Abstract
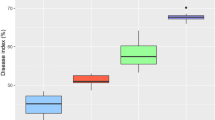
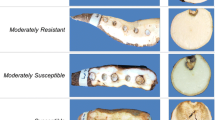
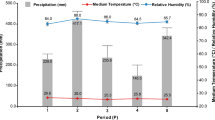
The interaction of twenty-two cassava genotypes with Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis, the causal agent of bacterial blight, was evaluated under field conditions in three different sites, in the forest, forest savanna transition and wet savanna zones of Togo. Although no genotype with disease resistance in all sites was found due to high genotype x environment interactions, genotypes with promising levels of tolerance were identified. Cassava bacterial blight severity was negatively correlated to cassava root yield in artificially inoculated plots in the forest zone in two years, and in non-in- oculated plots in the forest savanna transition zone and the wet savanna zone in the first and the second year, respectively. Evaluating symptom development, four genotypes (CVTM4, Main27, TMS30572, TMS92/0429) were resistant in at least one environment and moderately resistant in other environments, while three genotypes (Lagos, Toma289, Toma378) were over all susceptible. Combining symptom and yield data, seven genotypes (TMS92/0057, TMS29/0326, Cameroon, TMS92/ 0343, Ben86052, Lagos, Gbazékouté) were identified as tolerant. Due to high interaction with the environment and tolerance reactions of some genotypes, a prediction of yield loss due to bacterial blight and the determination of a threshhold for loss seems hardly possible.
Zusammenfassung
Die Interaktion von 22 Manioklinien mit Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis, dem Erreger des Bakterienbrandes, wurde unter Feldbedingungen in drei Ökozonen, der Waldzone, der Wald-Savannen-Übergangszone, und der Feuchtsavanne von Togo evaluiert. Obwohl wegen hoher SorteUmwelt-Interaktionen keine Linie mit Resistenz in allen Ökozonen gefunden wurde, konnten Genotypen mit einem vielversprechenden Toleranzlevel identifiziert werden. In künstlich inokulierten Versuchsfeldern in der Waldzone in zwei Jahren, und in natürlich infizierten Pflanzen in der Wald- Savannen-Übergangszone und der Feuchtsavannenzone im ersten bzw. zweiten Versuchsjahr war die Bakterienbrandstärke negativ mit dem Ertrag korreliert. Nach Symptomevaluierung waren vier Linien (CVTM4, Main27, TMS30572, TMS92/0429) in wenigstens einer Umgebung resistent und moderat resistent in den anderen Umgebungen, während drei Linien (Lagos, Toma289, Toma378) in jeder Umgebung anfällig waren. Bei Kombination von Befalls- und Ertragsdaten erwiesen sich sieben Linien (TMS92/0057, TMS29/0326, Cameroon, TMS92/0343, Ben86052, Lagos, Gbazékouté) als tolerant. Aufgrund der hohen Interaktion mit der Umwelt und der Toleranzreaktion einiger Linien sind eine Ertragsverlust vorhersage und die Festlegung einer Schadensschwelle kaum möglich.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Akparobi, S.O., A.O. Togun, I.J. Ekanayake, 1998: Assessment of cassava genotypes for resistance to cassava mosaic disease, cassava bacterial blight and cassava green mite at a low mid-altitude site in Nigeria. African Crop Sci. J. 6, 385–396.
Banito, A., E.K. Kpemoua, K. Wydra, 2002: Ecozonal variation in reaction of cassava genotypes from Togo to bacterial blight. New Aspects of Resistance Research on Cultivated Plants: Bacterial Diseases. Beitr. Züchtungsforsch. BAZ 9 (3), 67–70.
Banito, A., E.K. Kpemoua, K. Wydra, K. Rudolph, 2001: Bacterial blight of cassava in Togo: its importance, the virulence of the pathogen and the resistance of genotypes. In: S. DeBOER (ed.): Plant Pathogenic Bacteria, pp. 259–264. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands.
Boher, B., C.A. Agbobli, 1992: La bactériose vasculaire du manioc au Togo: charactérisation du parasite, répartition géographique et sensibilité variétale. Agron. Trop. 46, 131–136.
Boher, B., V. Verdier, 1994: Cassava bacterial blight in Africa: the state of knowledge and implications to designing control strategies. African Crop Sci. J. 2, 1–5.
Bondar, G., 1915: Molestia bacteriana da mandioca. Bolet. Agric., Sao Paulo 16, 513–524.
CIAT, 1995: Annual Report. Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical, Cali, Colombia.
CIAT, 1998: Annual Report. Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical, Cali, Colombia.
Dixon, A.G.O., E.N. Nukenine, 2000: Genotype x environment interaction and optimum resource allocation for yield and yield components of cassava. African Crop Sci. J. 8, 1–10.
DMN, 2001: Direction de la Météorologie Nationale Togolaise, Division de la Climatologie, Lomé, Togo.
Dye, D.B., 1962: The inadequacy of the usual determinative tests for the identification of Xanthomonas spp. New Zealand J. Sci. 5, 393–416.
Elango, F., J.C. Lozano, 1981: Pathogenic variability of Xanthomonas manihotis, the causal agent of cassava bacterial blight. Fitopatol. Bras. 6, 57–63.
Fanou, A., 1999: Epidemiological and ecological investigations on cassava bacterial blight and development of integrated methods for its control in Africa. PhD thesis, University of Göttingen, Germany.
Fokunang, C.N., C.N. Akem, A.G.O. Dixon, T. Ikotun, 2000a: Evaluation of a cassava germplasm collection for reaction to three major diseases and the effect on yield. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 47, 63–71.
Fokunang, C.N., T. Ikotun, A.G.O. Dixon, C.N. Akem, 2000b: Field reaction of cassava genotypes to anthracnose, bacterial blight, cassava mosaic disease and their effects on yield. African Crop Sci. J. 8, 179–186.
Hahn, S.K., E.R. Terry, K. Leuschner, I.O. Akobundu, C. Okali, R. Lal, 1979: Cassava improvement in Africa. Field Crops Res. 2, 193–226.
Harville, D.A., 1998: Mixed-model methodology: theoretical justifications and future directions. Proceedings of the Statistical Computing Section of the American Statistical Association, New Orleans, LA, USA, pp. 41–49.
Jeger, M.J., S.L.H. Viljanen-Rollinson, 2001: The use of the area under the disease-progress curve (AUDPC) to assess quantitative disease resistance in crop cultivars. Theor. Appl. Genet. 102, 32–40.
Jorge, V., M.A. Fregene, M.C. Duque, M.W. Bonierbale, J. Tohme, V. Verdier, 2000: Genetic mapping of resistance to bacterial blight disease in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Theor. Appl. Genet. 101, 865–872.
Korie, S., R.U. Okechukwu, 2000: Analyses of on-farm and augmented trials with Mixed Model ANOVA. In: S. Nokoe (ed.). Proceeding of SUSAN-IBS Meeting on Biometry and Quality of Life, 23–27 August, 1999, Ibadan, Nigeria. SUSAN-IBS, Nairobi, Kenya, pp. 74–83.
Kpemoua, E.K., B. Boher, M. Nicole, P. Calatayud, J.P. Geiger, 1996: Cytochemistry of defence responses in cassava infected by Xanthomonas campestris pv. manihotis. Can. J. Microbiol. 42, 1131–1143.
LAMOUROUX, M., 1979: Notice explicative No. 34. Carte pédologique du Togo au 1/1000000. Bondy, ORSTOM.
Lozano, J.C., 1986: Cassava bacterial blight: A manageable disease. Plant Dis. 70, 1089–1093.
Otoo, J.A., A.G.O. Dixon, R. Asiedu, J.E. Okeke, G.N. Maroya, K. Tougnon, O.O. Okoli, J.P. Tetteh, S.K. Hahn, 1994: Genotype x environment interaction studies with cassava. Symposium on Tropical Root Crops in a Developping Economy. Acta Hortic. 380, 144–148.
Restrepo, S., V. Verdier, 1997: Geographical differentiation of the population of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis in Colombia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63, 4427–4434.
Restrepo, S., M.C. Duque, V. Verdier, 2000a: Characterization of pathotypes among isolates ofXanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis in Colombia. Plant Pathol. 49, 680–687.
Restrepo, S., M.C. Duque, V. Verdier, 2000b: Resistance spectrum of selected Manihot esculenta genotypes under field conditions. Field Crops Res. 65, 69–77.
Sanchez, G., S. Restrepo, M.C. Duque, M. Bonierbale, V. Verdier, 1999: AFLP assessment of genetic variability in cassava accessions (Manihot esculenta) resistant and susceptible to the cassava bacterial blight (CBB). Genome 42, 163–172.
Scott, R.A., G.A. Miliken, 1993: A SAS program for analysing augmented randomized complete block designs. Crop Sci. 33, 865–867.
Shaner, G., R.E. Finney, 1977: The effect of nitrogen fertilization on the expression of slow-mildewing resistance in Knox wheat. Phytopathology 67, 1051–1056.
Terry, E.R., 1976: Factors affecting the incidence of CBB in Africa. Proceedings of the 4th Symposium of the International Society of Tropical Root Crops. CIAT, Cali, Colombia, pp. 179–184.
Vauterin, L., B. Hoste, K. Kersters, G.J. Swings, 1995: Reclassification ofXanthomonas. Int. J. Syst. Bact. 45, 472–489.
Verdier, V., S. Restrepo, G. Mosquera, V. Jorge, C. Lopez, 2004: Recent progress in the characterization of molecular determinants in the Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis — cassava interactions. Plant Mol. Biol. 56, 573–584.
Wolfinger, R.D., W.T. Federer, O. Cordero-Brana, 1997: Recovering information in augmented designs using SAS PROC GLM and PROC MIXED. Agron. J. 89, 856–859.
Wydra, K., 2002: The concept of resistance, tolerance and latency in bacterial diseases: examples from cassava and cowpea. New Aspects of Resistance Research on cultivated Plants. Beitr. Züchtungsforsch., BAZ 9 (3), 36–43.
Wydra, K., W. Msikita, 1998: An overview of the present situation of cassava diseases in West Africa. In: M.O. Akoroda, I.J. Ekanayake (eds.). Proceedings of the 6th Triennial Symposium of the International Society of Tropical Root Crops, Africa Branch (ISTRC-AB) on Root Crops for Poverty Alleviation., Lilongwe, Malawi, IITA and Government of Malawi, pp. 198–206.
Wydra, K., K. Rudolph, 1999: Development and implementation of integrated control methods for major diseases of cassava and cowpea in West Africa. Gött. Beitr. Land- Forst- wirtsch. Tropen Subtropen 133, 174–180.
Wydra, K., V. Verdier, 2002: Occurrence of cassava diseases in relation to environmental, agronomic and plant characteristics. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 93, 211–226.
Wydra, K., A. Banito, K.E. Kpémoua, 2007: Characterization of resistance of cassava genotypes to bacterial blight by evaluation of symptom types in different ecozones. Euphytica 155, 337–348.
Wydra, K., V. Zinsou, V. Jorge, V. Verdier, 2004: Identification of pathotypes of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis in Africa and detection of specific quantitative trait loci (QTL) for resistance to cassava bacterial blight. Phytopathology 94, 1084–1093.
Wydra, K., A. Fanou, R. Sikirou, M. Zandjanakou, V. Zinsou, K. Rudolph, 2001: Integrated control of bacterial diseases of cassava and cowpea in West Africa. In: S. DeBoer (ed.). Plant Pathogenic Bacteria, pp. 280–287. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands.
Zinsou, V., 2003: Studies on host plant resistance to cassava bacterial blight in combination with cultural control measures in ecozones of West Africa. PhD thesis, University of Hannover, Germany.
Zinsou, V., K. Wydra, B. Ahohuendo, V. Jorge, V. Verdier, 2002: Evaluation of cassava genotypes, including individuals of their genome mapping population, for resistance against bacterial blight. New Aspects of Resistance Research on cultivated Plants. Beitr. Züchtungsforsch., BAZ 9 (3), 31–35.
Zinsou, V., K. Wydra, B. Ahohuendo, B. Hau, 2004: Genotype x environment interactions in symptom development and yield of cassava genotypes in reaction to cassava bacterial blight. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 111, 217–233.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banito, A., Kpemoua, K.E. & Wydra, K. Expression of resistance and tolerance of cassava genotypes to bacterial blight determined by genotype x environment interactions. J Plant Dis Prot 115, 152–161 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356261
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356261