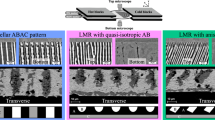
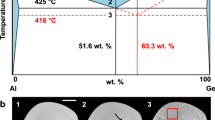
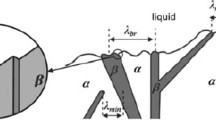
Abstract
In a review of work on unidirectionally solidified eutectics for optical, electronic and magnetic applications published in this journal in 19671, it was reported that many new materials were being prepared with interesting anisotropic properties. These materials contained parallel arrays of fibers of one phase in a matrix of the other, or parallel alternating lamellae of the two phases. At that time the major effort on controlled eutectics was concentrated on the formation of high strength materials, with a few isolated studies being directed toward preparing controlled eutectics for nonstructural applications. Since then, interest has grown in the nonstructural properties of controlled eutectics and a proportionately greater number of studies are now being devoted to that field of research. The purpose of this paper is to bring to the attention of the readers the results of some of these recent studies being conducted to develop new and improved materials for optical, magnetic and electronic applications by the unidirectional solidification of eutectic systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. S. Galasso: “Unidirectionally Solidified Eutectics for Optical, Electronic and Magnetic Applications”, Journal of Metals, Vol. 19, 1967, p. 17.
W. K. Liebmann and E. A. Miller: “Preparation, Phase-Boundary Energies and Thermoelectric Properties of InSb Eutectic Alloys with Ordered Microstructures”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 34. 1963. p. 2653.
A. Yue: “Thermoelectric and Thermomagnetic Properties of Mg-Mg17Al12 and Bi-Cd Eutectics”, Metallurgical Society of AIME, Fall Meeting, Philadelphia, Pa., Oct. 1969.
H. Weiss and M. Wilhelm: “Indiumantimonid mit gerichtet eingebauten, elektrisch gut leitenden Einschlussen: System InSb-NiSb”, Zeitschrift für Physik, Band 176, 1963, p. 399.
B. Paul, H. Weiss, and M. Wilhelm: “Die Polarisierende Wirkung Von Zweiphasigem Indiumantimonid Im Ultraroten”, Solid-State Electronics, Pergamon Press, Vol. 7, 1964, p. 835.
H. Weiss: Electron News, October 12, 1964, p. 42.
H. Weiss: “Die Feldplatte-Ein Neues Magnetisch Steuerbares Halbleiterbauelement”, Solid State Electronics, Pergamon Press, Vol. 9, 1966, p. 443.
A. Muller and M. Wilhelm: “Uber Den Gerichteten Einbau Von Schwermetallphasen in AniBv-Verbindungen Die Eutekt.ika GaSb-CrSb, GaSb-FeGa1.3, InAs-CrAs Und InAs-FeAs”, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, Pergamon Press, Vol. 26, 1965, p. 2029.
A. Muller and M. Wilhelm: “Uber Den Gerichteten Einbau Von Schwermatallphasen In AIIIBV-Verbindungen, Die Eutektika InSb-NiSb, InSb-FeSb, InSb-MnSb, Und InSb-CrSb”, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, Pergamon Press, Vol. 26, 1965, p. 2021.
H. Wagini and M. Wilhelm: “Magnetische and Elektrische Messungen am System InSb-Mn”, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung, Band 21a, Heft 3, 1966, p. 329.
A. Muller, and M. Wilhelm: “Gefügestörun.epn im Kristallisierenden Eutektikum InSb-NiSb Durch Periodiache Temperaturschwankungen der Schmelze”, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung, Band 02 a, Heft 9, 1965, p. 1190.
B. Reiss and Th. Renner: “Der Gerichtete Einbau von Schwermetallphase in GaAs”, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung, Band 21 a, Heft 5, 1966, p. 546.
H. Kandler and B. Reiss: “Zur Kristallstruktur der Intermetallischen Phases Mo As and M05AS4”, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung, Band 21 a, Heft 5, 1966, p. 549.
A. Muller and M. Wilhelm: “Periodische Temperaturschwankingen in Flussigem InSb als Ursache Schichtweisen Einbaus von Te in Kristallisierendes InSb”, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung, Band 19 a, Heft 2, 1964, p. 254.
A. Muller and M. Wilhelm: “Das Eutektikum InSb-Mg3Sb2”, Zeitschrift für Naturforschung, Band 21 a, Heft 5, 1966, p. 555.
A. Muller and M. Wilhelm: “Semiconductor Eutectics Having an AmBv Matrix with Special Consideration of the System InSb-NiSb”, International Conference on Crystal Growth, Boston, June, 1966.
U.S. Patent 3,226,225, (1965), Electronic Semiconductor Members and Method of their Manufacture.
U.S. Patent 3,267,405, (1966), Galvanomagnetic Semiconductor Devices.
U.S. Patent 3,331,045, (1967), Galvano-Magnetic Semiconductor Field Plate.
U.S. Patent 3,366,909, (1968), Contact-Free Electrical Signal Device.
“Feldplatten”—Magneto Resistors, Siemens Laboratories Brochure.
Infrarot-Detectoren OEN-Serie, Siemen Laboratories Brochure (August 1968).
B. Paul: “Optically Induced Ettingshausen-Nernst (OEN) Effect in Two-Phase InSb-NiSb”, Physical Society Meeting, Technical Committee on Semiconductors, March 1968.
B. Paul and H. Weiss: “Anisotropic InSb-NiSb as an Infrared Detector”, Solid State Electronics, Vol. 11, 1968, p. 979.
Br. Patent 1,119,215, (1968), Semiconductor Arrangements for Generating Electromagnetic Radiation in the Range Consisting of the Infrared and Visible Spectral Ranges.
C. T. Elliott and S. E. R. Hiscocks: “On the Electrical and Magnetoresistance Properties of Cd3As2-NiAs”, Brit. J. Appl. Phys. (J. Phys. D.), Vol. 2, 1969, p. 1083.
W. Albers and J. Verberkt: “The SnSe-SnSe2 Eutectic-A P-N Multilayer Structure” (to be published).
H. E. Cline, R. M. Rose, and J. Wulff: “Niobium-Thorium Eutectic Alloy as a High-Field, High current Superconductor”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 4, 1963, p. 1771.
H. E. Cline, R. M. Rose, and J. Wulff: “Research on Superconducting Niobium Thorium Alloy”, U.S. Nat’l Aeronaut. Space Admin. Rep CR54103, 1964.
O. S. Lutes and D. A. Clayton: “Superconductivity of Sn-Zn Eutectic Alloys”, Phys. Rev., Vol. 145, 1966, p. 218.
J D. Livingston: “Magnetization of Superconducting Cu-Pb Alloys”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 39, 1968, p. 3836.
J. D. Livingston, Private Communication.
S. A. Levy, Y. B. Kim, and R. W. Kraft: “Effect of Structure on the Superconducting Properties of Eutectic Alloys”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol 37, 1966, p. 3659.
J. D. Livingston: “Superconducting Properties of Eutectics”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 38, 1967, p. 2408.
J. A. Batt, F. C. Douglas and F. S. Galasso: “Optical Properties of Unidirectionally Solidified NaF-NaCl Eutectic”, Am. Cer. Soc. Bulletin, Vol. 48, 1969, p. 622.
D. L. Albright, G. P. Conrad II, and R. W. Kraft: “Magnetic Behavior of a Eutectic Alloy, Featuring an Aligned Array of Iron Rods”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 38, 1967, p. 2919.
F. Galasso, F. Douglas and J. Batt: “Characterization of the Fe-FexSb Eutectic System with Respect to Structure and Ferromagnetic Properties”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 38, 1967, p. 3241.
H. E. Cline and J. D. Livingston: “High Speed Directional Solidification of Sn-Pb Alloys”, General Electric Technical Information Series, No. 69-C-083, 1969.
J. D. Livingston: “Structure and Magnetic Properties of Au-Co Aligned Eutectic”, General Electric Technical Information Series, No. 69-C-255, 1969.
U.S. Patent 3,434,892, (1965), Directionally’ Solidified Permanent Magnet Alloys with Aligned Ferromagnetic Whiskers.
F. S. Galasso, W. L. Darby, F. C. Douglas and J. A. Batt: “Unidirectional Solidification of the BaFe12019-BaFe204 Eutectic”, Vol. 50, 1967, p. 333.
M. R. Jackson, R. N. Tauber, and R. W. Kraft: “Magnetic Anisotropy of MnSb-Sb Aligned Eutectic”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 39, 1968, p. 4452.
W. M. Yim and E. J. Stofko: “Preparation and Properties of Eutectic Bi-MnBi Single Crystals”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 38, 1967, p. 5211.
J. M. Noothoven van Goor and H. Zylstra: “Structural and Magnetic Properties of a Bi-MnBi Composite”, J. Appl. Phys., Vol. 39, 1968, p. 5471.
D. A. Colling and Ram Kossowky: “Magnetic Properties of Co-Nb and Co-Nb-Fe Unidirectionally Solidified Eutectic Composites”, Metallurgical Society of AIME, Fall Meeting, Philadelphia, Pa., Oct. 1969.
F. S. Galasso: High Modulus Fibers and Composites, Gordon and Breach, N. Y., 1969.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galasso, F.S., Douglas, F.C. & Batt, J.A. Recent Studies of Eutectics for Nonstructural Applications. JOM 22, 40–44 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03355646
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03355646