Abstract
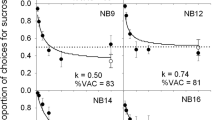
Rats were trained to run to an 8% sucrose solution. The Ss were then divided into four groups equated on mean log running time over the last four training trials. In the testing which followed, groups were run to a plain or complex goal box followed by a run to sugar. Mean log running time to sugar was less (faster) following exposure to a complex goal. A correlation of +.973 was found between group means of log running times to the plain and complex goal boxes and group means of log running times to sugar during testing. The results were interpreted as evidence of an activation effect (curiosity drive) as the consequence of exposure to a complex goal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BERLYNE, D. E. 1960. Conflict, arousal, and curiosity. New York: McGraw-Hill.
BERNSTEIN, L. 1957. The effects of variations in handling upon learning and retention. J. comp. physiol. Psychol., 50, 162–167.
BROWN, J. S., KALISH, H. I., & FARBER, I. E. 1951. Conditioned fear as revealed by the magnitude of startle response to an auditory stimulus. J. exp. Psychol., 41, 317–328.
DEUTSCH, J. A. 1960. The structural basis of behavior. Chicago: Univ. of Chicago Press.
HARLOW, H. F., HARLOW, MARGARET K., & MEYER, D. F. 1950. Learning motivated by manipulative drive. J. exp. Psychol., 40, 228–234.
LINDSLEY, D. B. 1951. Emotion. In S. S. Stevens (Ed.) Handbook of experimental psychology. New York: Pp. 473-516.
MALMO, R. B. 1959. Activation: a neuropsychological dimension. Psychol. Rev., 66, 367–386.
MILLER, N. E. 1963. Some reflections on the law of effect produce a new alternative to drive reduction. In M. R. Jones (Ed.) Nebraska symposium on motivation 1963. Lincoln: Univ. of Nebraska Press.
MONTGOMERY, K. C. 1954. The role of exploratory drive in learning. J. comp. physiol. Psychol., 47, 60–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by National Institute of Health Research Grant #MH 10600-01 and by a Faculty Research Grant-in-Aid from the California State College at Long Beach Foundation from funds provided by the College Foundation and the National Science Foundation. Thanks are given to Jim Borg and Ted Barkley for their services in carrying out the experiment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hommel, L.S. Increased Intensity of a Running Response Following Exposure to a Visually Complex Situation. Psychol Rec 16, 243–250 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03393665
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03393665