Abstract
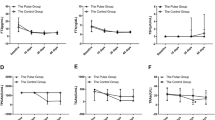
The effect of prednisone treatment and plasmapheresis was studied in two patients with Graves’ disease complicated by severe exophthalmos and/or pretibial myxedema. Titers of Thyrotropin Binding Inhibitory Immunoglobulins (TBII), Long Acting Thyroid Stimulator (LATS), antythyroid antibodies, and serum gammaglobulin concentrations, as well as clinical changes in exophthalmos and pretibial myxedema, were observed during the course of treatment. Steroid treatment lowered all of the abnormal antibody titers. Plasmapheresis did not change the TBII activity when determined using a fixed amount of immunoglobulin G fraction. However, serum gammaglobulin concentration was reduced by plasmapheresis, and therefore, total TBII activity in a unit of serum was reduced. Plasmapheresis also partially and temporarily resolved the pretibial myxedema, whereas no significant change in exophthalmos was observed. These results suggest that both steroid and plasmapheresis treatment are useful for lowering abnormal antibody titers in sera of patients with Graves’ disease, and that plasmapheresis can be of some value in the treatment of pretibial myxedema.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lindstrom J.M. Antibody to acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis. Prevalence, clinical correlates, and diagnostic values. Neurology (Minneap.) 26: 1054, 1976.
Flier J.S., Kahn C.R., Roth J., Bar R.S. Antibodies that impair receptor binding in an unusual diabetic syndrome with severe insulin resistance. Science 190: 63, 1975.
Dau P.C., Lindstrom J.M., Cassel C.K., Denys E.H., Shev E.E., Spitler L.E. Plasmapheresis and immunosuppressive drug therapy in myasthenia gravis. N.Engl. J. Med. 297:1134, 1977.
Muggeo M., Flier J.S., Abrams R.A., Harrison L.C., Deisserroth A.B., Kahn C.R. Treatment by plasma-exchange of a patient with auto-antibodies to the insulin receptor. N.Engl. J. Med. 300: 477, 1979.
Onaya T., Kotani M., Yamada T., Ochi Y. New in vitro tests to detect the thyroid stimulators in sera from hyperthyroid patients by measuring colloid droplet formation and cyclic-AMP in human thyroid slices. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 36: 859, 1973.
Smith B.R., Hall R. Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins in Graves’ disease. Lancet 2: 427, 1974.
Orgiazzi J., Williams D.E., Chopra I.J., Solomon D.H. Human thyroid adenyl cyclase stimulating activity in immunoglobulin G of patients with Graves’ disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 42: 341, 1976.
McKenzie J.M., Zakarija M. A reconsideration of a thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin as the cause of hyperthyroidism in Graves’ disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 42: 778, 1976.
Hall R., Smith B.R., Mukhtar E.D. Thyroid stimulators in health and disease. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf) 4: 213, 1975.
Winand R.J., Kohn L.D. The binding of [3H]-Thyrotropin and an 3H-labeled ex-ophthalmogenic factor by plasma membranes of retro-orbital tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 69: 1711, 1972.
Kuzuya N., Chiu S.C., Ikeda H., Uchimura H., Ito K., Naga-taki S. Correlation between thyroid stimulators and 3, 5, 3′-tri-iocldthyronine suppressibility in patients during treatment for hyperthyroidism with thiouramide drugs: comparison of assays by thyroid-stimulating and thyrotro-pin-displacing activities. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 48: 706, 1979.
Mukhtar E.D., Smith B.R., Pyle G.A., Hall R., Vice P. Relation of thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins to thyroid function and effects of surgery, radioiodine, and antithyroid drugs. Lancet 1: 713, 1975.
Ochi Y., DeGroot L.J. Studies on the immunological properties of LATS. Endocrinology 83: 845, 1968.
Robin N.I., Hagen S.R., Collaco F., Refetoff S., Selenkow H.A. Serum tests for measurement of thyroid funrtion. Hormones 2: 266, 1971.
Kriss J.P., Pleshakov V., Chien J. R. Isolation and identification of the long-acting thyroid stimulator and its relation to hyperthyroidism and circumscribed pretibial myxedema. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 24: 1005, 1964.
Green D.E., Snyder N.J., Solomon D.H. Glucocorticoid-induced disappearance of the long-acting thyroid stimulator in Graves’ ophthalmopathy. J. Clin. Invest. 42: 939, 1963.
akarija M., McKenzie J.M. Zoological specificity of human thyroid-stimulating antibody. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 47: 249, 1978.
Endo K., Kasagi K., Konishi J., Ikekubo K., Okuno T., Takeda Y., Mori T., Torizuka K. Detection and properties of TSH-binding inhibitor immunoglobulins in patients with Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 46: 734, 1978.
White R.G. Factors affecting the antibody response. Br. Med. Bull. 19: 207, 1963.
Dandona P., Marshall N.J., Bidey S.P., Nathan A., Havard C.W.H. Successful treatment of exophthalmos and pretibial myxedema with plasmapheresis. Br. Med. J. 1:374, 1979.
Dandona P., Marshall N.J., Bidey S.P., Nathan A., Havard C.W.H. Treatment of acute malignant exophthalmos with plasma exchange. In: Stockigt J.R., Nagataki S. (Eds.), Thyroid research VIII. Australian Academy of Science, Canberra, 1980, p.
Aoki N., Pinnamaneni K.M., DeGroot L.J. Studies on suppressor cell function in thyroid diseases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 48: 803, 1979.
Cheung H.S., Nicoloff J.T., Kamiel M.B., Spolter L, Nimni M.E. Stimulation of fibroblast biosynthetic activity by serum of patients with pretibial myxedema. J. Invest. Dermatol. 71:12, 1978.
Lockwood C.M., Rees A.J., Pearson T.A., Evans D.J., Peters D.K. Immunosuppression and plasma-exchange in the treatment of Goodpasture’s syndrome. Lancet 1: 711, 1976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by United States Public Health Service Grants AM-13377 and AM-27384.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuzuya, N., DeGroot, L.J. Effect of plasmapheresis and steroid treatment on thyrotropin binding inhibitory immunoglobulins in a patient with exophthalmos and a patient with pretibial myxedema. J Endocrinol Invest 5, 373–378 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03350535
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03350535