Abstract
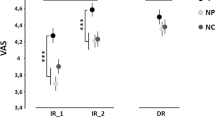
4 groups of male Ss were exposed to 3 minutes of continuous pain stimulation (immersion of the hand in cold water). Prior to stimulation, 3 of the groups received suggestions designed to reduce pain, while the fourth group (control) did not. Relaxation suggestions were effective in reducing subjective pain, whether given alone or together with suggestions to imagine the hand as numb. However, when relaxation suggestions were given together with suggestions to imagine the hand as warm, they were ineffective. Although subjective reports of pain differed among the groups, physiological measures did not.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BARBER, T. X., & CALVERLEY, D. S. 1969. Effects of hypnotic induction, suggestions of anesthesia, and distraction on subjective and physiological responses to pain. Paper presented at the Eastern Psychological Association, Philadelphia, April.
BARBER, T. X., & HAHN, Jr., K. W. 1962. Physiological and subjective responses to pain producing stimulation under hypnotically-suggested and waking-imagined “analgesia.” Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 65, 411–418.
BLITZ, B., & DINNERSTEIN, A. J. 1971. Role of attentional focus in pain perception: Manipulation of response to noxious stimulations by instructions. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 77, 42–45.
CHAVES, J. F., & BARBER, T. X. 1973. Cognitive strategies, modeling, and suggestion in attenuation of pain. Medfield, Mass: Medfield Foundation.
EVANS, M. B., & PAUL, G. L. 1970. Effects of hypnotically suggested analgesia on physiological and subjective responses to cold stress. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 35, 362–371.
SPANOS, N. P., BARBER, T. X., & LANG, G. In press. Cognition and self control: Cognitive control of painful sensory input. In H. London & R. Nisbett (Eds.), Cognitive alterations of feeling states. Chicago: Aldine.
WOLF, S., & HARDY, J. D. 1941. Studies on pain: Observations on pain due to local cooling and on factors involved in the “cold pressor” effect. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 20, 521–533.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, R.F.Q. Suggestions for Pain Reduction and Response to Cold-Induced Pain. Psychol Rec 24, 161–169 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03394230
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03394230