Abstract
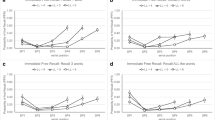
Process schizophrenics, reactive schizophrenics, and normal adult volunteers were tested for immediate free recall of 2-, 3-, and 4-pair word lists that were presented dichotically. Each pair consisted of one high-imagery and one low-imagery word. Amount recalled was an interactive function of imagery and list position and was similar for each list length. The groups differed in amount recalled but their patterns of recall as an interactive function of imagery and list position were virtually identical. Supplementary analyses tentatively linked the differences in amount recalled to processes underlying (a) the tendency to emit acoustically related intrusion errors, (b) the tendency to begin recall with items from the first list position, and (c) the tendency to preserve presentation structure in recall.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference Notes
TRAUPMANN, K. L., BERZOFSKY, M., & ALPERT, M. Process schizophrenics suboptimally implement active memory encoding strategies. Paper delivered at the annual meetings of the American Psychological Association, Chicago, Illinois, 1975.
TRAUPMANN, K. L. Short-term serial memory: the start of a process analysis of schizophrenic performance. Paper presented at Cognitive psycho pathology: Information processing in schizophrenia, S. Matthysse (Chair). Symposium held at the annual meetings of the Eastern Psychological Association, Boston, Massachusetts, 1977.
TRAUPMANN, K. L Short-term serial recall of schizophrenic patients as a function of retention interval. Manuscript in preparation, University of California, San Diego, California, 1979.
References
AMERICAN PSYCHIATRIC ASSOCIATION. 1968. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-II). Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association.
BADDELEY, A. D., & HITCH, G. J. 1977. Recency reexamined. In S. Dornic (Ed.), Attention and performance VI. Hillsdale, N.J.: Lawrence Erlbaum.
BORKOWSKI, J., & EISNER, H. C. 1968. Meaning fulness and abstractness in short-term memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 76, 56–60.
BULL, H. C., & VENABLES, P. H. 1974. Speech perception in schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry, 125, 350–354.
COHEN, B. Referent communication disturbances in schizophrenia. 1978. In S. Schwartz (Ed.), Language and cognition in schizophrenia. Hillsdale, N.J.: Lawrence Erlbaum.
DREWNOWSKI, A. 1980. Attributes and priorities in short-term recall: A new model of memory span. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 109, 208–250.
ESTES, W. K. 1972. An associative basis for coding and organization in memory. In A. W. Melton & E. Martin (Eds.), Coding processes in human memory. Washington, D.C.: Winston.
FRIEDRICH, D., EMERY, K., & FULLER, G. 1974. Performance of paranoid schizophrenics on a dichotic listening task. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 42, 583–587.
GERVER, D. 1967. Linguistic rules and the perception and recall of speech by schizophrenic patients. British Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 6, 204–211.
HAMMOND, N. V., & GRUZELIER, J. H. 1978. Laterality, attention and rate effects in the auditory temporal discrimination of chronic schizophrenics. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 30, 91–103.
KIMURA, D. 1967. Functional asymmetry of the brain in dichotic listening. Cortex, 3, 163–178.
KOH, S. D. 1978. Remembering of verbal materials by schizophrenic young adults. In S. Schwartz (Ed.), Language and cognition in schizophrenia. Hillsdale, N.J.: Lawrence Erlbaum.
KOH, S. D., KAYTON, L., & BERRY, R. 1973. Mnemonic organization in young non-psychotic schizophrenics. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 81, 299–310.
KOH, S. D., & PETERSON, R. A. 1978. Encoding orientation and the remembering of schizophrenic adults. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 87, 303–313.
LARSEN, S. F., & FROMHOLT, P. 1976. Mnemonic organization and free recall in schizophrenia. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 85, 527–533.
MCGHIE, A., CHAPMAN, J., & LAWSON, J. S. 1967. The effect of distraction on schizophrenic performance: (1) perception and immediate memory. British Journal of Psychiatry, 111, 383–390.
NIDORF, L. J. 1964. The role of meaningfulness in the serial learning of schizophrenics. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 20, 92.
PAIVIO, A. 1967. Paired-associate learning and free-recall of nouns as a function of con- creteness, specificity, imagery, and meaningfulness. Psychological Reports, 20, 239–245.
PAIVIO, A. 1971. Imagery and verbal processes. New York: Holt, Rinehart, & Winston.
PAIVIO, A., YUILLE, J. L., & MADIGAN, S. A. 1968. Concreteness, imagery, and meaningfulness values fo. 92. nouns. Journal of Experimental Psychology Monograph, 76, (1, Pt. 2).
SHAKOW, D. 1962. Segmental set: A theory of the formal psychological deficit in schizophrenia. Archivesof General Psychiatry, 6, 1–12.
STEFFY, R. A., & GALBRAITH, K. J. 1980. Relation between latency and redundancy-associated deficit in schizophrenic reaction time performance. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 89, 419–427.
TRAUPMANN, K. L. 1975. The effects of categorization and imagery on recognition and recall of process and reactive schizophrenics. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 84, 307–314.
TRAUPMANN, K. L. 1980. Encoding processes and memory for categorically related words by schizophrenic patients. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 89, 704–716.
TRUSCOTT, I. P. 1970. Contextual constraint and schizophrenic language. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psych ology, 35, 189–194.
WEINBERGER, E., & CERMAK, L. S. 1973. Short-term retention in acute and chronic paranoid schizophrenics. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 82, 220–225.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was conducted while the authors were Nimh postdoctoral trainees in experimental psychopathology at New York University Medical Center and was supported in part by Usphs Grants Mh8638 and Mh8618. The Carnegie Corporation’s support of the first author is also acknowledged.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Traupmann, K.L., Anderson, L.T. Imagery and The Short-Term Recall of Words by Schizophrenics. Psychol Rec 31, 47–56 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03394719
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03394719