Abstract
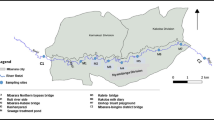
Seasonal variation in bacterial heavy metals biosorption from soap and brewery industrial effluent samples from Eziama River in Abia State were analyzed for Pb, Hg, Fe, Zn, As, and Mn, using atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Bioaccumulation of the metals by bacteria showed the following trend > Fe >Zn >As > Pb > Mn (Rainy Season) and Zn > Fe > Mn > As > Hg > Pb (Dry season). Statistical analysis using of variance (ANOVA) showed significant differences in concentrations of Pb, Hg, Fe, Zn, As, and Mn level between the sampling zones at Eziama River. Seasonal changes in heavy metal concentrations, showed increases in Pb, Fe, and As from 1.32 x 105 mg/L in the rainy season to 1.42 x 105 mg/L in the dry season. Fe increased from 40.35 x 105 mg/L to 42.1 x 105 mg/L, while As increased from 2.32 to 2.48 x 105 mg/L with a net increases of+56 and + 69 x 105 mg/L respectively. However, Hg, Zn, and Mn concentrations decreased in the rainy season from 40.54 x 105 mg/L to 39.24 x 105 mg/L, 1.65 to 0.62 x 105 mg/L respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agedengbe, K., Akinwole, A. O. and Babatunde, A. O., (2003). Effluents characteristics of selected industries in western Nigeria and implications for re-use in agricultural production. J. Environ. Exten., 4, 79–82.
Alloway, B. J., (1995). (Ed.) Heavy metals in soils 2nd Ed., Ch. 2. Blackie and Sons, Glasgow.
Alloway, B. J. and Ayres, D. Z., (1997). In Chemical Principles of Environmental Pollution 2nd Ed., Ch. 5. Blackie Academic & Professional, London.
Anger, W. K., (1984). Neurobehavioural testing of chemicals: impact on recomended standards. Neurobehav Toxic. Terat, 6, 147–153.
Anger, W. K., (1986). Workplace exposures. In: Annau, ZA, ed., Neurobehavioural toxicology. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 331–347.
Anger, W. K., Otto, D. A. and Letz, R., (1996). (Eds) Symposium on computerized behavioural testing of humans in neurotoxicology research. Neurotoxic. Terat., 18, 347–518.
Anonymous, OTA (Office of Technology Assessment). 1990. Neurotoxicity: Identifying and controlling poisons of nervous system. OTA Publication No. OTA-BA, Washington: US Government Printing Office.
Barnes, R. S. K., (2004). The distribution and habitat in the Knysna Estuary of the endemic South African mudsnail Hydrobia knysnaensis and the influence of intraspecific competition and ambient salinity on its abundance. African J. Aqua. Sci., 29(2), 205–211.
Dallas, H. F., (2004). Spatial variability in macroinvertebrate assemblages: comparing regional and multivariate approaches for classifying reference sites in South Africa. African J. Aqua. Sci., 29(2), 161–71
Dolk, H., Vrijheid, M., Armstrong, B., Abramsky, L., Bianchi, F., Garne, E., Nelen, V., Robert, E., Scott JES, Stone, D. and Tenconi, R., (1988)., Risk of congenital anomalies near hazardous-waste landfill sites in Europe: the Eurohazcon study. Lancet, 352, 423–27.
Dudka, S., Piotrowska, M. and Terelak, H., (1996)., Transfer of cadmium, lead, and zinc from industrially contaminated soil to crop plants: A field study. Environ Pollut, 94(2): 181–188.
El-Gohary, F. A., Abo-Elela, S. I. and Ali, H. I., (1987)., Management of wastewater from soap and food industries: a case study. Sei Total Environ., 66, 203–12.
Fergusson, J. E., (1990)., The Heavy Elements: Chemistry, Environmental Impact and Health Effects. Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Geschwind, S, Stolwijk, J., Bracken, M., (1992). Risk of congenital malformations associated with proximity to hazardous waste sites. Am J Epidemiol., 135, 1197–207.
Grassman, J. A., (1996)., Obtaining information about susceptibility from the epidemiological literature. Toxic, 3(1–3), 253–270.
Hanninen, H., Mantere, P., Hernberg, S., Seppalainen, A., and Kock, B. (1979). Subjective symptoms in low-level exposure to lead. Neurotoxic, 1, 333–348.
Havrilla, G. J., (1997). Handbook of Instrumental Techniques for Analytical Chemistry Frank Settle, Editor: X-RayFluorescence Spectrometry, Prentice Hall.
Hewitt, C. N., (1991). (Ed.) Instrument Analysis of Pollutants. Elsevier, London.
Johnson, B. L., (1997). Hazardous Waste: Human Health Effects. Toxicol Industr Health., 13(2–3), 121–43.
Johnson, B. L., (1997). Hazardous Waste: Human Health Effects. Toxic. Ind. Health., 13(2-3), 121–43.
Lajunen, L. H. J., (1992). Spectrochemical Analysis by Atomic Absorption and Emission. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge.
Lajunen, L. H. J., (1992). Spectrochemical Analysis by Atomic Absorption and Emission, Royal Society of Chemistry.
Manly, R., (1995). In Environmental Analytical Chemistry, Ch. 12. (eds. F.W. Fifield and P.J. Hains). 249–79. Blackie A and P, Glasgow.
Maskall, J., Whitehead, K. and Thornton, I., (1995). Heavy metal migration in soils and rocks at historical smelting sites. Environ. Geochem. Health, 17, 127–38.
Mitchell, C. S., Shear, M. S., Bolla, K. I. and Schwartz, B.S., (1996). Clinical evaluation of 58 organolead manufacturing workers. J. Occu. Environ. Med., 38(4), 372–378.
Muldoon, S. B., Cauley, J. A., Kuller, L. H., Morrow, L., Needleman, H. L., Scott, J. and Hooper, F. J., (1996). Effects of blood lead levels on cognitive function of older women. Neuroepid., 15(2), 62–72.
Murray, K. S., (1996). Statistical comparisons of heavy metal concentrations in river sediments. Environ Geol, 27(1), 54–58.
Needham, L. L., (1996). Proposed use of human exposure biomarkers in environmental legislation: Toxic substances control act. ACS Symposium Series, 643, 24–38
Odokuma, L. O. and Abah, A. E., (2003). Heavy metal biosorption by three bacteria isolated from a tropical river. Global. J. Environ. Sci., 2(2), 98–101.
Shaw, G, Schulman, J., Frisch, J. D, Cummins, S. K. and Harris, J. A., (1993). Congenital malformations and birthweight in areas with potential environmental contamination. Arch. Environ. Health., 47, 147–54.
Slavin, W., (1992). A comparison of atomic spectroscopic analytical techniques. Spec. Intern., 22–7.
Waldron, H. A., (1980). (Ed.) In Metals in the Environment, Ch. 6. Academic Press, London.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanu, I., Achi, O.K., Ezeronye, O.U. et al. Seasonal variation in bacterial heavy metal biosorption in water samples from Eziama river near soap and brewery industries and the environmental health implications. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 3, 95–102 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325912
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03325912