Abstract
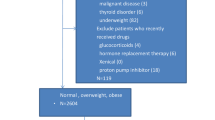
We aimed at investigating insulin resistance in children with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection. Fasting serum insulin and glucose levels were determined in 31 children with H. pylori (+) (H. pylori-infected group, 20 girls and 11 boys, median age 12 yr, range 6–17) and 29 H. pylori (−) (control group, 18 girls and 11 boys, median age 13 yr, range 5–16). Insulin resistance was assessed using homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) score. Fasting serum glucose levels did not differ significantly between H. pylori (+) and (−) children. Both HOMA-IR score and serum insulin levels were significantly higher in H. pylori-infected compared to control children. The findings of the present study suggested that there is a certain relation between H. pylori infection and insulin resistance in children.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fernandez-Real JM, Ricart W. Insulin resistance and chronic cardiovascular inflammatory syndrome. Endocr Rev 2003, 24: 278–301.
Festa A, D’Agostino R Jr, Howard G, Mykkanen L, Tracy RP, Haffner SM. Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of the insulin resistance syndrome: The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS). Circulation 2000, 102: 42–7.
Shiba T, Higashi N, Nishimura Y. Hyperglycaemia due to insulin resistance caused by interferon-gamma. Diabet Med 1998, 15: 435–6.
Kern PA, Ranganathan S, Li C, Wood L, Ranganathan G. Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2001, 280: E745–51.
Yamakawa T, Tanaka S, Yamakawa Y, et al. Augmented production of tumor necrosis factor alpha in obese mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1995, 75: 51–6.
Pickup JC, Mattock MB, Chusney GD, Burt D. NIDDM as a disease of the innate immune system: association of acute-phase reactants and interleukin-6 with metabolic syndrome X. Diabetologia 1997, 40: 1286–92.
Ventre J, Doebber T, Wu M, et al. Targeted disruption of the tumor necrosis factor-α, gene: metabolic consequences in obese and nonobese mice. Diabetes 1997, 46: 1526–31.
McMahon MM, Bistrian BR. Host defenses and susceptibility to infection in patients with diabetes mellitus. Infect Dis Clin N Am 1995, 9: 1–9.
Marshall BJ, Warren JR. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet 1984, 1: 1311–5.
Olbe L, Fandriks L, Hamlet A, Svennerholm AM, Thoreson AC. Mechanisms involved in Helicobacter pylori induced duodenal ulcer disease: an overview. World J Gastroenterol 2000, 6: 619–23.
Forman D, Newell DG, Fullerton F, et al. Association between infection with Helicobacter pylori and risk of gastric cancer: evidence from a prospective investigation. BMJ 1991, 302: 1302–5.
Nomura A, Stemmermann GN, Chyou PH, Kato I, Perez-Perez GI, Blaser MJ. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinoma among Japanese Americans in Hawaii. N Engl J Med 1991, 325: 1132–6.
Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Vandersteen DP, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1991, 325: 1127–31.
Fiedorek SC, Malaty HM, Evans DL, Graham DY. Factors influencing the epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection in children. Pediatrics 1991, 88: 578–82.
Taylor DN, Parsonnet J. Epidemiology and natural history of Helicobacter pylori infection. In: Blaser MJ, et al. eds. Infections of the Gastrointestinal Tract. New York, Raven Press. 1995, 551–63.
Graham DY, Malaty HM, Evans DG, Evans DJ Jr, Klein PD, Adam E. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori in an asymptomatic population in the United States. Effect of age, race and socioeconomic status. Gastroenterology 1991, 100: 1495–501.
Blaser MJ, Atherton JC. Helicobacter pylori persistence: biology and disease. J Clin Invest 2004, 113: 321–33.
Richter T, Richter T, List S, et al. Five-to 7-year-old children with Helicobacter pylori infection are smaller than Helicobacter-negative children: a cross-sectional population-based study of 3,315 children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2001, 33: 472–5.
Demir H, Saltik IN, Kocak N, Yuce A, Ozen H, Gurakan F. Subnormal growth in children with Helicobacter pylori infection. Arch Dis Child 2001, 84: 89–90.
Bravo LE, Mera R, Reina JC, Pradilla A, Alzate A, Fontham E. Impact of Helicobacter pylori infection on growth of children: a prospective cohort study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2003, 37: 614–9.
Guiraldes E, Duarte I, Pea A, et al. Proinflammatory cytokine expression in gastric tissue from children with Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2001, 33: 127–32.
Fan XG, Chua A, Fan XJ, Keeling PW. Increased gastric production of interleukin-8 and tumour necrosis factor in patients with Helicobacter pylori infection. J Clin Pathol 1995, 48: 133–6.
Begue RE, Mirza A, Compton T, Gomez R, Vargas A. Helicobacter pylori infection and insulin requirementamong children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatrics 1999, 103: e83.
Aydemir S, Bayraktaroglu T, Sert M, et al. The effect of Helicobacter pylori on insulin resistance. Dig Dis Sci 2005, 50: 2090–3.
Dixon MF, Genta RM, Yardley JH, Correa P. Classification and grading of gastritis: the Updated Sydney System. Am J Surg Pathol 1996, 20: 1161–81.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28: 412–9.
Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 2004, 27: 1487–95.
Bonora E, Targher G, Alberiche M, et al. Homeostasis model assessment closely mirrors the glucose clamp technique in the assessment of insulin sensitivity: studies in subjects with various degrees of glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care 2000, 23: 57–63.
Haffner SM, Kennedy E, Gonzalez C, Stern MP, Miettinen H. A prospective analysis of the HOMA model: the Mexico City Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 1996, 19: 1138–41.
Lebovitz HE. Insulin resistance and the insulin resistance syndrome. In: Clinician’s Manual on Insulin Resistance. London: Science Press 2002, 1–63.
Tresaco B, Bueno G, Pineda I, Moreno LA, Garagorri JM, Bueno M. Homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) index cut-off values to identify the metabolic syndrome in children. J Physiol Biochem 2005, 61: 381–8.
Keskin M, Kurtoglu S, Kendirci M, Atabek ME, Yazici C. Homeostasis model assessment is more reliable than the fasting glucose/insulin ratio and quantitative insulin sensitivity check index for assessing insulin resistance among obese children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2005, 115: c500–3.
Candelli M, Rigante D, Marietti G, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication rate and glycemic control in young patients with type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2004, 38: 422–5.
Perdichizzi G, Bottari M, Pallio S, Fera MT, Carbone M, Barresi G. Gastric infection by Helicobacter pylori and antral gastritis in hyperglycemic obeses and in diabetic subjects. New Microbiol 1996, 19: 149–54.
Oldenburg B, Diepersloot RJ, Hoekstra JB. High seroprevalence of Helicobacter pylori in diabetes mellitus patients. Dig Dis Sci 1996, 41: 458–61.
Kojecky V, Roubalik J, Bartonikova N. Helicobacter pylori in patients with diabetes mellitus. Vnitr Lek 1993, 39: 581–4.
Scarpello JHD, Sladen GE. Progress report: diabetes and the gut. Gut 1978, 19: 1153–62.
de Luis DA, de la Calle H, Roy G, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1998, 39: 143–6.
Dore MP, Bilotta M, Malaty HM, et al. Diabetes mellitus and Helicobacter pylori infection. Nutrition 2000, 16: 407–10.
Acbay O, Celik AF, Gundogdu S. Does Helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis enhance food-stimulated insulin release? Dig Dis Sci 1996, 41: 1327–31.
Oderda G, Vaira D, Dell’Olio D, et al. Serum pepsinogen I and gastrin concentrations in children positive for Helicobacter pylori. J Clin Pathol 1990, 43: 762–5.
Calam J. Helicobacter pylori modulation of gastric acid. Yale JBiolMed 1999, 72: 195–202.
Kyriazanos ID, Sfiniadakis I, Dimakos P, Gizaris V, Datsakis K, Dafnopoulou A. Impact of body mass index on fasting blood glucose concentration among Helicobacter pylori carriers. Dig Dis 2003, 21: 262–5.
Chu NF, Rimm FB, Wang DJ, Liou HS, Shieh SM. Clustering of cardiovascular disease risk factors among obese schoolchildren: The Taipei Children Heart Study. Am J Clin Nutr 1998, 67: 1141–6.
Luzza F, Parrello T, Sebkova L, et al. Expression of proinflammatory and Th1 but not Th2 cytokinesis enhanced in gastric mucosa of Helicobacter pylori infected children. Dig Liver Dis 2001, 33: 14–20.
Bontems P, Robert F, Van Gossum A, Cadranel S, Mascart F. Helicobacter pylori modulation of gastric and duodenal mucosal T cell cytokine secretions in children compared with adults. Helicobacter 2003, 8: 216–26.
Fernandez-Real JM, Ricart W. Insulin resistance and inflammation in an evolutionary perspective: the contribution of cytokine genotype/phenotype to thriftiness. Diabetologia 1999, 42: 1367–74.
Ashorn M. What are the specific features of Helicobacter pylori gastritis in children? Ann Med 1995, 27: 617–20.
Howard G, O’Leary DH, Zaccaro D, et al. Insulin sensitivity and atherosclerosis. The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study (IRAS) Investigators. Circulation 1996, 93: 1809–17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozdem, S., Akcam, M., Yilmaz, A. et al. Insulin resistance in children with Helicobacter pylori infection. J Endocrinol Invest 30, 236–240 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347431
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347431