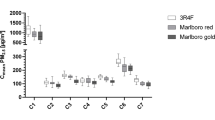
Abstract
Dynamic behavior of cigarette smoke particles inside the cabin of cars is investigated and the respirable suspended particles concentration during and after smoking cigarette is predicted in this study. This model is based on mass balance equations. Mechanisms of deposition on the surfaces and the exchange of air in the cabin are considered as sinks for emitted particles. The coagulation is accounted as a sink for smaller particles and as a source for larger particles. The various scenarios of smoking in the cars available in the literature are simulated in this study. Good agreement between the results of the present model and the experimental data, as well as the predictions of other available models, is achieved. The mean respirable suspended particle concentration in different scenarios is estimated and compared with Environmental Protection Agency’s health-based standards in order to specify the situations with respirable suspended particles concentrations exceeding the allowable limits. The results show that the concentration of particles due to the smoke of a single cigarette in a stationary medium sized car with the air conditioner off is 33.6 μg/m3 and nearly reaches the limits appointed by the Environmental Protection Agency for a 24 h incremental exposure (35 μg/m3). Corresponding values for moving cars have also been calculated and compared with the standards.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corner, J.; Pendlebury, E. D., (1951). The coagulation and deposition of a stirred aerosol. In Proc. Phys. Soc. B., 64(8), 645–654 (10 pages).
Drossinos, Y.; Housiadas, C., (2006). Aerosol flows, In: Crowe, C. T., eds., Multiphase flow handbook, CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton, FL.
Engelmann, R. J.; Pendergrass, W. R.; White, J. R.; Hall, M. E., (1992). The effectiveness of stationary automobiles as shelters in accidental releases of toxic materials. Atmos. Environ., 26A(17), 3119–3125 (7 pages).
Fletcher, B.; Saunders, C. G., (1994). Air change rates in stationary and moving motor vehicles. J. Hazard. Mater., 38(2), 243–256 (14 pages).
Fruina, S. A.; Winera, A. M.; Rodes C. E., (2004). Black carbon concentrations in California vehicles and estimation of in-vehicle diesel exhaust particulate matter exposures. Atmos. Environ., 38(25), 4123–4133 (11 pages).
Fuchs, N. A., (1964). The Mechanics of Aerosols, Dover Publication Inc., New York.
Gao, N. P.; Niu, J. L., (2007). Modeling particle dispersion and deposition in indoor environments. Atmos. Environ., 41(18), 3862–3876 (15 pages).
Gelbard, F.; Seinfeld, J. H., (1980). Simulation of multicomponent aerosol dynamics. J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 78(2), 485–501 (17 pages).
Hosea, M. E.; Shampine, L. F., (1996). Analysis and implementation of TR-BDF2. Appl. Numer. Math., 20(1–2), 21–37 (17 pages).
Klepeis, N. E.; Ott, W. R.; Switzer, P., (1996). A multiple-smoker model for predicting indoor air quality in public lounges. Environ. Sci. Tech., 30(9), 2813–2820 (8 pages).
Klepeis, N. E.; Apte, M. G.; Gundel, L. A.; Sextro, R. G.; Nazaroff, W. W., (2003). Determining size specific emission factors for environmental smoke particles. Aerosol Sci. Tech., 37(10), 780–790 (11 pages).
Klepeis, N. E.; Nazaroff, W. W., (2006). Modeling residential exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke. Atmos. Environ., 40, 4393–4407 (15 pages).
Knibbs, L. D.; De Dear, R. J.; Atkinson, S. E., (2009). Field study of air change and flow rate in six automobiles. Indoor Air, 19(4), 303–313 (11 pages).
Lai, A. C. K.; Nazaroff, W. W., (2000). Modeling indoor particle deposition from turbulent flow onto smooth surfaces. J. Aerosol Sci., 31(4), 463–476 (4 pages).
Lai, A.C.K., (2005). Modeling indoor coarse particle deposition onto smooth and rough vertical surfaces. Atmos. Environ., 39(21), 3823–3830 (8 pages).
Lai, A. C. K.; Nazaroff, W. W., (2005). Supermicron particle deposition from turbulent chamber flow onto smooth and rough vertical surfaces. Atmos. Environ., 39, 4893–4900 (8 pages).
Lipowicz, P. J., (1988). Determination of cigarette smoke particle density from mass and mobility measurements in a millikan cell. J. Aerosol Sci., 19(5), 587–89 (3 pages).
Long, C. M.; Suh, H. H.; Catalano, P. J.; Koutrakis, P., (2001). Using time- and size-resolved particulate data to quantify indoor penetration and deposition behavior. Environ. Sci. Tech., 35, 2089–2099 (11 pages).
Maskarinec, M. P.; Jenkins, R. A.; Counts, R. W.; Dindal, A. B., (2000). determination of exposure to environmental tobacco smoke in restaurant and tavern workers in one US city. J. Expo. Analys. Environ. Epid., 10, 36–49 (14 pages).
Miller, S. L.; Nazaroff, W. W., (2001). Environmental tobacco smoke particles in multizone indoor environments. Atmos. Environ., 35, 2053–2067 (15 pages).
Nazaroff, W. W.; Cass, G. R., (1989). Mathematical modeling of indoor aerosol dynamics. Environ. Sci. Tech., 23(2), 157–166 (10 pages).
Nazaroff, W. W.; Hung, W. Y.; Sasse, A. G. B. M.; Gadgil, A. J., (1993). Predicting Regional Lung Deposition of Environmental Tobacco Smoke Particles. Aerosol Sci. Tech., 19(3), 243–254 (12 pages).
Nazaroff, W. W.; Klepeis, N., (2003). Environmental Tobacco Smoke Particles, In: Moraswka, L. and Salthammer, T., eds., Indoor Environment: Airborne Particles, and Settled Dust, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.
Offermann, F. J.; Sextro, R. G.; Fisk, W. J.; Grimsrud, D. T.; Nazaroff, W. W.; Nero, A. V.; Rezvan, K. L.; Yater, J., (1985). Control of respirable particles in indoor air with portable air cleaners. Atmos. Environ., 19(11), 1761–1771 (11 pages).
Omidvari, M.; Nouri, J. (2009). Effects of noise pollution on traffic policemen. Int. J. Environ. Res., 3(4), 645–652. (8 pages).
Ott, W. R.; Langan, L.; Switzer, P., (1992). A time series model for cigarette smoking activity patters: model validation for carbon monoxide and respirable particles in an automobile. J. Expo. Analys. Environ. Epid., 2(Suppl. 2), 175–200 (26 pages).
Ott, W. R.; Switzer, P.; Robinson, J., (1996). Particle concentrations inside a tavern before and after prohibition of smoking: Evaluating the performance of an indoor air quality model. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc., 46, 1120–1134 (15 pages).
Ott, W. R.; Klepeis, N.; Switzer, P., (2008). Air change rates of motor vehicles and in-vehicle pollutant concentrations from secondhand smoke. J. Expos. Analys. Environ. Epid., 18(3), 312–325 (14 pages).
Park, J.; Spengler J. D.; Yoon, D.; Dunnyahn, T.; Lee, K.; Oxkaynak, H., (1998). Measurements of the air exchange rate of stationary vehicles and estimation of in-vehicle exposure. J. Expos. Analys. Environ. Epid., 8(1), 65–78 (14 pages).
Phillips, K.; Howard, D. A.; Bentley, M. C.; Alvan, G., (1998). Measured exposures by personal monitoring for respirable suspended particles and environmental tobacco smoke of housewives and office workers resident in Bremen, Germany. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health, 71(3), 201–212 (12 pages). 764
Pirjola, L.; Parviainen, H.; Hussein, T.; Valli, A.; Hameri, K.; Aaalto, P.; Virtanen, A.; Keskinen, J.; Pakkanen, T.A.; Makela, T.; Hillamo, R. E., (2004). “Sniffer”—a novel tool for chasing vehicles and measuring traffic pollutants. Atmos. Environ., 38(22), 3625–3635 (11 pages).
Rees, V. W.; Connolly, G. N., (2006). Measuring air quality to protect children from secondhand smoke in cars. Am. J. Prev. Med., 3(5), 363–368 (6 pages).
Reinhardt, H.; Kobori, S., (). The different standard test method for cabin air filters in Japan, USA and Europe, In: 5th International Filtration Conference, November 7th–8th, Osaka, Japan.
Repace, J., (2007). Exposure to secondhand smoke, In Ott, W. R., Steinemann, A. C. and Wallace, L. A., Exposure Analysis, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, p. 214.
Rodes, C.; Sheldon, L.; Whitaker, D.; Clayton, A.; Fitzgerald, K.; Flanagan, J.; DiGenova, F.; Hering, S.; Frazier, C., (1998). Measuring concentrations of selected air pollutants inside California vehicles, Report prepared for California EPA. http://www.arb.ca.gov/research/abstracts/95-339.htm#Main (accessed 29 Oct, ).
Salam, M. A.; Shirasuna, Y.; Hirano, K.; Masunaga, S., (2011). Particle associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the atmospheric environment of urban and suburban residential area. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 8(2), 255–266 (12 pages).
Sendzik, T.; Fong, G. T.; Travers, M. J.; Hyland, A., (2009). An Experimental Investigation of Tobacco Smoke Pollution in Cars. Nicotine Tob. Res., 11(6), 627–634 (8 pages).
Sextro, R. G.; Gross, E.; Nazaroff, W. W., (). Determination of emissions profiles for indoor particle phase environmental tobacco smoke. In: Annual Meeting of the American Association for Aerosol Research, Traverse City, Michigan. Results reported in Nazaroff et al., 1993.
Sohn, M. D.; Apte, M. G.; Sextro, R. G.; Lai, A. C. K., (2007). Predicting size-resolved particle behavior in multizone buildings. Atmos. Environ., 41(7), 1473–1482 (10 pages).
Tang, U. W.; Wang, Z., (2006). Determining gaseous emission factors and driver’s particle exposures during traffic congestion by vehicle-following measurement techniques. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc., 56(11),1532–1539 (8 pages).
Thatcher, T. L.; Lai, A. C. K.; Moreno-Jackson, R.; Sextro, R. G.; Nazaroff, W. W., (2002). Effects of room furnishings and air speed on particle deposition rates indoors. Atmos. Environ., 36(11), 1811–1819 (9 pages).
Xu, M. D.; Nematollahi, M.; Sextro, R.G.; Gadgil, A. J.; Nazaroff, W. W., (1994). Deposition of tobacco smoke particles in a low ventilation room. Aerosol Sci. Tech., 20(2), 194–206 (13 pages).
Zhao, B.; Wu, J., (2007). Particle deposition in indoor environments: Analysis of influencing factors. J. Hazard. Mater., 147(1–2), 439–448 (10 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saber, E.M., Bazargan, M. Dynamic behavior modeling of cigarette smoke particles inside the car cabin with different ventilation scenarios. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 8, 747–764 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326259
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326259