Abstract
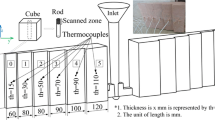
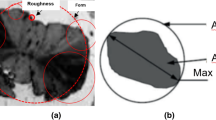
The suggested approaches, including an automated SEM/EDX (Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy Dispersive X-ray) analysis of graphite nodule nuclei and a special algorithm to convert two-dimensional to three-dimensional graphite nodule size distribution, were tested. The “soft” quenching technique was applied to develop small graphite nodules and increase probability to reveal non-metallic heterogeneous nuclei using automated SEM/EDX analysis. Ternary diagrams present experimental statistics of the graphite nuclei chemistry. A special algorithm for the conversion of diameters of two-dimensional sections of graphite nodules to the real three-dimensional distribution of spherical particles was developed. This algorithm is based on inverse simulation. The developed program calculates a three-dimensional nodule diameter distribution curve, the real average diameter, and volumetric nodule number. The examples of practical applications of these methods for spherical graphite characterization in different ductile iron castings are provided. Heterogeneous nucleation of graphite nodules is discussed based on the novel experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loper, C.R., “Inoculation of Cast Iron—Summary of Current Understanding,” AFS Transactions, vol. 107, pp. 523–528 (1999).
Skaland, T., Doctoral Thesis, Metallurgisk Institutt, Trondheim, Norway (1992).
Igarashi, Y. and Senri Okada, S., “Observation and analysis of the nucleus of spheroidal graphite in magnesium treated ductile iron,” Int. J. Cast Metals Res., 11 (1998).
Wang, C.H. and Fredriksson, H.J., “The Mechanism of Inoculation of Cast Iron Melts,” Proc. 48th Int. Foundry Congress (1981).
Lekakh, S. and Bestyzev, N., “Ladle Metallurgy of High Quality Cast Iron,” Nauka&Tekhnika, Minsk, USSR (1992).
Singh, V., Lekakh, S., and Peaslee, K., “Using Automated Inclusion Analysis for Casting Process Improvements.” Proceedings of the Steel Founders’ Society of America 62th Annual Technical and Operating Conference, Chicago (2008).
Lekakh, S., Richards, V., and Peaslee, K., “Thermochemistry of Non-metallic Inclusions in DI,” The Carl Loper Cast Iron Symposium, AFS (2009).
Lekakh, S., Qing, J., Richards, V., Peaslee, K., “Graphite Nodule Size Distribution in Ductile Iron,” AFS Proceedings (2013).
Lekakh, S., Richards, V., “Effect of Si Segregation on Low Temperature Toughness of Ductile Iron,” AFS Proceedings (2012).
Lekakh, S., Robertson, D., and Loper, C.R., “Thermochemistry and Kinetics of Iron Melt Treatment,” World Foundry Congress Proceedings, UK (2006).
Lekakh, S. and Loper, C. R., “Improving Inoculation of Ductile Iron,” AFS Proceedings (2003).
Skaland, T., “Nucleation Mechanism in Ductile Iiron,” Proc. AFS Cast Iron Inoculation Conference (2005).
Lekakh, S., Richards, V., “Determining Solidification Parameters of Alloy Steels,” AFS Proceedings (2011).
Murcia, S.C., Ossa, E.A., and Celentano, D.J., “Nodule Evolution of Ductile Cast Iron During Solidification,” Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, (Published online: 26, October 2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lekakh, S., Harris, M. Novel Approaches to Analyze Structure of Ductile Iron. Inter Metalcast 8, 41–49 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03355581
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03355581