Abstract
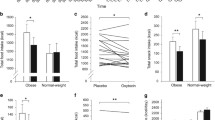
The response of plasma oxytocin to an iv bolus injection of crystalline insulin (0.15 U/kg) was evaluated in 14 normal weight [mean body mass index (BMI) = 23] and in 9 obese (mean BMI = 42) men. Similar blood glucose decrements after insulin injection were observed in the two groups. Obese and normal weight subjects presented similar basal oxytocin levels. In both groups, oxytocin rose significantly during the insulin tolerance test (ITT); however, the peak oxytocin response in the obese men was significantly lower than in the normal weight subjects. Obese men were restudied after substantial weight loss. Basal oxytocin levels and glucose response to insulin did not change after weight reduction. The oxytocin response to the ITT was significantly higher than before slimming and did not differ from that observed in the normal weight subjects. A significant negative correlation between BMI values and oxytocin peak levels during ITT was observed in the lean controls and obese subjects (r = 0.516, p< 0.02). These results demonstrate that in obese subjects the oxytocin secretory response during an insulin tolerance test is reduced, suggesting the existence of a hypothalamic-pituitary disorder in obesity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fish H.R., Chernow B., O’Brian J.T. Endocrine and neurophysiologic responses of the pituitary to insulin-induced hypoglycemia: a review. Metabolism 35: 763, 1986.
Baylis P.H., Heath D.A. Plasma arginine-vasopressin response to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia. Lancet 2: 428, 1977.
Baylis P.H., Zerbe R.L., Robertson G.L. Arginine vasopressin response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 53: 935, 1981.
Fisher B.M., Baylis P.H., Frier B.M. Plasma oxytocin, arginine vasopressin and atrial natriuretic peptide response to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia in man. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 26: 179, 1987.
Glass A.R., Burman K.D., Dahms W.T., Boehm T.M. Endocrine function in human obesity. Metabolism 30: 89, 1981.
Coiro V., Chiodera P. Effect of obesity and weight loss on the arginine-vasopressin response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 27: 253, 1987.
National Diabetes Data Group Classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and other categories of glucose intolerance. Diabetes 28: 1039, 1979.
Chiodera P., Louis F., Legros J.J. Simultaneous radioimmunoassay for plasma argininevasopressin and oxytocin using DEAE sephadex A 25 extraction. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 7: 287, 1984.
Sofroniew M.V., Madler M., Muller O.A., Scriba P.C. A method for the consistent production of high quality antisera to small peptide hormones. Fresenius Z. Anal. Chem. 290: 163, 1978.
Baylis P.H. Posterior pituitary function in health and disease. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 12: 747, 1983.
Weitzman R.E., Glatz T.H., Fisher D.A. The effect of haemorrhage and hypertonic saline on plasma oxytocin and arginine vasopressin in conscious dogs. Endocrinology 103: 2154, 1978.
Hems D.A., Rodrigues L.M., Whitton P.D. Rapid stimulation by vasopressin, oxytocin and angiotensin II of glycogen degradation in hepatocyte suspension. Biochem. J. 172: 311, 1978.
Whitton P.D., Rodrigues L.M., Hems D.A. Stimulation by vasopressin, angiotensin and oxytocin of gluconeogenesis in hepatocyte suspensions. Biochem. J. 176: 893, 1978.
Altszuler N., Hampshire J. Oxytocin infusion increases plasma insulin and glucagon levels and glucose production and uptake in the normal dog. Diabetes 30: 112, 1981.
Spruce B.A., Mc Culloch A.J., Burd J., Orskov H., Heaton A., Baylis P.H., Alberti K.G.M.M. The effect of vasopressin infusion on glucose metabolism in man. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 22: 463, 1985.
Ritter R.C., Slusser P.G., Stone S. Glucoreceptors controlling feeding and blood glucose: location in the hindbrain. Science 213: 451, 1981.
Mizuno Y., Oomura H. Glucose responding neurons in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the rat: in vitro study. Brain Res. 307: 109, 1984.
Nussey S.S., Ang V.T.Y., Jenkins J.S. Responses of neurohypophysial peptides to hypertonic saline and insulin-induced hypoglycaemia in man. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 24: 97, 1986.
Oomura Y., Kita H. Insulin acting as a modulator of feeding through the hypothalamus. Diabetologia 20: 290, 1981.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coiro, V., Passeri, M., Davoli, C. et al. Oxytocin response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in obese subjects before and after weight loss. J Endocrinol Invest 11, 125–128 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03350119
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03350119