Abstract
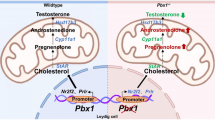
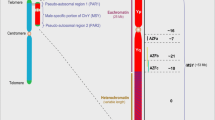
Microdeletions of the AZFb region of the human Y chromosome usually result in severe consequences for spermatogenesis. AZFb contains at least four kinds of genes/gene families. These include a number of RBMY genes, which are clustered in the AZFb deletion interval. They are amongst the oldest genes on the mammalian Y chromosome, and are related to the gene encoding hnRNPG (RBMX) on the X chromosome. A retroposon-derived version of these genes is found on chromosome 11 that might replace the function of these genes during meiosis, during which time the X and Y chromosomes are transcriptionally inactivated. Each of these genes encodes proteins with an RNA binding motif, and interacts with more ubiquitously expressed proteins involved in pre-mRNA splice site selection. These findings imply that important pre-mRNA processing pathways might be disrupted in the germ cells of AZFb men.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McElreavey K., Krausz C. Male infertility and the Y chromosome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 64: 928–933.
Lahn B.T., Page D.C. Functional coherence of the human Y chromosome. Science 1997, 278: 675–680.
Girardi S.K., Mielnik A., Schlegel P.N. Submicroscopic deletions in the Y chromosome of infertile men. Hum. Reprod. 1997, 12: 1635–1641.
Krausz C., Quintana Murci L., Barbaux S., Siffroi J. P., Rouba H., Delafontaine D., Souleyreau Therville N., Arvis G., Antoine J.M., Erdei E., Taar J.P., Tar A., Jeandidier E., Plessis G., Bourgeron T., Dadoune J.P., Fellous M., McElreavey K.A. High frequency of Y chromosome deletions in males with nonidiopathic infertility. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84: 3606–3612.
Brandell R.A., Mielnik A., Liotta D., Ye Z., Veeck L.L., Palermo G.D., Schlegel P.N. AZFb deletions predict the absence of spermatozoa with testicular sperm extraction: Preliminary report of a prognostic genetic test. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 13: 2812–2815.
Ma K., Inglis J.D., Sharkey A., Bickmore W.A., Hill R.E., Prosser E.J., Speed R.M., Thomson E.J., Jobling M., Taylor K., Wolfe J., Cooke H.J., Hargreave T.B., Chandley A.C. A Y-chromosome gene family with RNA-binding protein homology — Candidates for the azoospermia factor AZF controlling human spermatogenesis. Cell 1993, 75: 1287–1295.
Kenan D.J., Query C.C., Keene J.D. RNA recognition — Towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem. Sci.1991, 16: 214–220.
Chai N.N., Salido E.C., Yen P.H. Multiple functional copies of the RBM gene family, a spermatogenesis candidate on the human Y chromosome. Genomics 1997, 45: 355–361.
Chandley A.C., Cooke H.J. Human male-fertility — Y-linked genes and spermatogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1994, 3: 1449–1452.
Glaser B., Hierl T., Taylor K., Schiebel K., Zeitler S., Papadopoullos K., Rappold G., Schempp W. High-resolution fluorescence in situ hybridization of human Y-linked genes on released chromatin. Chromosome Res. 1997, 5: 23–30.
Pasantes J.J., Rottger S., Schempp W. Part of the RBM gene cluster is located distally to the DAZ gene cluster in human Yq11.23. Chromosome Res. 1997, 5: 537–540.
Prosser J., Inglis J.D., Condie A., Ma K., Kerr S., Thakrar R., Taylor K., Cameron J.M., Cooke H.J. Degeneracy in human multicopy RBM (YRRM), a candidate spermatogenesis gene. Mamm. Genome 1996, 7: 835–842.
Chai N.N., Zhou H.Y., Hernandez J., Najmabadi H., Bhasin S., Yen P.H. Structure and organization of the RBMY genes on the human Y chromosome: Transposition and amplification of an ancestral autosomal HnRNPG. Genomics 1998, 49: 283–289.
Vogt P.H., Edelmann A., Kirsch S., Henegariu O., Hirschmann P., Kiesewetter F., Kohn F.M., Schill W.B., Farah S., Ramos C., Hartmann M., Hartschuh W., Meschede D., Behre H.M., Castel A., Nieschlag E., Weidner W., Grone H.J., Jung A., Engel W., Haidl G. Human Y chromosome azoospermia factors (AZF) mapped to different subregions in Yq11. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1996, 5: 933–943.
Elliott D.J., Millar M.R., Oghene K., Ross A., Kiesewetter F., Pryor J., McIntyre M., Hargreave T.B., Saunders P.T.K., Vogt P.H., Chandley A.C., Cooke H. Expression of RBM in the nuclei of human germ cells is dependent on a critical region of the Y chromosome long arm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94: 3848–3853.
Yen P.H. A long-range restriction map of deletion interval 6 of the human Y chromosome: A region frequently deleted in azoospermic males. Genomics 1998, 54: 5–12.
Graves J.A.M. The origin and function of the mammalian Y-chromosome and Y-borne genes — an evolving understanding. Bioessays 1995, 17: 311–320.
Delbridge M.L., Harry J.L., Toder R., ONeill R.J.W., Ma K., Chandley A.C., Graves J.A.M. A human candidate spermatogenesis gene, RBM1, is conserved and amplified on the marsupial Y chromosome. Nat. Genet. 1997, 15: 131–136.
Elliott D.J., Ma K., Kerr S.M., Thakrar R., Speed R., Chandley A.C., Cooke, H. An RBM homologue maps to the mouse Y chromosome and is expressed in germ cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1996, 5: 869–874.
Mahadevaiah S.K., Odorisio T., Elliott D.J., Rattigan A., Szot M., Laval S.H., Washburn L.L., McCarrey J.R., Cattanach B.M., Lovell Badge R., Burgoyne P.S. Mouse homologues of the human AZF candidate gene RBM are expressed in spermatogonia and spermatids, and map to a Y chromosome deletion interval associated with a high incidence of sperm abnormalities. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1998, 7: 715–727.
Burgoyne P.S. Male sterility — Fruit(less) flies provide a clue. Nature 1996, 381: 740–741.
Delbridge M.L., Lingenfelter P.A., Disteche C.M., Graves J.A.M. The candidate spermatogenesis gene RBMY has a homologue on the human X chromosome. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22: 223–224.
Mazeyrat S., Saut N., Mattei M.G., Mitchell M.J. RBMY evolved on the Y chromosome from a ubiquitously transcribed X-Y identical gene. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22: 224–226.
Lahn B.T., Page D.C. Four evolutionary strata on the human X chromosome. Science 1999, 286: 964–967.
Elliot D.J., Venables J.P., Newton C.S., Lawson D., Boyle S., Eperon I.C., Cooke H.S. An evolutionary conserved germ cell-specific hnRNp is encoded by a tetrotransposed gene. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9: 2117–2124.
Kikyo N., Tada M., Tada T., Surani M.A. Mapping of the eukaryotic initiation factor EIF-1A gene, Eif1a, to mouse chromosome 12D-E by FISH. Mamm. Genome 1997, 8: 376.
Venables J.P., Vernet C., Chew L., Elliott D.J., Cowmeadow R.B., Wu J., Cooke H.J., Artzt K., Eperon I.C. T-STAR/ETOILE: a novel relative of SAM68 that interacts with an RNA-binding protein implicated in spermatogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999, 8: 959–969.
Venables J.P., Elliott D.J., Makarova O.V., Makarov E.M., Cooke H.J., Eperon I.C. RBMY, a probable human spermatogenesis factor, and other HnRNP G proteins interact with Tra2 beta and affect splicing. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9: 685–694.
Elliott D.J., Bourgeois C.F., Klink A., Stevenin J., Cooke H. A mammalian germ cell-specific RNA-binding protein interacts with ubiquitously expressed proteins involved in splice site selection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97: 5717–5722.
Vernet C., Artzt K. STAR, a gene family involved in signal transduction and activation of RNA. Trends Genet. 1997, 13: 479–484.
Elliott D.J. Splicing and the single cell. Histol. Histopathol. 1999, 15: 239–249.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elliott, D.J. RBMY genes and AZFb deletions. J Endocrinol Invest 23, 652–658 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03343789
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03343789