Abstract
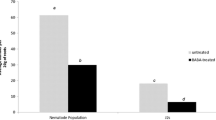
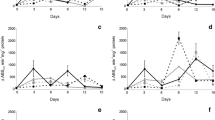
ß-aminobutyric acid (BABA) is a simple, nonprotein amino acid that exhibits postinfectional activity against nematodes, fungi, bacteria and tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), but its activity against phytoplasmas has never been examined before. The aim of this research was to examine possible postinfectional activity of BABA against phytoplasma reference strains AY-A and KVI in Catharanthus roseus shoots grown in vitro. Shoots were grown on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium supplemented with different concentrations of BABA (10 μM, 100 μM, 1 mM, 10 mM, 100mM), through five subcultures. The length of the shoots infected with phytoplasma strain AY-A was measured at the beginning and at the end of the first three subcultures. Only in the first subculture BABA supported shoot elongation. The presence of phytoplasmas was confirmed by nested PCR in both AY-A and KVI-infected shoots after the first and the fifth subculture, showing that in these experimental conditions BABA had no curative effect against phytoplasmas.
Zusammenfassung
ß-Aminobuttersäure (BABA) ist eine einfache nicht proteinogene Aminosäure mit postinfektioneller Aktivität gegenüber Nematoden, Pilzen, Bakterien und dem Tabakmosaikvirus (TMV), aber ihre Wirkung gegenüber Phytoplasmen wurde bisher nicht untersucht. Das Ziel dieser Untersuchung war die überprüfung der möglichen postinfektionellen Aktivität gegenüber den Phytoplasmen-Referenz-stämmen AY-A und KVI in in-vitro-Sprosskulturen von Catharanthus roseus. Die Sprosse wurden in Murashige-Skoog-Medium (MS) in Gegenwart unterschiedlicher BABA-Konzentrationen (10 μM, 100 μM, 1 mM, 10 mM, 100 mM) fünfmal subkultiviert. Die Länge der mit dem Phytoplasmenstamm AY-A infizierten Sprosse wurde zu Beginn und am Ende der ersten drei Subkulturen gemessen. BABA verstärkte das Sprosswachstum nur in der ersten Subkultur. Phytoplasmen beider Stämme wurden mit Hilfe der nested PCR nach der ersten und der letzten Subkultivierung nachgewiesen, so dass BABA unter den gewählten experimentellen Bedingungen keinen kurativen Effekt gegenüber Phytoplasmen aufwies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Andersen, M. T., Beever, R. E., Sutherland, P. W., Forster, R. L. (2001): Association of Candidatus Phytoplasma australiense with sudden decline of cabbage tree in New Zealand. Plant Dis. 85, 462–469.
Bradel, B. G., Preil, W., Jeske, H. (2000): Remission of the free-branching pattern of Euphorbia pulcherrima by tetracycline treatment. J. Phytopathol. 148, 587–590.
Chang, C. J., Franklin, L. (2002): Effects of terpene on growth of spiroplasmas and Mycoplasma iowae. In: Abstract Proceedings, 14th International Congress of the International Organization for Mycoplasmology (IOM), 7–12 July 2002, Vienna, Austria, 149.
Cohen, Y. (1994a): ß-Aminobutyric acid induces systemic resistance against Peronospora tabacina. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 44, 273–288.
Cohen, Y. (1994b): Local and systemic control of Phytophthora infestans in tomato plants by DL-3-amino-n-butanoic acids. Phytopathology 84, 55–59.
Cohen, Y. R. (2002): ß-aminobutyric acid-induced resistance against plant pathogens. Plant Dis. 86, 448–457.
Cohen, Y., Reuveni, M., Baider, A. (1999): Local and systemic activity of BABA (DL-3-aminobutyric acid) against Plasmopara viticola in grapevines. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 105, 351–361.
Davis, R. E., Whitcomb, R. F., Steere, R. L. (1968): Remission of aster yellows disease by antibiotics. Science 161, 793–794.
Duncan, D. B. (1955): Multiple range and multiple F-tests. Biometrics 11, 1–42.
Freitag, J. H., Smith, S. H. (1969): Effects of tetracyclins on symptom expression and leafhopper transmission of aster yellows. Phytopathology 59, 1820–1823.
Gundersen, D. E., Lee, I.-M. (1996): Ultrasensitive detection of phytoplasmas by nested-PCR assays using two universal primer pairs. Phytopathol. Medit. 35, 144–151.
IRPCM Phytoplasma/Spiroplasma Working Team — Phytoplasma Taxonomy Group (2004): ‘Candi-datus Phytoplasma’, a taxon for the wall-less, non-helical prokaryotes that colonize plant phloem and insects. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 54, 1243–1255.
Jagoueix-Eveillard, S., Tarendeau, F., Guolter, K., Danet, J.-L., Bove, J. M., Garnier, M. (2001): Catharanthus roseus genes regulated differentially by mollicute infections. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 14, 225–233.
Jakab, G., Cottier, V., Toquin, V., Rigoli, R., Zimmerli, L., Metraux, J.-P., Mauch-Mani, B. (2001): ß-Aminobutyric acid-induced resistance in plants. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 107, 29–37.
Kamińska, M., Śliwa, H. (2003): Effect of antibiotics on the symptoms of stunting disease of Magnolia liliiflora plants. J. Phytopathol. 151, 59–63.
Lee, I.-M., Bertaccini, A., Vibio, M., Gundersen, D. E. (1995): Detection of multiple phytoplasmas in perennial fruit trees with decline symptoms in Italy. Phytopathology 85, 728–735.
McCoy, R. E., Caudwell, A., Chang, C. J., Chen, T. A., Chiykowski, L. N., Cousin, M. T., Dale, J. L., De Leeuw, G. T. N., Golino, D. A., Hackett, B. C., Kirkpatrick, B. C., Marwitz, R., Petzold, H., Sinha, R. C., Sugiura, M., Whitcomb, R. F., Yang, I. L., Zhu, B. M., Seemüller, E. (1989): Plant diseases associated with mycoplasma-like organisms. In: Whitcomb, R. F., Tully, J. G. (eds.): The Mycoplasmas, vol. 5: Spiroplasmas, Acholeplasmas, and Mycoplasmas of Plants and Arthropods, pp. 545–640. Academic Press, San Diego, CA.
Montano, H. G., Davis, R. E., Dally, E. L., Hogenhout, S., Pimentel, J. P., Brioso, P. S. T. (2001): ‘Candidatus Phytoplasma brasiliense’, a new phytoplasma taxon associated with hibiscus witches’ broom disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51, 1109–1118.
Murashige, T., Skoog, F. (1962): A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15, 473–497.
Oshima, K., Kakizawa, S., Nishigawa, H., Jung, H.-Y., Wei, W., Suzuki, S., Arashida, R., Nakata, D., Miyata, S.-I., Ugaki, M., Namba, S. (2004): Reductive evolution suggested from the complete genome sequence of a plant-pathogenic phytoplasma. Nature Genet. 36, 27–29.
Schaff, D. A., Lee, I.-M., Davis, R. E. (1992): Sensitive detection and identification of mycoplasmalike organisms by polymerase chain reactions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 186, 1503–1509.
Šarić, A., Cvjetković, B. (1985): Mycoplasma-like organisms associated with apple proliferation and pear decline like disease of pear. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 68, 61–67 (in Croatian with English abstract).
Šeruga, M., Škorić, D., Botti, S., Paltrinieri, S., Juretić, N., Bertaccini, A. F. (2003): Molecular characterization of a phytoplasma from the aster yellows (16SrI) group naturally infecting Populus nigra L. ‘Italica’ trees in Croatia. Forest Pathol. 33, 113–125.
Siegrist, J., Orober, M., Buchenauer, H. (2000): Beta-aminobutyric acid-mediated enhancement of resistance in tobacco to tobacco mosaic virus depends on the accumulation of salicylic acid. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 56, 95–106.
Silue, D., Pajot, E., Cohen, Y. (2002): Induction of resistance to downy mildew (Peronospora parasitica) in cauliflower by DL-ß-amino-n-butanoic acid (BABA). Plant Pathol. 51, 97–102.
Zimmerli, L., Jakab, C., Metraux, J.-P., Mauch-Mani, B. (2000): Potentiation of pathogen-specific defense mechanisms in Arabidopsis by ß-aminobutyric acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 12920–12925.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ćurković Perica, M., Šeruga Musić, M. Effect of β-aminobutyric acid on phytoplasma-infected Catharan-thus roseus shoots. J Plant Dis Prot 112, 544–549 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356151
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356151