Abstract
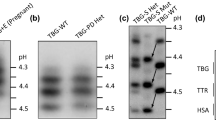
Low serum total thyroxine (TT4) and triiodothyronine (TT3) is found in approximately 40% of Australian Aborigines. Studies were carried out to characterize the properties of thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) in these Australian Aborigines to explain the observed reduction of thyroid hormone concentration in their serum. TBG from Aborigines with low serum TT4 concentrations was compared to TBG fram Aborigines with normal TT4 concentration and Caucasians and American Blacks with normal or reduced serum TBG levels due to familial partial TBG deficiency. TBG from Aborigines with low serum TT4 concentrations had a reduced affinity for thyroid hormone (Ka). The Ka for T4 was 54% and for T3 30% of the Ka values for TBG from Aborigines with normal TT4 concentration or non-Aborigines. Maximal binding values were in agreement with TBG measurements by RIA for Aborigines with low or normal serum TT4 and for non-Aborigines. An increase in the rate of heat denaturation of TBG at temperatures from 54 to 60 C was also observed in sera from Aborigines with low TT4. The heat lability was lowered by 2 C. The low concentration of TT4 in serum of these Aborigines could not explain this higher heat lability of TBG since only addition of greater than 80-fold the physiologic T4 concentration obliterated the difference of heat inactivation by denaturation. Nevertheless, decreased T4 occupancy of this TBG with lower affinity for thyroid hormone may explain reduced stability at high temperatures. There were no differences in the microheterogeneity by isoelectric focusing between TBGs from Aborigines with low serum TT4 concentration and those with normal TT4 or non-Aborigines. From data on maximal binding capacity and TBG measurement by radioimmu-noassy it could be determined that TBG in these Aborigines as in non-Aborigines has a single thyroid hormone binding site. These results indicate that euthyroid Aborigines with low serum TT4 and TT3 concentrations have a variant TBG with reduced affinity for these hormones. The difference between this variant TBG as compared to the more common type of TBG in non-Aborigines appears to reside in the polypeptide chain rather than in the carbohydrate moiety. It fully accounts for the reduced serum total thyroid hormone concentration in the presence of clinical euthyroidism with normal serum free T4 and thyrotropin levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
White G.H., Morice R. Diagnostic biochemical tests in Aboriginals Med. J. Aust. (Spec. Suppl.) 1: 6, 1980.
Dick M. and Watson F. Prevalent low serum thyroxine-binding globulin level in Western Australian Aborigines. Med. J. Aust. 1: 115,1980.
Watson F., Dick M., Khin D.T. Laboratory evaluation of thyroid function in Australian Aborigines. Med. J. Aust. 1: 66, 1983.
Same D.H., Refetoff S., Murata Y., Dick M., Watson F. Variant thyroxihe-binding globulin in serum of Australian Aborigines: A comparison with familial TBG deficiency in Caucasians and American Blacks. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 8: 217, 1985.
Dick M., Watson F, A possible variant of thyroxine-binding globulin in Australian Aborigines. Clin. Chim. Acta 116: 361, 1981.
Stevens V., White E.L, Barlow J.W, Csicsmann J.M., Stockigt J.R. The thyroid hormone binding abnormality in Australian Aborigines. Clin. Biochem., 3: 88, 1982 (Abstract)
Refetoff S. Thyroid hromone transport. In: DeGroot L.J. (Ed.), Endocrinology. Grune & Stratton, New York, 1979, vol. 1 p. 347.
Gershengorn M.C., Glinoer D., Robbins J. Transport and metabolism of thyroid hormone. In: DeVisscher M. (Ed.), The thyroid gland. Raven Press, New York, 1980, p. 81.
Same D., Barokas K., Scherberg N.H., Refetoff S. Elevated serum thyroglobulin level in congenital thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) deficiency J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 57: 665, 1983.
Refetoff S., Hagen S.R., Selenkow H.A. Estimation of the T4 binding capacity of serum TBG and TBPA by a single T4 load-ion exchange resin method: Comparison to two unrelated methods, survey of the population and abnormalities in various diseases. J. Nucl. Med. 13: 2, 1972.
Scatchard G. The attractions of proteins for small molecules and ions. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sei. USA 51: 660, 1949.
Refetoff S.rMurata Y., Vassart G., Chandramouli V., Marshall J.S. Radioimmunoassays specific for the tertiary and primary structures of thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG): Measurement of denatured TBG in serum. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 59: 269, 1984.
Sterling K.S., Hamada S., Takemura Y., Brenner M.A., Newman E.S., Inada M. Preparationand properties of thyroxine-binding alpha globulin (TBG). J.Clin. Inyest. 50: 1758, 1971.
Green A.M., Marshall J.S., Pensky J., Stanbury J.B. Thyroxine-binding globulin: Characterization of the binding site with a fluorescent dye as a probe. Science 175: 1378, 1972.
Sutherland R.L, Simpson-Morgan M.W. The thyroxine-binding properties of serum proteins. A competitive binding technique employing Sephadex G-25. J. Endocrinol. 65: 319,1975.
Gartner R., Henze R. Horn K., Pickardt CR., Scriba P.C. Thyroxine-binding globulin: Investigation of microheter-ogeneity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 52: 657, 1981.
Nilsson S.F., Peterson P.A. Studies on thyroid hormone-binding proteins. I. The subunit structure of human thyroxine-binding globulin and its interaction with ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 250: 8543, 1975.
Korcek L, Tabachnick M. Thyroxine-protein interactions: Interaction of thyroxine and triiodothyronine with human thyroxine-binding globulin. J. Biol. Chem. 25):3558,1976.
Snyder S.M., Cavalieri R.R., Goldfine, I.D., Ingbar S.H., Jorgensen E.C. Binding of thyroid hormones and their analogues to thyroxine-binding globulin in human serum. J. Biol. Chem., 251: 6489, 1976.
Tabachnick M., Korcek L Thyroxine-protein interactions: Binding constants for interaction of thyroxine analogues with the thyroxine binding site on human thyroxine-binding globulin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 537: 169, 1978.
Harpen M.D., Lee W.N.P., Siegel J.A., Greenfield M.A. Serum binding of triiodothyronine: theoretical and practical implications for in vitro triiodothyronine uptake. Endocrinology 110: 1732, 1982.
Refetoff S., Robin N.I., Alper C.A. Study of four new kindreds with inherited thyroxine binding globulin (TBG) abnormalities: Possible mutations of a single gene locus. J. Clin. Invest. 5): 848, 1972.
Grimaldi S., Edelhoch H., Robbins J. Effects of thyroxine binding on the stability, conformation, and fluorescence properties of thyroxine-binding globulin. Biochemistry 21: 145, 1982.
Hocman G. Human thyroxine binding globulin (TBG). Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 91: 45, 1981.
Daiger S.P., Rummel D.P., Wang L, Cavalli-Sforza LL Detection of genetic variation with radioactive ligands. IV. X-linked, polymorphic genetic variation of thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). Am. J. Hum. Genet. 33: 640, 1981.
Grimaldi S., Bartalena L, Ramacciotti C, Robbins J. Polymorphism of human thyroxine-binding globulin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 57: 1186 1983.
Refetoff S., Fang V.S., Marshall J.S. Studies on human thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG): IX. Some physical, chemical and biological properties of radioiodinated TBG and partially desialylated TBG (STBG). J.Clin. Invest. 56: 177, 1975.
Cheng S.-Y., Morrone S., Robbins J. Effect of deglycosylation on the binding and immuno-reactivity of human thyroxine-binding globulin. J. Biol. Chem. 254: 8830, 1979.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Portions of this work were presented at the 13th Annual Meeting of the European Thyroid Association, Madrid, Spain, July 11–15, 1983. Support in part USPHS Grants AM 15070 and AM 06169.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murata, Y., Refetoff, S., Sarne, D.H. et al. Variant thyroxine-binding globulin in serum of Australian Aborigines: its physical, chemical and biological properties. J Endocrinol Invest 8, 225–232 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03348482
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03348482