Abstract
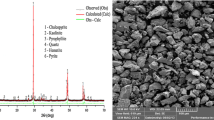
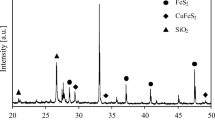
Smelting of copper concentrates results in the discharge of millions of tons of SO, to the atmosphere each year. Because of increasing concern with air pollution, the Bureau of Mines has developed a hydro-metallurgical procedure to obtain elemental sulfur from chalcopyrite by means of the following reaction: CuFeS2 + 3FeCl3 → CuCl + 4FeCl2 + 2S. Under optimum conditions, 99.9% of the copper and 73.7% of the iron was extracted in 2 hr from a typical mill concentrate containing ~ 75% CuFeS2 and 15% FeS2. At the same time, 70.5% of the sulfur was oxidized to the elemental form. The leach was highly selective; gangue minerals, including pyrite, were not attacked, thus accounting for the relatively low recoveries of iron and sulfur.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rohrman, F. A. and J. H. Ludwig: Journal of Metals, 1968, Vol. 20, p. 46.
Ermilov, V. V., Tkachenko, O. B. and Tseft, A. L.; Tr. Inst. Met. Obogashch, 1969, Vol. 30, pp. 3–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haver, F.P., Wong, M.M. Recovery of Copper, Iron, and Sulfur from Chalcopyrite Concentrate using a Ferric Chloride Leach. JOM 23, 25–29 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03355683
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03355683