor in toxicosis-based conditioning in rats. Animal Learning and Behavior, 10, 288–292.
WAGNER, A. R. (1981). Sop: A model of automatic memory processing in animals behavior. In N. E. Spear & R. R. Miller (Eds.), Information processing in animals. Memory mechanisms. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klein, S.B., Elder, R. The Elusiveness of Gustatory Potentiation of an Environmental Aversion. Psychol Rec 37, 55–67 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395873
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03395873