Abstract
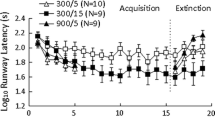
The effects of partial delay of reward in training and partial delay-box confinement in extinction were investigated using a within-type experimental design in both training and extinction.One alley of a Grice discriminator led to immediate reward, while the other alley led to 30-sec. delay on two-thirds of the trials. Half of Ss were extinguished with 30-sec. delay-box confinements on two-thirds of the trials in the former delay alley and no delay in the other alley; half had no delay in either alley. In contrast to the results from between-type experiments, partial delay produced less resistance to extinction and changes in delay from training to extinction had no effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AMSEL, A., RASHOTTE, M. E., & MACKINNON, J. R. 1966. Partial reinforcement effects within subjects and between subjects. Psychological Monographs, 80, No. 20 (whole No. 628).
CAPALDI, E. J., & POYNER, H. B. 1965. Nonreward confinement duration: The complement of reward magnitude. Psychonomic Science, 3, 515–516.
GRICE, G. R., & HUNTER, J. J. 1964. Stimulus intensity effects depend upon the type of experimental design. Psychological Review, 71, 247–256.
RENNER, K. E. 1964. Delay of reinforcement: A historical review. Psychological Bulletin, 61, 341–361.
TOMBAUGH, T. N. 1966. Resistance to extinction as a function of the interaction between training and extinction delays. Psychological Reports, 19, 791–798.
WIKE, E. L. 1966. Secondary reinforcement: Selected experiments. New York: Harper & Row.
WIKE, E. L., MELLGREN, R. L., & COUR, C. A. 1967. Delayed reward, delay-box confinement, and instrumental performance: A within-type design. Psychological Reports, 21, 857–862.
WIKE, E. L., & MCWILLIAMS, J. 1967. The effects of long-term training with delayed reward and delay-box confinement on instrumental performance. Psychonomic Science, 9, 389–390. (a)
WIKE, E. L. & McWILLIAMS, J. 1967. Duration of delay, delay-box confinement, and runway performance. Psychological Reports, 21, 865–870. (b)
WIKE, E. L., MELLGREN, R. L., & WIKE, S. S. 1968. Runway performance as a function of delayed reinforcement and delay-box confinement. Psychological Record, 18, 9–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by a grant GB4299 from the National Science Foundation and a grant from the Biomedical Research Fund of The University of Kansas.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wike, E.L., Atwood, M.E. The Effects of Delayed Reward and Delay-Box Confinement Upon Instrumental Performance: A Within-Type Design. Psychol Rec 20, 57–62 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03393908
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03393908