Abstract
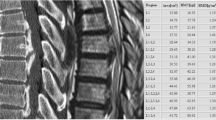
Type Ia pseudohypoparathyroidism (PHP Ia) is an unusual inherited disease. PHP Ia often causes extraskeletal calcifications and even soft tissue ossifications. Patients may present neurologic symptoms and signs related to hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia. We report here a 38-yr-old woman with PHP Ia who had two uncommon neurologic complications. One was involuntary movements related to basal ganglia calcification, and the other was myelopathy owing to ossifications of the posterior longitudinal ligament and multiple herniated intervertebral disks. Aggressive body weight control and corrections of hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, and elevated PTH may be important to prevent these unusual neurologic complications. Regular and careful neurologic examinations should be performed for early diagnosis and treatments of these spinal lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright F, Burnett CH, Smith PH, et al. Pseudohypoparathyroidism: An example of Seabright-Bantan syndrome. Endocrinology 1942, 30: 922–32.
Spiegel AM. Mutations in G proteins and G protein-coupled receptors in endocrine disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996, 81: 2434–42.
Marguet C, Mallet E, Basuyau JP, et al. Clinical and biological heterogeneity in pseudohypoparathyroidism syndrome. Results of a multicenter study. Horm Res 1997, 48: 120–30.
Walters RO. Idiopathic hypoparathyroidism with extrapyramidal and myopathic features. Arch Dis Child 1979, 54: 236–8.
Muenter MD, Whisnant JP. Basal ganglia calcification, hypoparathyroidism, and extrapyramidal motor manifestations. Neurology 1968, 18: 1075–83.
Illum F, Dupont E. Prevalences of CT-detected calcification in the basal ganglia in idiopathic hypoparathyroidism and pseudohypoparathyroidism. Neuroradiology 1985, 27: 32–7.
Evans BK, Donley DK. Pseudohypoparathyroidism, parkinsonism syndrome, with no basal ganglia calcification. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1988, 51: 709–13.
Pearson DW, Durward WF, Fogelman I, et al. Pseudohypoparathyroidism presenting as severe Parkinsonism. Postgrad Med J 1981, 57: 445–7.
Kowdley KV, Coull BM, Orwoll ES. Cognitive impairment and intracranial calcification in chronic hypoparathyroidism. Am J Med Sci 1999, 317: 273–7.
Kanda T, Nagashima T, Oda M, et al. Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism with recurrent polyneuropathy: an autopsy report with special reference to the peripheral nervous system. J Neurol Sci 1991, 103: 42–7.
Okazaki T, Takuwa Y, Yamamoto M, et al. Ossification of the paravertebral ligaments: a frequent complication of hypoparathyroidism. Metabolism 1984, 33: 710–3.
Cullen DR, Pearce JM. Spinal cord compression in pseudohypoparathyroidism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1964, 27: 459–62.
Cavallo A, Meyer WJ, III, Bodensteiner JB, Chesson AL. Spinal cord compression: an unusual manifestation of pseudohypoparathyroidism. Am J Dis Child 1980, 134: 706–7.
Alam SM, Kelly W. Spinal cord compression associated with pseudohypoparathyroidism. J R Soc Med 1990, 83: 50–1.
Yamamoto Y, Noto Y, Saito M, et al. Spinal cord compression by heterotopic ossification associated with pseudohypoparathyroidism. J Int Med Res 1997, 25: 364–8.
Iwase T, Nokura K, Mizuno T, Inagaki T. Spastic tetraparesis in a patient with pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism. J Neurol 2002, 249: 1457–8.
Firooznia H, Golimbu C, Rafii M. Case report 312. Diagnosis: progressive paraparesis in a woman with pseudohypoparathyroidism (PHP) with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament from C4 to T 5. Skeletal Radiol 1985, 13: 310–3.
Goadsby PJ, Lollin Y, Kocen RS. Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism and spinal cord compression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1991, 54: 929–31.
Okada K, Iida K, Sakusabe N, et al. Pseudohypoparathyroidism-associated spinal stenosis. Spine 1994, 19: 1186–9.
Epstein NE. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligment: diagnosis and surgical management. Neurosurgery Quarterly 1992, 2: 223–41.
Tsai CL, Liu HC, Chen HT. Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine in Chinese. Taiwan Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi 1978, 77: 678–84.
Li KK, Chung OM, Chang YP, So YC. Myelopathy caused by ossification of ligamentum flavum. Spine 2002, 27: E308–312.
Okazaki T, Takuwa Y, Yamamoto M, et al. Ossification of the paravertebral ligaments: a frequent complication of hypoparathyroidism. Metabolism 1984, 33: 710–3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Tseng, F., Su, D. et al. Multiple intracranial calcifications and spinal compressions: Rare complications of type la pseudohypoparathyroidism. J Endocrinol Invest 28, 646–650 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347265
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03347265