Abstract
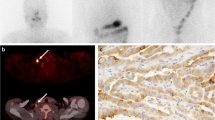
The aim of the present study was to evaluate total and membranous Na+/I− symporter (NIS) expressions in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) tissue, correlation of NIS expression between primary and metastatic lymph node (LN) PTC tissues, and relationship of NIS expression with I131 whole body scan (WBS) uptake between primary and metastatic LN PTC tissues by analyzing 17 pairs of primary and metastatic LN PTC tissues. Staining positivity was calculated, and staining intensity was graded as negative (0), weak (1+), moderate (2+) and strong (3+). In primary PTC tissues, positivities and intensities of normal cells were higher than those of carcinoma cells but had no correlation with those in matched metastatic LN PTC tissues. In classic type, positivities, intensities and membranous intensities (mIS) were correlated between primary and matched metastatic LN PTC tissues. In patients aged younger than 45 yr, positivities and intensities in primary PTC tissues had correlation with those in matched metastatic LN PTC tissues. Positivities, intensities, mlS and pathological subtype of carcinoma cells in primary PTC tissues were not correlated with age, tumor size, TNM stage, MACIS score and thyroglobulin (Tg) levels at the time of I131 WBS. Sensitivity, specificity, as well as positive and negative predicted values of mlS in patients with I131 WBS uptake were 69.2, 75, 90 and 42.9% in primary PTC tissues, and 92.3, 100, 100 and 80% in metastatic LN PTC tissues. The results of mIS taken either as positive or negative were correlated with those of I131 WBS after controlling for age. Our results demonstrate that PTC tissues have altered total and membranous NIS expressions, suggesting that NIS expression in primary PTC tissues may predict NIS expression and I131 WBS uptake in matched metastatic LN PTC tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carrasco N. Iodide transport in the thyroid gland. Biochem Biophys Acta 1993, 1154: 65–82.
Dai G, Levy O, Carrasco N. Cloning and characterization of the thyroid iodide transporter. Nature 1996, 379: 458–60.
Smanik PA, Liu Q, Furminger TL, et al. Cloning of the human sodium symporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996, 226: 339–45.
Eskandari S, Loo DDF, Dai G, Levy O, Wright EM, Carrasco N. Thyroid Na+/I−. Mechanism, stoichiometry, and specificity. J Biol Chem 1997, 272: 27230–8.
Schmutzler C, Kohrle J. Implication of the molecular characterization of the sodium-iodide symporter (NIS). Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 1998, 106: S1–S10.
Filetti S, Bidart JM, Arturi F, Caillou B, Russo D, Schlumberger M. Sodium/iodide symporter: a key transport system in thyroid cancer cell metabolism. Eur J Endocrinol 1999, 141: 443–57.
Arturi F, Russo D, Giuffrida D, Schlumberger M, Filetti S. Sodium-iodide symporter (NIS) gene expression in lymphnode metastases of papillary thyroid carcinomas. Eur J Endocrinol 2000, 143: 623–7.
McDougall IR. In vivo radionuclide tests and imaging. In: Braverman LE, Utiger RD eds. The Thyroid. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. 2005, 309–28.
Arturi F, Russo D, Giuffrida D, et al. Early diagnosis by genetic analysis of differentiated thyroid cancer metastases in small lymph nodes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997, 82: 1638–41.
Lazar V, Bidart JM, Caillou B, et al. Expression of the Na+/I− symporter gene in human thyroid tumors: a comparison study with other thyroid-specific genes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999, 84: 3228–34.
Caillou B, Troalen F, Baudin E, et al. Na+/I− symporter distribution in human thyroid tissues: an immunohistochemical study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998, 83: 4102–6.
Ryu KY, Senokozlieff ME, Smanik PA, et al. Development of reverse transcription-competitive polymerase chain reaction method to quantitate the expression levels of human sodium iodide symporter. Thyroid 1999, 9: 405–9.
Spitzweg C, Heufelder AE, Morris JC. Thyroid iodine transport. Thyroid 2000, 4: 321–30.
Russo D, Manole D, Arturi F, et al. Absence of sodium/iodide symporter gene mutations in differentiated human thyroid carcinomas. Thyroid 2001, 11: 37–9.
Saito T, Endo T, Kawaguchi A, et al. Increased expression of the sodium/iodide symporter in papillary thyroid carcinomas. J Clin Invest 1998, 101: 1296–300.
Dohan O, Baloch Z, Banrevi Z, Livolsi V, Carrasco N. Predominant intracellular overexpression of the Na+/I− symporter (NIS) in a large sampling of thyroid cancer cases. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001, 86: 2697–700.
Park HJ, Kim JY, Park KY, Gong G, Hong SJ, Ahn IM. Expressions of human sodium iodide symporter mRNA in primary and metastatic papillary thyroid carcinomas. Thyroid 2000, 10: 211–7.
Arturi F, Russo D, Bidart JM, Scarpelli D, Schlumberger M, Filetti S. Expression pattern of the pendrin and sodium/iodide symporter genes in human thyroid carcinoma cell lines and human thyroid tumors. Eur J Endocrinol 2001, 145: 129–35.
Castro MR, Bergert ER, Goellner JR, Hay ID, Morris JC. Immunohistochemical analysis of sodium iodide symporter expression in metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: correlation with radioiodine uptake. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001, 86: 5627–32.
Min&J-J, Chung J-K, Lee YJ, et al. Relationship between expression of the sodium/iodide symporter and 131I uptake in recurrent lesions of differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Eur JNuclMed 2001, 28: 639–45.
Arturi F, Russo D, Schlumberger M, et al. Iodide symporter gene expression in human thyroid tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998, 83: 2493–6.
Hedinger C, Williams ED, Sobin LH. The WHO histological classification of thyroid tumors: a commentary on the second edition. Cancer 1989, 63: 908–11.
American Joint Committee on Cancer. Cancer staging manual. New York: Springer-Verlag. 2002, 77–87.
Hay ID, Bergstralh EJ, Goellner JR, et al. Predicting outcome in papillary thyroid carcinoma: development of a reliable prognostic scoring system in a cohort of 1779 patients surgically treated atone institution during 1940 through 1989. Surgery 1993, 114: 1050–8.
Gerard AC, Daumerie C, Mestdagh C, et al. Correlation between the loss of thyroglobulin iodination and the expression of thyroid-specific proteins involved in iodine metabolism in thyroid carcinomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 4977–83.
Kim HM, Lee HC, Park KS, et al. A study on the urinary iodide excretion in normal subjects and patients with thyroid disease. Korean J Intern Med 1985, 29: 625–31.
Tonacchera M, Viacava P, Agretti P, et al. Benign nonfunctioning thyroid adenomas are characterized by a defective targeting to cell membrane or a reduced expression of the sodium iodide symporter protein. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002, 87: 352–7.
Wapnir IE, van de Rijn M, Nowels K, et al. Immunohistochemical profile of the sodium/iodide symporter in thyroid, breast, and other carcinomas using high density tissue microarrays and conventional sections. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88: 1880–8.
Trapasso F, Iuliano R, Chiefari E, et al. Iodide symporter gene expression in normal and transformed rat thyroid cells. Eur J Endocrinol 1999, 140: 447–51.
Smanik PA, Ryu KY, Theil KS, Mazzaferri EL, Jhiang SM. Expression, exon-intron organization, and chromosome mapping of human sodium iodide symporter. Endocrinology 1997, 138: 3555–8.
Riedel C, Levy O, Carrasco N. Post-transcriptional regulation of the sodium/iodide symporter by thyrotropin. J Biol Chem 2001, 276: 21458–63.
Kaminsky SM, Levy O, Salvador C, Dai G, Carrasco N. Na+/I− symport activity is present in membrane vesicles from thyrotropin-derived non-I—transporting cultured thyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994, 91: 3789–93.
Venkataraman GM, Yatin M, Marcinek R, Ain KB. Restoration of iodide uptake in dedifferentated thyroid carcinoma: relationship to human Na+/I− symporter gene methylation status. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999, 84: 2449–57.
Trouttet-Masson S, Selmi-Ruby S, Bernier-Valentin F, et al. Evidence for transcriptional and posttranscriptional alterations of the sodium/iodide symporter expression in hypofunctioning benign and malignant thyroid tumors. Am J Pathol 2004, 165: 25–34.
Schlumberger M, Challeton C, de Vathaire F, et al. Radioactive iodine treatment and external radiotherapy for lung and bone metastases from thyroid carcinoma. J Nucl Med 1996, 37: 598–605.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.J., Choi, K.C., Han, J.P. et al. Relationship of sodium/iodide symporter expression with I131 whole body scan uptake between primary and metastatic lymph node papillary thyroid carcinomas. J Endocrinol Invest 30, 28–34 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347392
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347392