Abstract
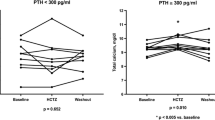
The aim was to study the effect of calcium supplementation 477 mg twice daily on BP in patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism during an intervention study (6 weeks) and after 954 mg during a short study (3 h). The intervention study was a placebo-controlled, double-blind, cross-over, while the short study gave a placebo and calcium in random order on separate days. The participants were obtained from an epidemiological survey in Tromsø 1994–1995 that included more than 27.000 subjects. The re-examination was performed in 2000/2001 at the University Hospital of North Norway, Norway. There were 18 subjects with secondary hyperparathyroidism and 28 control subjects in the intervention study while there were 14 cases and 8 control subjects in the short study. The results showed that in the subjects with secondary hyperparathyroidism after calcium supplementation in the intervention study there was an increase in serum calcium from 2.28±0.09 to 2.36±0.06 mmol/l (mean±SD) and a decrease in serum PTH from 8.6±1.6 to 6.5±2.4 pmol/l. However, there was no significant difference in either systolic or diastolic BP between calcium supplementation and placebo (138.3±21.0 vs 135.9±17.0 mm Hg and 80.9±11.1 vs 78.9±9.5 mm Hg, respectively). Similar results were seen in the control group. In the short study, serum calcium increased and serum PTH decreased after oral calcium, but the BP did not differ as compared to when placebo was given. To conclude, in the present setting we did not find any effect on BP by calcium supplementation in subjects with moderate secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harlan W.R., Hull A.L., Schmouder R.L., Landis J.R., Larkin F.A., Thompson F.E. High blood pressure in older Americans. The first national health and nutrition examination survey. Hypertension 1984, 6: 802–829.
McCarron D.A., Morris C.D., Henry H.J., Stanton J.L. Blood pressure and nutrient intake in the United States. Science 1984, 224: 1392–1398.
McCarron D.A., Morris C.D. Blood pressure response to oral calcium on persons with mild to moderate hypertension. Ann. Intern. Med. 1985, 103 (6 pt 1): 825–831.
Henry H.J., McCarron D.A., Morris C.D., Parrott-Garcia M. Increasing calcium intake lowers blood pressure: The literature reviewed. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1985, 85: 182–185.
Rao R.M., Yan Y., Wu Y. Dietary calcium reduces blood pressure, parathyroid hormone, and platelet cytosolic calcium responses in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 1994, 7: 1052–1057.
Hatton D.C., McCarron D.A. Dietary calcium and blood pressure in experimental models of hypertension. Hypertension 1994, 23: 513–530.
Cappuccio F.P., Elliott P., Allender P.S., Pryer J., Follman D.A., Cutler J.A. Epidemiologic association between dietary calcium intake and blood pressure: a meta-analysis of published data. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 142: 935–945.
Bucher H.C., Cook R.J., Guyatt et al. Effects of dietary calcium supplementation on blood pressure. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. JAMA 1996, 275: 1016–1022.
Allender P.S., Culter J.A., Follmann D., Cappuccio F.P., Pryer J., Elliott P. Dietary calcium and blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Ann. Intern. Med. 1996, 124: 825–831.
Jorde R., Sundsfjord S., Haug E., Bønaa K.H. Relation between low calcium intake, parathyroid hormone, and blood pressure. Hypertension 2000, 35: 1154–1159.
Ellison D.H., Shneidman R., Morris C., McCarron D.A. Effects of calcium infusion on blood pressure in hypertensive and normotensive humans. Hypertension 1986, 8: 497–505.
Jorde R., Bønaa K.H., Sundsfjord J. Population based study on serum ionised calcium, serum parathyroid hormone, and blood pressure. The Tromsø study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 141: 350–357.
Souberbielle J-C., Cormier C., Kindermans C. et al. Vitamin D status and redefining serum parathyroid hormone reference range in the elderly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86: 3086–3090.
Glendenning P., Vasikaran S.D. Vitamin D status and redefining serum parathyroid hormone reference range in the elderly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87: 946–947.
Pfeifer M., Begerow B., Minne H.W., Nachtigall D., Hansen C. Effects of a short-term vitamin D3 and calcium supplementation on blood pressure and parathyroid hormone levels in elderly woman. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86: 1633–1637.
Grobbee D.E., Hofman A. Effect of calcium supplementation on diastolic blood pressure in young people with mild hypertension. Lancet 1986, 2: 703–707.
Gillman M.W., Hood M.Y., Moore L.L., Nguyen U.D.T., Singer M.R., Andon M.B. Effect of calcium supplementation on blood pressure in children. J. Pediatr. 1995, 127: 186–192.
Dwyer J.H., Dwyer K.M., Scibner R.A. et al. Dietary calcium, calcium supplementation, and blood pressure in African American adolescents. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68: 648–655.
Zoccali C., Mallamaci F., Delfino D. et al. Double-blind randomized, crossover trial of calcium supplementation in essential hypertension. J. Hypertens. 1988, 6: 451–455.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleh, F.N., Jorde, R. & Sundsfjord, J. Effet of calcium supplementation on blood pressure in patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism. J Endocrinol Invest 26, 35–41 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345120
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345120