Abstract
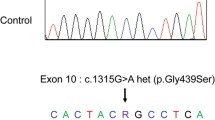
Gitelman’s syndrome is a recessively inherited renal tubular disorder characterized by low plasma potassium and magnesium levels, reduced calcium excretion, metabolic alkalosis, and increased plasma renin activity and plasma aldosterone concentration with normal blood pressure levels. A 23-yr-old man was referred to our department for further evaluation of hypokalemia. The patient also had hypomagnesemia and markedly reduced urinary calcium excretion. Renal clearance studies and gene analysis of the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter (TSC) were performed in the patient. In response to an iv injection of furosemide, chloride clearance (CCl) increased markedly, while distal fractional chloride reabsorption CH2O/ (CH2O+CCl) was considerably reduced. In contrast, thiazide ingestion had no significant effects on these parameters. The patient had compound heterozygous mutations in the alleles encoding the TSC gene, one of which has not been formerly reported. Renal clearance studies and TSC gene analysis by amplification and direct sequencing are useful diagnostic tools for confirming a diagnosis of Gitelman’s syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gitelman HJ, Graham JB, Welt LG. A new familial disorder characterized by hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. Trans Assoc Am Physicians 1966, 79: 221–35.
Schurman SJ, Shoemaker LR. Bartter and Gitelman syndromes. Adv Pediatr 2000, 47: 223–48.
Simon DB, Nelson-Williams C, Bia MJ, et al. Gitelman’s variant of Bartter’s syndrome, inherited hypokalaemic alkalosis, is caused by mutations in the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter. Nat Genet 1996,12: 24–30.
Tsukamoto T, Kobayashi T, Kawamoto K, Fukase M, Chihara K. Possible discrimination of Gitelman’s syndrome from Bartter’s syndrome by renal clearance study: report of two cases. Am J Kidney Dis 1995, 25: 637–41.
Ring T, Knoers N, Oh MS, Halperin ML. Reevaluation of the criteria for the clinical diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 2002, 17: 612–6.
Kockerling A, Reinalter SC, Seyberth HW. Impaired response to furosemide in hyperprostaglandin E syndrome: evidence for a tubular defect in the loop of Henle. J Pediatr 1996, 129: 519–28.
Sutton RA, Mavichak V, Halabe A, Wilkins GE. Bartter’s syndrome: evidence suggesting a distal tubular defect in a hypocalciuric variant of the syndrome. Miner Electrolyte Metab 1992, 18: 43–51.
Tajima T, Kobayashi Y, Abe S, et al. Two novel mutations of thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter (TSC) gene in two sporadic Japanese patients with Gitelman syndrome. Endocr J 2002, 49: 91–6.
Tago N, Kokubo Y, Inamoto N, Naraba H, Tomoike H, Iwai N. A high prevalence of Gitelman’s syndrome mutations in Japanese. Hypertens Res 2004, 27: 327–31.
Lemmink HH, van den Heuvel LP, van Dijk HA, et al. Linkage of Gitelman syndrome to the thiazide-sensitive sodiumchloride cotransporter gene with identification of mutations in Dutch families. Pediatr Nephrol 1996, 10: 403–7.
Yahata K, Tanaka I, Kotani M, et al. Identification of a novel R642C mutation in Na/Cl cotransporter with Gitelman’s syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 1999, 34: 845–53.
Cruz DN, Shaer AJ, Bia MJ, Lifton RP, Simon DB, Yale Gitelman’s and Bartter’s Syndrome Collaborative Study Group. Gitelman’s syndrome revisited: an evaluation of symptoms and health-related quality of life. Kidney Int 2001, 59: 710–7.
Lemmink HH, Knoers NV, Karolyi L, et al. Novel mutations in the thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter gene in patients with Gitelman syndrome with predominant localization to the C-terminal domain. Kidney Int 1998, 54: 720–30.
Syren ML, Tedeschi S, Cesareo L, et al. Identification of fifteen novel mutations in the SLC12A3 gene encoding the Na-Cl Co-transporter in Italian patients with Gitelman syndrome. Hum Mutat 2002, 20: 78.
Sabath E, Meade P, Berkman J, et al. Pathophysiology of functional mutations of the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter in Gitelman disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2004, 287: F195–203.
Ogihara T, Katsuya T, Ishikawa K, et al. Hypertension in a patient with Gitelman’s syndrome. J Hum Hypertens 2004, 18: 677–9.
Cruz DN, Simon DB, Nelson-Williams C, et al. Mutations in the Na-Cl cotransporter reduce blood pressure in humans. Hypertension 2001, 37: 1458–64.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kageyama, K., Terui, K., Shoji, M. et al. Diagnosis of a case of Gitelman’s syndrome based on renal clearance studies and gene analysis of a novel mutation of the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter. J Endocrinol Invest 28, 822–826 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347574
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347574