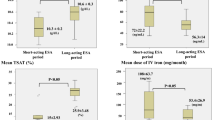
Abstract
Background: Erythropoietin (EPO) is an oxygen-regulated hormone promoting the differentiation of erythroid progenitor cells. Apart from hypoxia, few data is available about release by secretagogues including hormones. Aim: To investigate EPO serum concentration in subjects with endocrine diseases. Material and methods: A retrospective study evaluating serum EPO concentrations in serum leftovers from subjects with various endocrine disorders. Results: EPO is not noticeably influenced by thyroid hormone or cortisol concentrations and the relationship with hemoglobin concentration is preserved. In acromegalic patients, the latter is lost but EPO is neither statistically influenced by GH/IGF-I. This may reflect a dual action of GH and/or IGF-I on erythroid progenitors proliferation as well as on EPO synthesis. Conclusion: EPO is not noticeably modified by endocrine disorders although GH and or IGF-I may alter EPO relationship with blood hemoglobin concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carnot P, DeFlandre C. Sur l’activité hématopoïétique du sérum au cours de la régénération du sang. C R Acad Sci (Paris) 1906, 143: 1384–6.
Jelkmann W. Erythropoietin after a century of research: younger than ever. Eur J Haematol 2007, 78: 183–205.
Fisher JW. Erythropoietin: physiology and pharmacology update. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2003, 228: 1–14.
Cazzola M, Mercuriali F, Brugnara C. Use of recombinant human erythropoietin outside the setting of uremia. Blood 1997, 89: 4248–67.
Otto T, Fandrey J. Thyroid hormone induces hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha gene expression through thyroid hormone receptor beta/retinoid x receptor alpha-dependent activation of hepatic leukemia factor. Endocrinology 2008, 149: 2241–50.
Lim GB, Dodic M, Earnest L, Jeyaseelan K, Wintour EM. Regulation of erythropoietin gene expression in fetal sheep by glucocorticoids. Endocrinology 1996, 137: 1658–63.
Kelly JJ, Martin A, Whitworth JA. Role of erythropoietin in cortisol-induced hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 2000, 14: 195–8.
Sohmiya M, Kato Y. Human growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I inhibit erythropoietin secretion from the kidneys of adult rats. J Endocrinol 2005, 184: 199–207.
Mossuz P, Girodon F, Donnard M, et al. Diagnostic value of serum erythropoietin level in patients with absolute erythrocytosis. Haematologica 2004, 89: 1194–8.
Cazzola M. Use of recombinant human erythropoietin in anemia of malignancy. Med Oncol 1998, 15 (Suppl 1): S1–2.
Bergamaschi S, Giavoli C, Ferrante E, et al. Growth hormone replacement therapy in growth hormone deficient children and adults: Effects on hemochrome. J Endocrinol Invest 2006, 29: 399–404.
Sohmiya M, Kato Y. Effect of long-term administration of recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) on plasma erythropoietin (EPO) and haemoglobin levels in anaemic patients with adult GH deficiency. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2001, 55: 749–54.
Sohmiya M, Kakiba T, Kato Y. Therapeutic use of continuous subcutaneous infusion of recombinant human erythropoietin in malnourished predialysis anemic patients with diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Endocrinol 1998, 139: 367–70.
Tian ZG, Woody MA, Sun R, et al. Recombinant human growth hormone promotes hematopoietic reconstitution after syngeneic bone marrow transplantation in mice. Stem Cells 1998, 16: 193–9.
Ratajczak MZ, Kuczynski WI, Onodera K, et al. A reappraisal of the role of insulin-like growth factor I in the regulation of human hematopoiesis. J Clin Invest 1994, 94: 320–7.
Muta K, Krantz SB, Bondurant MC, et al. Distinct roles of erythropoietin, insulin-like growth factor I, and stem cell factor in the development of erythroid progenitor cells. J Clin Invest 1994, 94: 34–43.
Zhu T, Goh EL, Graichen R, et al. Signal transduction via the growth hormone receptor. Cell Signal 2001, 13: 599–616.
Price EA. Aging and erythropoiesis: current state of knowledge. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2008, 41: 158–65.
Ershler WB, Sheng S, McKelvey J, et al. Serum erythropoietin and aging: a longitudinal analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc 2005, 53: 1360–5.
Grellier P, Chanson P, Casadevall N, et al. Remission of polycythemia vera after surgical cure of acromegaly. Ann Intern Med 1996, 124: 495–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klein, E., Brossaud, J., Gatta, B. et al. Erythropoietin levels in endocrinopathies. J Endocrinol Invest 34, 427–430 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346707
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346707