Abstract
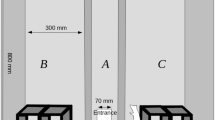
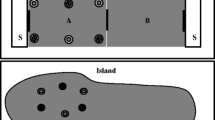
Two experiments evaluating open-field foraging behavior of rats that had received prior taste aversion conditioning to liquid saccharin are reported. In both studies each rat had free access to six foraging patches containing powdered laboratory chow (three plain, three saccharin-adulterated). As consumption at the saccharin-adulterated patches was significantly less for taste-aversion treated animals than at the plain patches, generalization of a taste aversion to a different type of ingestive stimulus in a different environment was demonstrated. The possible relationship of these data to environmental potentiation effects is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BARKER, L. M., BEST, M. R., & DOMJAN, M. (1977). Learning mechanisms in food selection. Waco, TX: Baylor University Press.
BEST, M. R. (1975). Conditioned and latent inhibition in taste-aversion learning: Clarifying the role of learned safety. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 1, 97–113.
BEST, M. R., DAVIS, S. F., NASH, S. M., & MEACHUM, C. L. (1985). Taste aversion learning: Locus of conditioning affects straight runway performance. Paper presented at the meeting of the American Psychological Association, Los Angeles, CA.
DOMJAN, M. (1975). Poison-induced neophobia in rats: Role of stimulus generalization of conditioned taste aversions. Animal Learning & Behavior, 3, 205–211.
FENWICK, S., MIKULKA, P. J., & KLEIN, S. B. (1975). The effect of different levels of pre-exposure to sucrose on the acquisition and extinction of a conditioned taste aversion. Behavior Biology, 14, 231–235.
GARCIA, J., & KOELLING, R. A. (1966). Relation of cue to consequence in avoidance learning. Psychonomic Science, 4, 123–124.
LOGUE, A. W. (1979). Taste aversion and the generality of the laws of learning. Psychological Bulletin, 56, 343–349.
MELCER, T., & TIMBERLAKE, W. (1985). Poison avoidance and patch (location) selection in rats. Animal Learning & Behavior, 13, 60–68.
NACHMAN, M. (1963). Learned aversion to the taste of lithium chloride and generalization to other salts. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology, 56, 343–349.
PARKER, L., & REVUSKY, S. (1982). Generalized conditioned flavor aversions: Effects of toxicosis training with one flavor on the preference for different novel flavors. Animal Learning & Behavior, 10, 505–510.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, S.F., Richard, M.M. & Nash, S.M. Open-Field Foraging: The Influence of Prior Taste-Aversion Conditioning. Psychol Rec 36, 365–373 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03394955
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03394955