Abstract
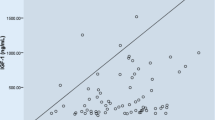
Osteoporosis is characterized by impairment of bone mass and deterioration of bone microscopic structure, resulting in increased bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture. Recent reports have indicated that reduced plasma levels of IGF-I are associated with osteoporosis in both males and females. Moreover, there is accumulating clinical evidence that treatment with GH or IGF-I has beneficial effects on bone mass and bone remodeling in men with idiopathic osteoporosis, in the elderly and in hypopituitary patients. As correlative studies on IGF-I, IGF-BP3 and bone mass in the elderly are lacking, we studied the relationships between serum IGF-I, IGF-BP3, bone mineral density (BMD), body mass index (BMI), calciotropic hormones and age in 102 premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Our study indicates that the reduction of the anabolic processes mediated by IGF-I may account for the slow and progressive loss of bone mass that take place after the age of 40-50 years. In addition, nutritional caloric or proteic deficit may add to the effects of GH, age and other factors in decreasing IGF-I synthesis and therefore further contribute to the development of primary osteoporosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanis J.A., Melton L.J. III, Christiansen C., Johnston C.C., Khaltaev N. The diagnosis of osteoporosis. J. Bone Min. Res. 1994, 9: 1137–1141.
Rudman D. Growth hormone, body composition and aging. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1985, 33: 800–807.
Holly J.M.P., Wass J.A.H. Insulin-like growth factors: autocrine, paracrine or endocrine? New perspectives on the somatomedin hypothesis in the light of recent developments. J. Endocrinol. 1989, 122: 611–618.
Ljunghall S., Johansson A.G., Burman P., Kampe O., Lindh E., KarIsson F.A. Low plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) in male patients with idiopathic osteoporosis. J. Intern. Med. 1992, 232: 59–64.
Yamamoto H., Sohmiya M., Oka N., Kato Y. Effect of age and sex on plasma insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) levels in normal adults. Acta Endocrinol. 1991, 124: 497–500.
Cuttler L., Van Vliet G., Conte F.A., Kaplan S.L., Grumbach M.M. Somatomedin-C levels in children and adolescence with gonadal dysgenesis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1985, 60: 1087–1092.
Jackson S., Undewood L.E., Clemmons D.R. Effect of calorie or protein restriction on insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and IGF-binding proteins in children and adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80: 443–449.
Moller S., Juul A., Becker U., Flyvbjerg A., Skakkebaek N.E., Henriksen J.H. Concentrations, release and disposal of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding proteins (IGFBP), IGF-I and growth hormone in different vascular beds in patients with cirrhosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80: 1148–1157.
Froesch E.R., Hussain M.A., Schmid C., Zapf J. Insulin-like growth factor-I: physiology, metabolic effects and clinical uses. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 1996, 12: 195–215.
Blum W.F., Albertsson-WikIond K., Rosberg S., Forgensen L., Ranke M.B. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP-3) reflects spontaneous growth hormone (GH) secretion. Horm. Res. 1990, 33 (Suppl. 3): 3–9.
Kurland E.S., Rosen C.J., Cosman F., McMahon D., Chan F., Shane E., Lindsay R., Dempster D., Bilezikian J.P. Insulin-like growth factor-I in man with idiopathic osteoporosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82: 2799–2805.
Wuster C., Blum W.F., Schlemilch S., Ranke M.B., Ziegler R. Decreased serum levels of insulin-like growth factors and IGF binding protein 3 in osteoporosis. J. Intern. Med. 1993, 234: 249–255.
Sugimoto T., Nishiyama K., Kuribayashi F., Chihara K. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) 1, IGF-binding protein (IGFBP)-2, and IGFBP-3 in osteoporotic patients with and without spinal fractures. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1997, 12: 1272–1279.
Barret-Connor E., Goodman-Gruen D. Gender differences in insulin-like growth factor and bone mineral density association in old age: the Rancho Bernardo Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1998, 13: 1343–1349.
Johansson A.G., Lindh E, Blum W.F. Effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 in men with idiopathic osteoporosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81: 44–48.
Marcus R., Butterfield G., Holloway L. Effects of short term administration of recombinant human growth hormone to elderly people. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1990, 70: 519–527.
Johansson A.G., Rosen T., Bosaeus I. Two years of growth hormone (GH) treatment increases bone mineral content and density in hypopituitary patients with adult-onset GH deficiency. A double blind randomized placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81: 3352–3359.
Calò L., Cantaro S., Marchini F., Giannini S., Castrignano R., Gambaro G., Antonello A., Baggio B., D’Angelo A., Williams H.E., Borsatti A. Is hydrochlorothiazide-induced hypocalciuria due to inhibition of prostaglandin E2 synthesis? Clin. Sci. 1990, 78: 321–325.
Reid I.R., Plank L.D., Evans M.C. Fat mass is an important determinant of whole body bone density in premenopausal women but not in men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1992, 75: 779–782.
Harris S., Dallal G.E., Dawson-Hughes B. Influence of body weight on rates of change in bone density of the spine, hip, and radius in postmenopausal women. Calcif. Tissue Inter. 1992, 50: 19–23.
Harris S.T., Genant H.K., Baylink D.J., Gallagher J.C., Karp S.K., McConnell M.A., Green E.M., Stoll R.M. The effects of estrone (Ogen) on spinal bone density of postmenopausal women. Arch. Intern. Med. 1991, 151: 1980–1984.
Riggs B.L., Melton L.J. Involutional osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 314: 1676–1686.
Kurland E.S., Rosen C.J., Cosman F., McMahon D., Chan F., Shane E., Lindsay R., Dempster D., Bilezikian J.P. Insulin-like growth factor-I in man with idiopathic osteoporosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82: 2799–2805.
Wuster C., Blum W.F., Schlemilch S., Ranke M.B., Ziegler R. Decreased serum levels of insulin-like growth factors and IGF binding protein 3 in osteoporosis. J. Intern. Med. 1993, 234: 249–255.
Sugimoto T., Nishiyama K., Kuribayashi F., Chihara K. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) 1, IGF-binding protein (IGFBP)-2, and IGFBP-3 in osteoporotic patients with and without spinal fractures. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1997, 12: 1272–1279.
Barret-Connor E., Goodman-Gruen D. Gender differences in insulin-like growth factor and bone mineral density association in old age: the Rancho Bernardo Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1998, 13: 1343–1349.
Johansson A.G., Lindh E, Blum W.F. Effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 in men with idiopathic osteoporosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81: 44–48.
Marcus R., Butterfield G., Holloway L. Effects of short term administration of recombinant human growth hormone to elderly people. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1990, 70: 519–527.
Johansson A.G., Rosen T., Bosaeus I. Two years of growth hormone (GH) treatment increases bone mineral content and density in hypopituitary patients with adult-onset GH deficiency. A double blind randomized placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81: 3352–3359.
Calò L., Cantaro S., Marchini F., Giannini S., Castrignano R., Gambaro G., Antonello A., Baggio B., D’Angelo A., Williams H.E., Borsatti A. Is hydrochlorothiazide-induced hypocalciuria due to inhibition of prostaglandin E2 synthesis? Clin. Sci. 1990, 78: 321–325.
Reid I.R., Plank L.D., Evans M.C. Fat mass is an important determinant of whole body bone density in premenopausal women but not in men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1992, 75: 779–782.
Harris S., Dallal G.E., Dawson-Hughes B. Influence of body weight on rates of change in bone density of the spine, hip, and radius in postmenopausal women. Calcif. Tissue Inter. 1992, 50: 19–23.
Harris S.T., Genant H.K., Baylink D.J., Gallagher J.C., Karp S.K., McConnell M.A., Green E.M., Stoll R.M. The effects of estrone (Ogen) on spinal bone density of postmenopausal women. Arch. Intern. Med. 1991, 151: 1980–1984.
Riggs B.L., Melton L.J. Involutional osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 314: 1676–1686.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calò, L., Castrignano, R., Davis, P.A. et al. Role of insulin-like growth factor-I in primary osteoporosis: A correlative study. J Endocrinol Invest 23, 223–227 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03343711
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03343711