Abstract
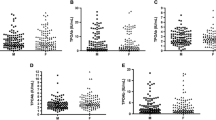
Thyroid hormone autoantibodies (THAA) disrupt the equilibrium between thyroid hormones and their binding proteins. This may lead to spurious estimations of free thyroxine (FT4) and triiodothyronine (FT3) by radioimmunoassay (RIA). In the present study we highlight the importance of THAA by examining the frequency of THAA in consecutive sera sent to a routine district hospital laboratory. Over a period of six months, sera were collected from 200 consecutive hypothyroid, 200 hyperthyroid and seven patients whose clinical and biochemical thyroid status were contradictory. A further 200 patients with non-thyroid autoimmune conditions, 20 patients with insulin autoantibodies and 100 healthy blood transfusion donors were studied. In all sera, both effects of antigen removal on THAA detection and where THAA were found, the effect of their removal on FT4, were examined. The frequencies of THAA amongst hypothyroid, hyperthyroid and non-thyroid autoimmune conditions were 7%, 1.5% and 7.5% respectively, whilst no THAA were found in insulin autoantibody positive patients and 100 blood transfusion donors. However, THAA frequency was highest in those patients whose biochemical thyroid status was widely inappropriate to clinical state (5/7 = 64%). Sera stripped of thyroid hormones prior to THAA detection had significantly higher antibody activity than unstripped sera (p = 0.0027 and p = 0.0123 for T3 and T4 binding respectively). Free thyroxine levels measured by the Amerlex-M RIA kit after antibody removal fell in all 21 THAA positive sera tested. The correlation coefficient between antibody activity in serum with percentage fall in FT4 was 0.79 (Spearman’s Rank Correlation Test). This study defines the frequency of THAA in blood samples submitted to a routine district hospital laboratory, and underlines the importance of removing THAA to the correct interpretation of thyroid hormone estimations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oppenheimer J.H. Role of plasma protein in the binding, distribution and metabolism of the thyroid hormones. N. Engl. J. Med. 278: 1153, 1968.
Midgeley J.E.M., Wilkins T.A. New methods of free thyroid hormone assay. In: Bitollan CA. (Ed.), Physiol. Peptides and Trends in RIA. Elsevier, Amsterdam, N. Holland 1981, p. 215.
Staeheli V., Vallotton M.B., Burzei A. Detection of anti-thyroxine and anti-triiodothyronine antibodies in different thyroid conditions. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 47: 669, 1975.
Premachandra B.N., Blumenthal H.T. Abnormal binding of thyroid hormone in sera from patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 35: 743, 1967.
Rodriguez-Espinosa J., Gornez-Gerique J.A., Ordonez-Lianos J., Sodevila-Bosh J., Concustell-Bas E. Circulant anti-triiodothyronine antibodies in patients with Graves’ disease: Effects on measurements of T3 with different RIA procedures. Clin. Chem. Acta 106: 173, 1980.
Resetkova E. Strbak V., Hrilica P. Incidence of thyroid hormone autoantibodies in patients with thyroid disease with respect to diagnosis, other types of autoantibodies, duration of disease and treatment. Endocrinol. Exp. 23: 105, 1989.
Sakata S.O. Nakamura S, Miura K. Autoantibodies against thyroid hormone or iodothyronine: Implications in diagnosis, thyroid function, treatment and pathogenesis. Ann. Intern. Med. 103: 579, 1985.
Allan D.J., Murphy F. Needham C.A., Barron N., Wilkins T.A., Midgeley J.E.M. Sensitive test for thyroid hormone binding antibodies in serum. Lancet 2: 824, 1982.
Dixon K. Measurement of antibody to insulin in serum. Clin. Chem. 20: 1275, 1974.
Robbins I., Rail J.E., Rawson R.H. An unusual instance of thyroxine binding by human serum gammaglobulin. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 16: 573, 1956.
Ikekubo K., Konishi J., Endo K., Nakajima K., Okuno T., Kasagi K., Mori T., Nagata I., Torizuka K. Antithyroxine and anti-triiodothyronine antibodies in three cases of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Acta Endocrinol. (Copenh.) 89: 557, 1978.
Trimarchi F., Bevenga S, Constante G, Barbera C, Melluso R., Marcocci C, Chiovato L, De Luca F., Consolo F. Identification and characterization of circulating thyroid hormone autoantibodies in thyroid diseases, in autoimmune nonthyroid illnesses and in lymphoreticular system disorders. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 6: 203, 1983.
Karlsson F.A., Wibell L., Wide L. Hypothyroidism due to thyroid-binding antibodies. N. Engl. J. Med. 296: 1146, 1977.
Ginsberg J., Segal D., Ehrlich R.M., Walfish P.G. Inappropriate T3 and T4 radioimmunoassay levels secondary to circulating thyroid hormone antibodies. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 8: 113, 1978.
Premachandra B.N., Ibrahim I.I. Thyroxine antibody versus serum protein binding of T4 in the cold: differential charcoal absorption of T4 from immuno and conventional T4 binding sites. In: Harlan W.A., Orr J.S. (Eds.), Thyroid Hormone Metabolism. New York Academic Press, 1975, p. 281.
Premachandra B.N., Walfish P.G. Effects and clinical significance of exogenous thyroxine therapy in patients with circulating thyroid hormone antibodies. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 78: 63, 1982.
Kronvall G., Williams R.C. Differences in anti-protein-A activity among IgG subgroups. J. Immunol. 103: 828, 1969.
Ochi Y., Shiomi K, Hachiga T., Yoshimura M.J. Miyazaki T. Immunological analysis of abnormal binding of thyroid hormone in the gammaglobulin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 35: 743, 1972.
Copping S., Byfield P.G.M. The role of thyroid hormone autoantibodies in serum transport. Acta Endocrinol. (Copenh.) 121: 551, 1989.
Premachandra B.N., Ginsberg J., Walfish P.G. Binding of reverse triiodothyroxine to serum immunoglobulins in man and the rabbit. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 50: 802, 1980.
Beck Peccoz E., Rommeli P.B., Cattaneo M.G., Faglia G., White E.L., Barlow J.W. Stockigt J.R. Evaluation of free thyroxine methods in the presence of iodothyronine-binding autoantibodies. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 58: 726, 1984.
Stockigt J.R., De Garis M., Cziczman J., Barlow J.W., White E.L., Hurley D.M. Limitations of a new free thyroxine assay (Amerlex Free T4). Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 15: 313, 1981.
Mullinger R.N., Walker G. Free thyroxine in thyroid disease (letter). Clin. Chem. 28: 1394, 1982.
Bhagat C-I, Garcia-Webb P., Watson F., Beilby J.P. Interference in RIA of TT4 and FT4 due to thyroid hormone binding antibodies. Clin. Chem. 29: 1324, 1983.
Desai R.M., Bredenkamp B., Jialal I., Omar M.A.K., Rajput M.C., Joubest S.M. Autoantibodies to thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Clin. Chem. 34: 944, 1988.
Benvenga S, Trimarchi F, Robbins J. Circulating thyroid hormone antibodies. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 10: 605, 1987.
Premachandra B.N., Blumenthal H.T. Abnormal binding of thyroid hormone in sera from patients with Hashimoto’s disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 27: 931, 1967.
Hehrmann R., Hoffken B., Von zur Muhlen A., Creutzig H., Thiele J., Hesch R.D. Anti-thyroid hormone autoantibodies under experimental and clinical conditions. Horm. Metab. Res. 9: 326, 1977.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vyas, S.K., Wilkin, T.J. Thyroid hormone autoantibodies and their implications for free thyroid hormone measurement. J Endocrinol Invest 17, 15–21 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03344956
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03344956